This is an automatically translated article.
The pineal gland or third eye is a small endocrine gland in the nervous system. It produces melatonin and is key to the body's internal synchronization that helps regulate circadian rhythms including signals such as fatigue, sleepiness, wakefulness, or alertness at different times of the day.
1. Pineal gland
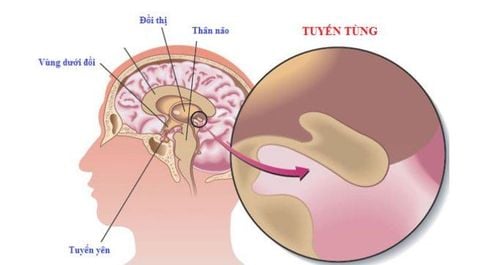
The pineal gland is a small, bean-shaped gland in the brain. It is considered a mysterious organ because its function was discovered last of the endocrine glands. The pineal gland is known as the third eye from the location deep in the center of the brain that is connected to light. Researchers think it produces and regulates several hormones including melatonin. Melatonin (a hormone derived from serotonin) is best known for its role in sleep regulation - maintaining circadian rhythms, and regulating reproductive hormones. The pineal gland is one of the secretory peripheral nervous system organs in which a blood-brain barrier does not exist at the capillary level. The pineal gland often appears calcified in X-rays, due to the accumulation of fluorine, calcium, and phosphorus compounds with age.
The pineal gland also plays a role in regulating female hormone levels and it can affect fertility and the menstrual cycle. That's partly because melatonin is produced and secreted by the pineal gland. Many studies have shown that melatonin has a protective effect against cardiovascular problems such as atherosclerosis and high blood pressure. However, more research is needed on melatonin's potential functions.
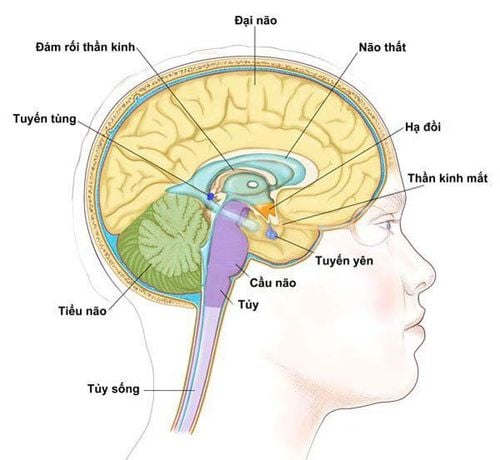
Vị trí tuyến tùng trong cơ thể người
2. The role of the pineal gland in the endocrine system
The main function of the pineal gland is to produce melatonin. Melatonin has many different functions in the central nervous system, the most important of which is to help regulate sleep patterns. Melatonin production is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light. Light-sensitive neurons in the retina detect light and send signals to the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCNs), which synchronize the suprachiasmatic particles with the day-night cycle. Nerve fibers then transfer daylight information from the suprachiasmatic granules to the central nucleus accumbens (PVN), then to the spinal cord, and through the sympathetic system to the cervical ganglion (SCG) and from there into Pineal gland .
2.1. Regulation of the Pituitary
Studies in rodents have shown that the pineal gland affects pituitary secretion of the sex hormones that are follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing hormone (LH). Mucosectomy performed in rodents did not produce a change in pituitary weight, but caused an increase in the levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and and luteinizing hormone (LH) in the gland. Administration of melatonin did not return follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels to normal, suggesting that the pineal gland affects pituitary secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and and luteinizing hormone (LH) through via an undescribed transmission molecule.
The pineal gland contains receptors for the regulation of compounds that act as neurotransmitters (which are short polypeptide chains), endothelin when injected in quantities of picoole into the cerebral ventricles. It will induce a calcium-mediated increase in the glucose metabolism of the pineal gland.
