This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Huu Thang - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Ha Long International HospitalThe risk of electric shock depends on the type of current such as: how much high-voltage current is flowing, how much current passes through the body, the person's overall health, and how quickly the victim is treated. An electric shock can cause burns, or it may not leave visible marks on the skin. In either case, an electrical current passing through the body can cause internal damage, cardiac arrest, or other injury. Under certain circumstances, even a small amount of electricity can be fatal.
1. Injury due to electric shock
Electrical injury occurs by 3 mechanisms:
Direct effect of electric current on body tissue. Converts electrical energy into thermal energy causing deep burns and superficial burns. Mechanical damage from lightning strikes, muscle contractions, or injuries following a fall due to electric shock. On contact, direct current (DC) will push or push the victim away from the power source so the victim has a shorter duration of current exposure but a higher potential for combined injury. In contrast, alternating current (AC) tends to stick to the victim (usually the hand) and draw the victim closer to the power source thereby prolonging the exposure time causing more severe tissue damage.
2. What to do in case of electric shock caused by electric shock
Some signs of an electric shock victim:
Severe burns Panic Shortness of breath Heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) Cardiac arrest Muscle pain and spasms Seizures Loss of consciousness

Do not touch the injured person if he or she is still exposed to an electric current. Call 911 or your local emergency number if the source of the burn is a high voltage wire or lightning. Do not approach high voltage wires until the power has been turned off, overhead lines are usually not insulated. Stay at least 20 feet (about 6 meters) away - further if ropes jump and there is an electrical short. Do not move a person with an electrical injury immediately unless the person is in danger. While waiting for medical help, you should:
Turn off the power, if possible. Otherwise, move the source away from you and the person in distress, using a dry, non-conductive object made of cardboard, plastic, or wood. Start CPR if the person shows no signs of circulation, such as breathing, coughing, or movement. Try not to let the shock person get cold. Use a cotton pad: cover any burned area with a sterile gauze dressing, if available, or a clean cloth. Do not use blankets or towels, as cotton fibers can stick to the burn. In case the victim has not lost consciousness:
Let the victim go to a well-ventilated, quiet place to take care of him or her to regain consciousness. Then invite a nurse, doctor or take the victim to the nearest medical facility for monitoring and care. In case the victim has lost consciousness:
Place the victim in a well-ventilated, quiet place. Loosen clothes, belts, dig out the victim's mouth. Have the casualty sniff ammonia or urine. Friction of the victim's whole body to heat up. Invite a doctor or nurse to come or take the victim to the nearest medical facility for monitoring and care. In case the victim has stopped breathing
Take the victim to fresh air; Loosen clothes, belts, dig out the victim's mouth. If the tongue is retracted, it must be pulled out. Perform CPR immediately, must be done continuously, patiently until the doctor's opinion makes a decision.
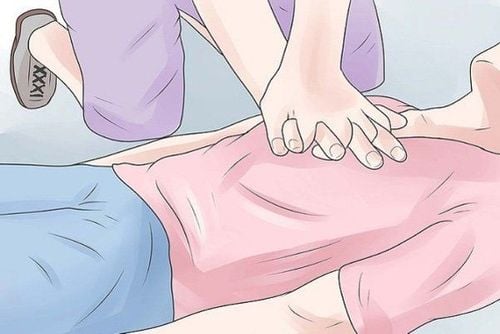
When performing rescue breathing combined with chest compressions, you need to do the following steps:
Put the victim lying on his back, widen the clothes, belt, dig out the victim's mouth, Place the casualty's head slightly backward. The rescuer stands or kneels next to the victim, crosses his hands on the victim's left chest (heart position) and then uses his whole body strength to press quickly, forcefully, compressing the victim's chest for about 5 cm, pressing frequency is about 100 - 120 times/min. The motto is "squeeze quickly, press hard, without interruption and let the chest inflate completely after each squeeze". Simultaneously with cardiac compression is artificial respiration: it is best to have a gauze pad or handkerchief placed on the victim's mouth, the rescuer sitting next to the head takes one hand to cover the victim's nose, the other hand holds the mouth. The victim opens his mouth to take a deep breath to get a lot of air into his lungs, then closes his mouth to the victim's mouth and blows into the inflated chest (or covers his mouth to blow into the victim's nose when he can't) breathe for him. victims 12 to 16 times/minute. The ratio of chest compressions to CPR in adults is 30/2. Remember that giving first aid to someone who has received an electric shock is urgent work, as quickly as possible. Must be very calm and persistent to save.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Mayoclinic.org