This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Trinh Thi Phuong Nga - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalOsteochondroma is a common benign bone tumor of the growing bone age. To diagnose osteochondrosis, in addition to clinical examination and taking medical history, the doctor can prescribe many imaging techniques such as X-ray, CT scan, MRI scan,...
1. What is osteochondrosis?
Osteochondroma is the most common benign bone tumor of growing bones, occurring due to an overgrowth of cartilage and bone near the ends of bones. A chondroma looks like a hard bump near a joint. The exact cause of this disease is currently unknown, some theories suggest that the disease is related to genetic factors, but it is not yet definitively confirmed. Osteochondromas most commonly occur in bones that have developed cartilage such as the long bones of the legs (femur, tibia), bones in the hands (arm bones, forearms), pelvis, or shoulder blades. The disease usually occurs at the age when the skeletal system is developing, that is, between the ages of 10 and 30 years old. A child's cartilaginous tumor will get bigger as the child gets older. And when the child's skeletal system stops growing, the tumor stops growing too. The frequency of the disease is the same in men and women.When suffering from osteochondrosis, the patient may have one or more symptoms such as:
Appears under the skin a hard, palpable, close to bone, painless, non-moving tumor. Children with the disease have a lower height than normal for their age. Children often have one leg (arm) longer than the other due to a morphological deformity (curvature, curvature) of the arm or leg Pain in the muscles adjacent to the tumor Feeling uncomfortable, pressured when exercising However, in many cases, people with bone tumors will have no symptoms until the tumor grows to a large size or the tumor is discovered incidentally when performing imaging techniques to diagnose the disease. other diseases.
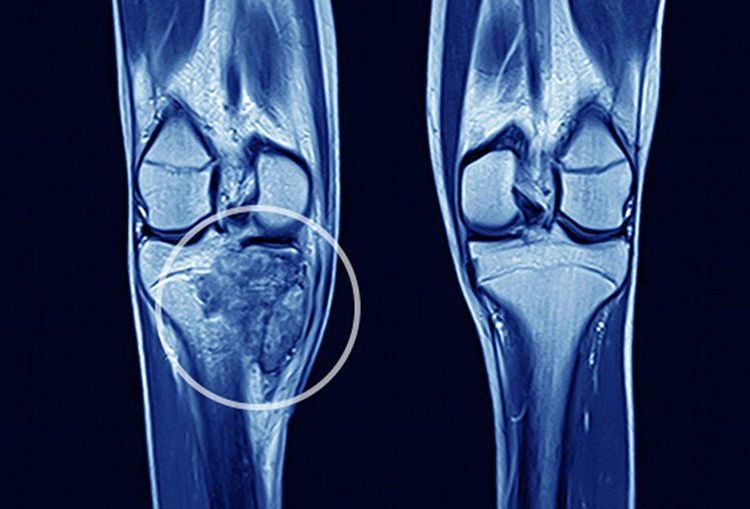
2. Diagnosis of osteochondrosis by what medical methods?
To diagnose osteochondroma, in addition to the clinical examination and taking the medical history, the doctor will assign the patient to perform a number of imaging techniques as follows:X-ray: usually a technique First-line is indicated for the characterization of bone lesions. X-rays help to show a clear picture of the dense structure of bone, the growth of bone associated with osteochondrosis. More importantly, the X-ray image allows to determine the exact location and size of the osteochondral tumor, each tumor related to the synovial cartilage,... Computed tomography (CT) helps to identify the limb. detailed bone lesions, showing the presence of calcification and the condition of the surrounding soft tissues. CT scan allows to evaluate osteochondrosis more clearly and distinguish it from other lesions, especially when the tumor is in difficult locations such as shoulder blades, ribs, pelvis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): is a method that helps to accurately describe the morphology of the tumor, helps to determine whether the tumor is continuous with the bone cortex and at the same time distinguishes osteochondroma from other lesions on the surface. the bone. MRI scans allow a better assessment of the surrounding soft and bony lesions. MRI can also be used to look for cartilage on the surface of a tumor and to detect vascular complications caused by the tumor.
3. How is osteochondrosis treated?
Most patients with osteosarcoma can live peacefully with the disease as long as the tumor does not overgrow and cause symptoms that affect the patient's quality of life. Patients need to have regular check-ups so that the doctor can monitor the growth of bones and tumors.Surgical measures to remove the tumor can be performed, if the bone and cartilage tumor causes pain, greatly affects aesthetics and movement. The surgical intervention should be done at a late stage when the child has reached adulthood, if early intervention is likely to be higher.
When being diagnosed with osteochondrosis, the patient needs to be examined, monitored and periodically re-examined according to the doctor's appointment. In some cases, the doctor may appoint the patient to perform surgery so as not to affect the health.
Currently, Vinmec is implementing a lot of periodic health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with very preferential price policy.
The advantage of Vinmec's health check-up packages is that customers will be screened and screened by a system of modern equipment to help support the best diagnosis today such as PET/CT, MRI, CT machines. 640, the world's leading advanced ultrasound machine system, international standard laboratory system,... After a general examination, if any diseases are detected, customers can use services from other specialties at the hospital with outstanding quality of treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.