This is an automatically translated article.
The endocrine system is made up of many different glands. The hypothalamus, pituitary, and pineal glands are located in the brain. The thyroid and parathyroid glands are located in the neck. The thymus is located between the lungs, the adrenals are above the kidneys, and the pancreas is behind the stomach. The ovaries (if female) or testicles (if male) are located in the pelvic area.
1. The role of the endocrine system
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, chemicals produced in the body to regulate the functioning of cells or organs. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by the body. They work to transfer information from one set of cells to another to coordinate the functions of different parts of the body. These hormones regulate growth, body metabolism, and the development of sexual function.
The endocrine system is regulated by feedback in much the same way as a thermostat in a room temperature. As for the hormones regulated by the pituitary gland, a signal is sent from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland in the form of a “releasing hormone”, which stimulates the pituitary gland to release “stimulating hormone” into the circulation.
Stimulating hormone then signals the target gland to secrete its hormone. As the level of this hormone increases in the circulatory system, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland stop producing releasing hormone and stimulating hormone thereby slowing down the secretion of the target gland. This system leads to the stabilization of hormones in the blood and is regulated by the pituitary gland.
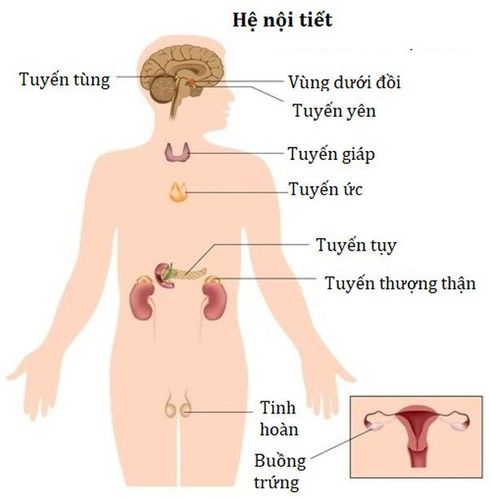
Hình ảnh hệ thống nội tiết
2. Structure of the endocrine system
The composition of the endocrine glands includes the following main glands: hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland, pineal gland and reproductive organs (ovaries and sperm). The pancreas is also part of this system, which plays a role in hormone production as well as in digestion.2.1. Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is located in the lower central part of the brain. This part of the brain is important in the regulation of satiety, metabolism, and body temperature. In addition, it secretes hormones that either stimulate or inhibit the release of hormones in the pituitary gland.
Of the hormones released, the hormones secreted into the arteries (physiological portal systems) carry them directly to the pituitary gland, these releasing hormones signal the release of stimulating hormones. The hypothalamus also secretes a hormone called somatostatin that causes the pituitary gland to stop producing growth hormone.
Vị trí vùng dưới đồi
2.2. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain below the hypothalamus and is no larger than a pea. It is often considered an important part of the endocrine system because it produces hormones that control many of the functions of other endocrine glands. When the pituitary gland does not produce one or more hormones or does not produce enough, it causes hypopituitarism.
The pituitary gland is divided into two parts: anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior lobe produces hormones that are regulated by the hypothalamus:
Growth hormone. Stimulates bone and tissue growth (growth hormone deficiency leads to faulty growth). Growth hormone deficiency in adults leads to problems maintaining body fat and muscle and bone mass. It is also related to emotional state. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Stimulate the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone (a lack of thyroid hormone or a defect in the pituitary gland or the thyroid gland itself would be called hypothyroidism). Adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH). Stimulates the adrenal glands to produce certain steroid related hormones. Luteal-stimulating hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Hormones that control sexual function and the production of sex steroids, estrogen and progesterone in women or testosterone in men. Prolactin. Hormones that stimulate milk production in women
The posterior lobe produces hormones that are not regulated by the hypothalamus:
Dilatation hormone . Control of renal dehydration. Oxytocin. Hormones that stimulate milk production The hormones released by the pituitary gland are actually produced in the brain and carried to the pituitary gland via nerves and they are stored in the pituitary gland.
