This is an automatically translated article.
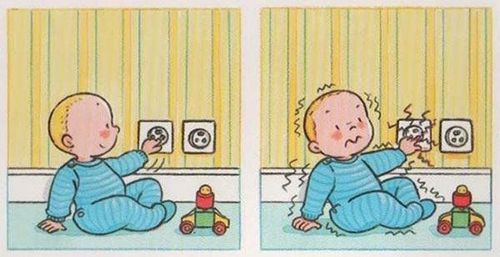
The article was consulted with MSc Duong Van Sy - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Electric shock in children is a common daily life accident, it causes damage to organs in the child's body such as kidneys, nerves, skeletal muscles, etc. It can even be life threatening to children. Electric shock accidents can happen to anyone, including children.
1. Some things parents need to know about electric shock in children
Electric shock is a dangerous accident that can cause many types of damage to the body (cardiac arrest, breathing stops and organ damage with a high risk of death or severe sequelae), but in general can be prevented.There are two types of electric current: alternating current (AC) used in daily life... and direct current (DC) found in batteries, car electrical systems, high voltage power lines and lightning bolts. ...
On contact, direct current (DC) will push or hurl the victim away from the power source so that the victim has a shorter duration of current exposure but a higher potential for combined injury. In contrast, alternating current (AC) tends to stick to the victim (usually the hand) and draw the victim closer to the power source thereby prolonging the exposure time causing more severe tissue damage.
Electrical injury occurs by 3 mechanisms: (1) direct effect of electric current on body tissue; (2) converts electrical energy into thermal energy causing deep burns and superficial burns; (3) mechanical injury from lightning strikes, muscle contractions, or injuries following a fall due to electric shock.
2. Is there any effect on children getting electric shock?
When being electrocuted, children will be greatly affected mentally and physically.Children will have cardiac arrhythmias, sudden cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation, ... can even lead to death in children. Injury to both central and peripheral nervous systems. Superficial, partial-thickness, and full-thickness can occur after electrical injury in a child. Causes periosteal burns, destruction of bone cytoplasm and bone necrosis. Bones can also be broken from a fall, an explosion injury, or from muscle spasticity. In addition, there can be damage to the child's internal organs such as the lungs, stomach, small intestine, and colon and cause fistula complications, perforation, secondary bacterial infection, infection (sepsis), and ultimately death death.
3. Treatment of electric shock in children

Emergency treatment Treatment of complications Support for emergency cases:
Quickly separate the child from the power source by cutting off the power, taking care to avoid direct contact to the patient before the power is cut off. If the patient is in an emergency situation: It is necessary to immobilize the patient's cervical vertebrae if in doubt. Emergency respiratory arrest cardiac arrest for the patient if any. Support breathing by giving the patient oxygen or endotracheal intubation. Treatment of arrhythmias: ventricular extrasystoles, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation with antiarrhythmic drugs and defibrillation with defibrillators (arrhythmia treatment regimens). Shock resuscitation for patients: fluid resuscitation and vasopressors according to CVP guidelines. Anticonvulsants with intravenous diazepam. Patients with kidney failure need hemodialysis. Treatment of complications
Treatment of electrolyte disorders. Myoglobinuria: IV fluids at one and a half times the basal requirement to increase myoglobin excretion and prevent acute renal failure, monitor CVP and urine retention 1-2 ml/kg/hour. Treatment of burns depends on the severity from mild to severe (burn protocol). Treatment of other combined injuries such as trauma, gastrointestinal bleeding due to stress. Pain relief with paracetamol 10-15mg/kg/time or IV or morphine 0.1mg/kg/time IV. Monitor patient during treatment
Need to monitor patient's vital signs by checking SpO2 every 30 minutes - 1 hour during resuscitation or new hospital admission. Import and export translation every 8 hours for the first 24 hours. When the patient is stable, it is necessary to continue measuring and monitoring the ECG for 24 hours, promptly detecting and treating arrhythmias, although delayed arrhythmias are rare. Electric shock is a dangerous accident, especially for children, so when a child is electrocuted, parents need to know how to handle it first and quickly take the child to a medical facility for diagnosis. timely diagnosis and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.