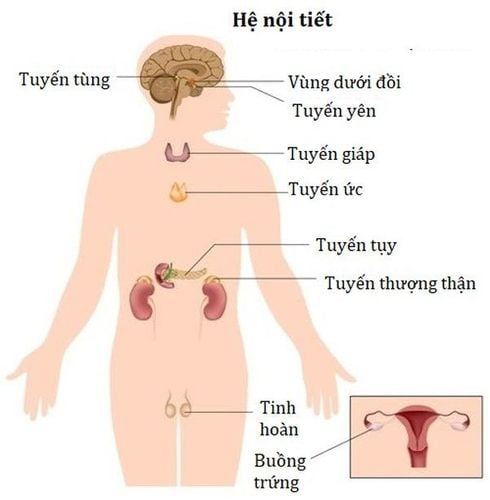
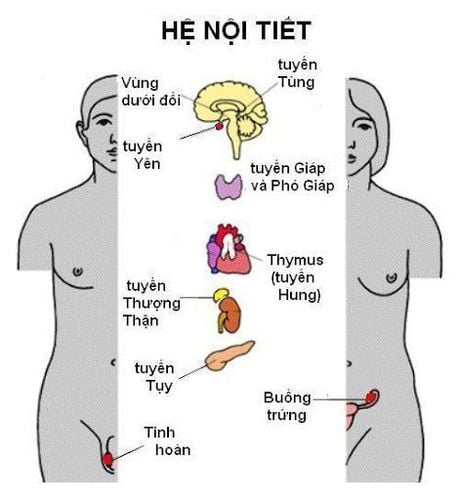
Hình ảnh hệ nội tiết con người
2.2. Regulation of Bone Metabolism
Studies in rats suggest that melatonin is derived from the pineal gland to regulate bone deposition. Melatonin mediates activity through the MT2 receptor. This process may represent a potential new target in the treatment of osteoporosis. Because, study showed the therapeutic effects of oral therapeutic administration of melatonin in a mouse model of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
2.3. Circadian rhythm
Circadian rhythm is a 24-hour circadian cycle characterized by sleep-wake patterns. Daylight and darkness help regulate circadian rhythms. Light exposure suppresses melatonin release and controls circadian rhythms
Melatonin secretion is low during the day and high at night, which will likely affect the body's response to light cycles (length) of day versus night). Light cycles affect sleep patterns, but the extent to which melatonin affects sleep patterns is controversial.
2.4. Reproduction
Melatonin suppresses secretion of the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates gonadal activity (follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones support proper growth and functioning. fusion of the ovary and testicle.
Tuyến tùng có vai trò trong hoạt động của tuyến sinh dục
3. Some health problems related to the pineal gland
3.1 The pineal gland and heart health
Retrospective research on the link between melatonin and heart health shows evidence that melatonin produced by the pineal gland can positively impact heart and blood pressure. And research has concluded that melatonin can be used to treat cardiovascular disease.
3.2. The pineal gland and female hormones
There is some evidence that light exposure and related melatonin levels may affect a woman's menstrual cycle. Reduced melatonin levels may also play a role in the development of irregular menstrual cycles.
3.3. Pineal gland and mood stability
The size of the pineal gland may indicate an increased risk of certain mood disorders. Recent research suggests that a lower pineal gland volume may increase the risk of developing schizophrenia and other mood disorders.

Định kỳ kiểm tra sức khỏe, giúp mọi người phát hiện bệnh lý sớm
3.4. Pineal gland and cancer
Some studies suggest that there may be a link between impaired pineal gland function and cancer risk. Research in mice has found evidence of lowered pineal gland function through overexposure to light leading to cell damage and an increased risk of colon cancer.
3.5. Pineal gland and melatonin
If you have trouble sleeping, it could be a sign that the pineal gland is not producing the right amount of melatonin. To control the amount of melatonin in the body, melatonin supplements can be used. They will help the body to rearrange the circadian rhythm and supplement this substance will help the body fall asleep faster. However, melatonin supplements can cause side effects such as: drowsiness, grogginess in the morning, increased blood pressure, a slight drop in body temperature, anxiety, and confusion. For optimal use of these drugs should be consulted by a doctor to avoid unwanted side effects. References: webmd.com, endocrineweb.com, healthline.com, en.wikipedia.org
SEE MORE
Pineal gland: Structure and function Understanding pineal gland tumors What makes up the endocrine system?