2.3. Thyroid gland The thyroid gland is located in the lower front part of the neck. This gland produces thyroid hormone that regulates metabolism in the body. It also plays a role in the growth and development of bones and the nervous system of children. The pituitary gland controls the release of thyroid hormone and helps maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, muscle tension, and reproductive function.
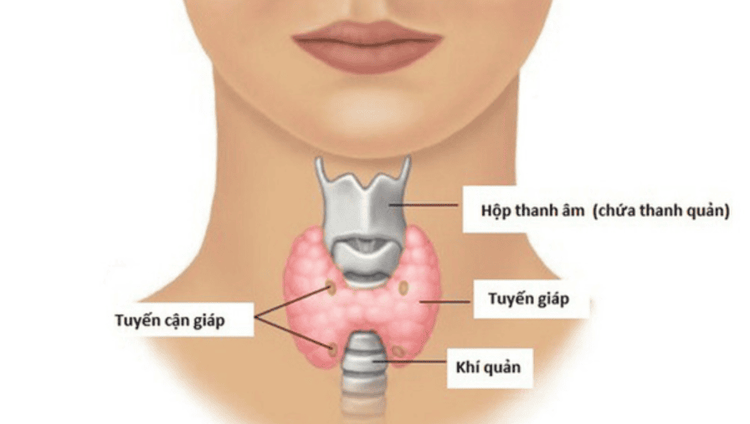
Vị trí tuyến giáp
2.4. Parathyroid glands The parathyroid glands are two pairs of small glands that are embedded in the surface of the thyroid gland. They release parathyroid hormone and have a role in regulating blood calcium levels and bone metabolism.
2.5. The two adrenal glands are triangular glands located on top of each kidney. The adrenal glands are made up of two parts. The outer part is called the adrenal cortex and the inner part is called the adrenal medulla.
The outer part produces the hormone corticosteroid which regulates the body's metabolism, salt and water balance in the body, immune system and sexual function. The interior or adrenal medulla produces catecholamines (eg, adrenaline). These hormones help the body deal with physical and mental stress by increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
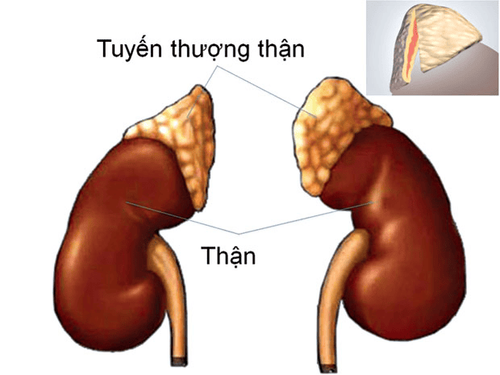
Tuyến thượng thận
2.6. The pineal gland is located deep in the center of the brain. Its function is to regulate a number of hormones including melatonin - the hormone that helps regulate sleep, also known as the circadian rhythm.
In addition, the pineal gland plays a role in the regulation of female hormones, affecting the menstrual cycle and fertility.
2.7. Pancreas The pancreas is a long, flat organ located in the abdomen, made up of two endocrine and exocrine glands. The pancreas is surrounded by the small intestine, stomach, liver, gallbladder, and spleen.
The pancreas plays an important role in converting food into fuel for the body's cells. It does this by producing digestive enzymes that are released into the intestines to digest food. It also makes other hormones control blood sugar.
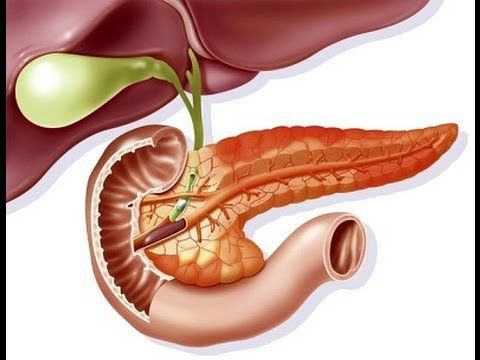
Vị trí tuyến tụy
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Articles refer to sources: webmd.com, emedicinehealth.com, healthline.com
MORE:
Treatment of hormonal disorders Signs of declining estrogen - what happens when estrogen drops? Neuroendocrine tumors: Classification and symptoms