This is an automatically translated article.
Blood lipid metabolism disorder, also known as dyslipidemia, is a risk factor for a number of diseases that seriously affect health (atherosclerosis, cerebral stroke, myocardial infarction). There are many causes of dyslipidemia such as: daily diet, lifestyle, exercise regimen, genetic factors..., in which daily diet plays an important role. best.1. What is dyslipidemia?
Dyslipidemia is an individual or simultaneous imbalance in lipid components (hypercholesterolemia, increased LDL-C, increased triglycerides and decreased HDL-C in the blood). Blood lipid metabolism disorder is a risk factor for a number of diseases that seriously affect health such as atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, cerebral stroke,...
2. Causes of dyslipidemia
Here are some common causes of dyslipidemia:
The patient's diet (eating a lot of saturated fat, also known as "bad fat"). Obesity (Excess energy). Lifestyle: Inactivity, smoking, drinking a lot of alcohol... Genetic factors (Family disorders of blood lipid metabolism).
3. Diet choice for people with chronic dyslipidemia
Here are some tips on food selection and food preparation for patients with dyslipidemia that can be referred to:
Reduce fat (lipid) intake: This is an important principle in which the daily nutrient composition has saturated fatty acids <10%, total fat not more than 30% and cholesterol <300mg/day. Fat in food is divided into 2 types, saturated fat and unsaturated fat. Patients should avoid or reduce saturated fat or "bad fat" such as: animal fat, eggs, whole milk, animal organs, cheeses, ice cream. In contrast, eating unsaturated fats or "good fats" helps reduce cholesterol, triglycerides, prevent plaque, foods containing Omega 3 and Omega 6 . Seafood such as: stingray, tuna, mackerel, salmon, carp, carp ... are foods rich in omega 3. Legumes are a rich source of omega 6: black beans, peas, red beans, soybeans... in addition, some vegetable oils are also rich in omega 6 (sesame oil, sesame oil, sunflower oil...). Increase fiber: Fiber in vegetables and fruits reduces blood fat by reducing harmful lipids (LDL-C), increasing beneficial lipids (HDL-C). If the diet is high in butter, cholesterol will increase, but when adding fiber to the diet, cholesterol will be reduced by up to 20%. Fiber can reduce triglycerides, prevent obesity, because foods rich in fiber take longer to digest, making the body fuller for a long time, thereby reducing appetite. oxidants (A, C, E. zinc...): reduce blood lipids and increase blood circulation, thus reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Drink enough water: The National Institute of Nutrition recommends that each person should drink 40 ml of water/kg/day (eg: 1 person of 50 kg should drink ~ 2 liters of water/day). Limit alcohol, soft drinks, tobacco: It is necessary to limit alcohol as much as possible to reduce the risk of increased complications for patients with dyslipidemia: coronary heart disease, stroke... How to prepare food: Choose steamed or boiled foods. Reduce eating greasy fried foods, do not eat fast food.
4. Some foods recommended for patients with chronic lipid disorders
Patients with chronic lipid metabolism disorders in addition to using drugs also need to have a reasonable diet combined with regular exercise and sports. In fact, there are many foods that, when eaten, also have the effect of reducing blood lipids and here are some plants and fruits we can refer to when we have high blood fat:
Green beans: Beans Green is the perfect food for weight loss because it is low in fat, rich in protein and fiber, helping to lower a high level of cholesterol in the blood system. Green bean porridge can be eaten with sugar or salt (fish sauce) is a very popular and good food in the summer. Tofu and products made from soybeans (soybean milk, soy yogurt...): contains about 11% protein, 5% fat, is a common food, available in large and small markets. and appear frequently in daily meals. Tofu and soybean products provide important protein in the diet of subjects with lipid metabolism disorders, overweight, obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and some other common diseases. in old age. Black beans: Very rich in fiber, which helps lower cholesterol, soluble fiber also helps prevent a rapid rise in blood sugar, after meals. Black beans are low in calories and do not contain fat, which is a great food for people with lipid metabolism disorders, type 2 diabetes. Red beans: Contains very little fat, cholesterol and is rich in protein. Red beans are high in fiber, the soluble fiber found in red beans also helps lower blood cholesterol by promoting cholesterol through the digestive tract before being absorbed by the body. Red beans are also rich in antioxidants, antioxidants are needed to protect cells from the harmful effects of free radicals, reduce the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease,.... Cashew: The fats Cashew nuts account for about 47%, including over 80% unsaturated fats, the ratio of unsaturated and saturated fats is 4:1 which is very beneficial. Unsaturated fats or "good fats" not only do not increase blood lipids, but also regulate and reduce blood lipids, thereby helping to avoid cardiovascular diseases. Kale vegetable: Eating spinach soup daily is effective for people with high blood fat, atherosclerosis, cerebrovascular accident due to embolism, embolism. Apples: Rich in vitamin C and fiber, help strengthen the vessel wall, reduce atherosclerosis. Besides, apples also help prevent constipation, support weight loss for overweight and obese people. Pomegranate: May help limit the formation of plaque in the arteries and the risk of stroke (a consequence of lipid metabolism disorders). Red grapes: The compound Resveratrol in the skin of red grapes (green grapes do not have this substance) works to prevent red blood cells from sticking together, reducing the risk of blood clots, increasing good cholesterol (HDL-C), and lower bad cholesterol (LDL-C). Red grapefruit: Not only rich in soluble fiber but also stimulates appetite, has the effect of burning fat, reducing blood lipids in the body, especially cholesterol. Seaweed: A very beneficial food for health because it contains a lot of iodine and magnesium, which works in preventing the formation of cholesterol plaques in the vessel walls. In addition, seaweed also contains polysaccharide laminaria, which can reduce total cholesterol and triglycerides. Mushrooms (such as shiitake, reishi, wood ear) are effective in reducing both cholesterol and blood triglycerides. Below is the Vietnamese food composition table - Nutrition Institute 2017 provides:
Table 1. Common foods rich in fiber
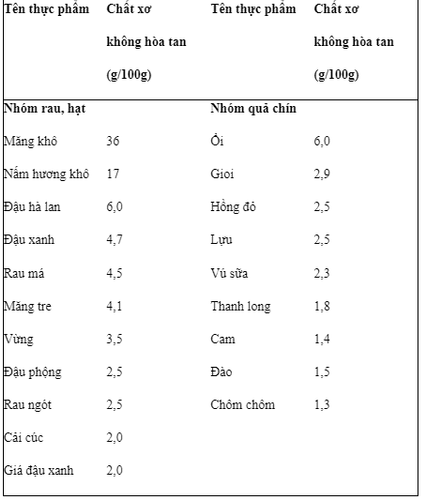
Table 2. Common foods with high cholesterol
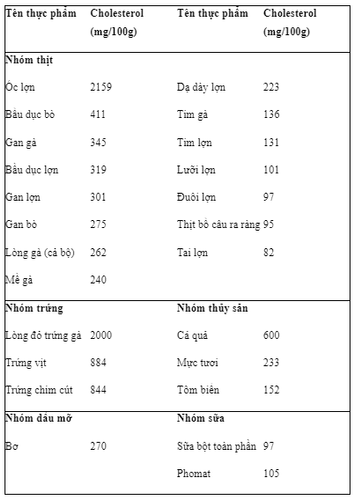
Patients with dyslipidemia need to strictly follow a scientific diet, lifestyle and exercise regimen. The fact that the patient adheres to a reasonable diet and knows how to choose the right food contributes to the patient's good control of blood lipid indexes such as cholesterol, blood triglycerides, etc., to limit the risk of serious complications that may occur. may happen.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.