This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thanh Nam - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has over 10 years of experience in the field of Diagnostic Imaging.Vascular hyperplasia is the presence of more blood vessels in the lesion than in the surrounding parenchyma due to the abnormal growth of neoplastic vessels within the lesion. The role and mechanism of action of anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer treatment has mainly been studied based on vascular proliferation in malignant tumors.
1. Benign and malignant tumor formation
Tumors also come in two types, benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous), both of which share some similarities in terms of their formation. Normally, most cells have a certain lifespan. After a number of cycles of asexual reproduction or self-division, cells will have time to function according to function and gradually enter a predetermined process of death, also known as "programmed death". For each "old" cell that dies, a new "young" cell is born to replace its spatial position, as well as take over the same function as the cell that gave birth to it. If the above procedure goes on smoothly, the tumor will not appear.However, there are still cases where "old" cells refuse to die, while new cells are still born. If the new cells still retain the old differentiation function, then a benign tumor appears. This is called the result of a genetic mutation in a benign tumor.
In contrast, malignant tumors are formed when the above gene mutation process is also accompanied by:
Uncontrolled duplication of immature cells; New cells have no function or are poorly differentiated; Produce substances that stimulate the growth of new blood vessels; Produce substances capable of destroying the outer layer of the tumor to invade nearby organs. In particular, the term “metastasis” refers to the process by which cells separate from the original tumor and enter new blood vessels, or lymph nodes, to colonize and grow in one or more other organ structures. in the body.
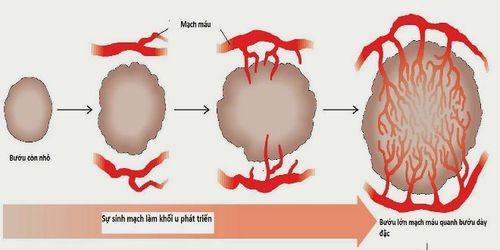
2. Tumor-nurturing role of vascular proliferation
When very young, the phenomenon of vascular proliferation has not appeared, the tumor is just a bunch of cells with simple characteristics:Inability to thrive; No big growth; Non-invasive and breaks down barriers to vascular entry; Therefore, cancer cells have not been able to metastasize far to nearby organizations and cause harm to the patient. However, during the survival of malignancies, they produce substances that stimulate abnormal neoplastic angiogenesis (vessel walls without muscle layer, wide vessels, low impedance, ...) Blood flow to tumors is greater than normal, providing enough nutrients for them to grow and develop rapidly, especially at metastasis.
According to sharing from cancer treatment experts, the small metastases that want to grow larger must completely depend on the formation and new production of the blood vessels responsible for feeding the malignant tumor. At the same time, in the process of development, the tumor itself must also produce substances that stimulate the proliferation of new blood vessels to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients.
3. The relationship between cancer treatment and anti-angiogenesis drugs

Liver cancer: When contrast material is injected into the liver, at the tumor site, this substance concentrates at a very high rate; Breast cancer : In the advanced stage, around the lesions, there are many proliferative and zigzag blood vessels; Lung cancer : The tumor wants to grow, it needs to have blood vessels to nourish, especially in the spreading stage; Thyroid cancer: Signs of a suspected malignancy on ultrasound include thyroid gland with central vascular hyperplasia, hypoechoic, irregular margins, and internal calcifications. . In addition, cases of endometritis (due to retained placenta after stillbirth) when ultrasound can also detect vascular proliferation in the uterus.
Therefore, when it comes to therapies for solid organ cancer tumors, the essential role of anti-angiogenic drugs is often emphasized by doctors. Vascular antibiotics are one of the initial achievements of targeted therapy and can now be applied in practice.
Based on the mechanism that cancer cells want to survive, grow and develop, as well as metastasize, they must be nourished by blood sources, anti-angiogenesis therapy is the use of drugs that block the New blood vessels form and proliferate to avoid supplying nutrients to the tumor.
In terms of etiology, this is considered the optimal treatment. The advantage of this vascular antibiotic measure will be more specific when using monoclonal antibodies acting on the cells that make up the vascular wall of the blood vessels feeding the tumor, as well as focusing on inhibiting the establishment and proliferation of tumors. of new blood vessels, while not affecting normal blood vessels.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.