This is an automatically translated article.
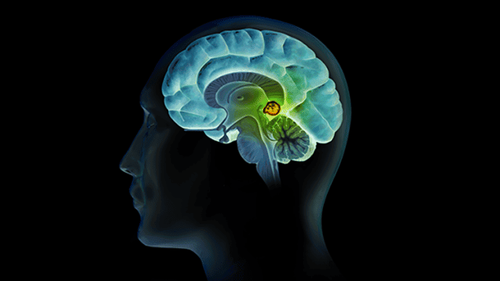
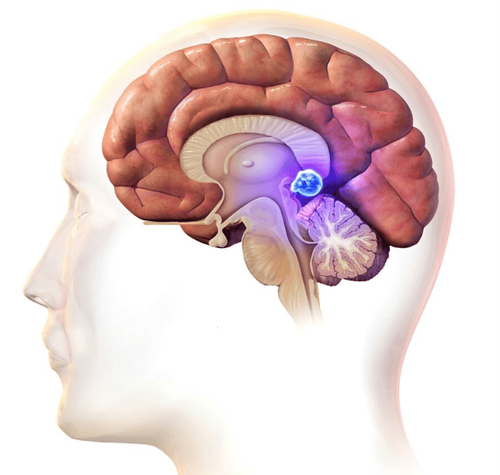
The pineal gland is also known as the pineal gland. The pineal gland is a hidden part of the brain, hiding under the stem connecting the two hemispheres, as small as a pea. In the afternoon, the pineal gland secretes the hormone melatonin, which puts us to sleep.
1. What is the pineal gland?
The pineal gland is a small endocrine gland located in the nervous system. The pineal gland is a small endocrine gland located in the brain of vertebrates, in the epithelium, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, and is concealed in a groove, where two pieces of the thalamus (thalamus) meet. The pineal gland is shaped like a small pineal located near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres in the groove where the two thalamus meet. The pineal gland contains mainly pinealocytes, which are cells that produce the hormone melatonin, and glial cells—a special type of brain cell that supports neurons (cells that transmit information to other cells). .2. What does the pineal gland secrete?
The pineal gland secretes melatonin which is a hormone that helps regulate circadian rhythms. Melatonin is produced according to the amount of light the body is exposed to. The pineal gland releases a larger amount of melatonin when it's dark, causing the body to feel sleepy. Many supplements provide melatonin as a natural sleep aid.
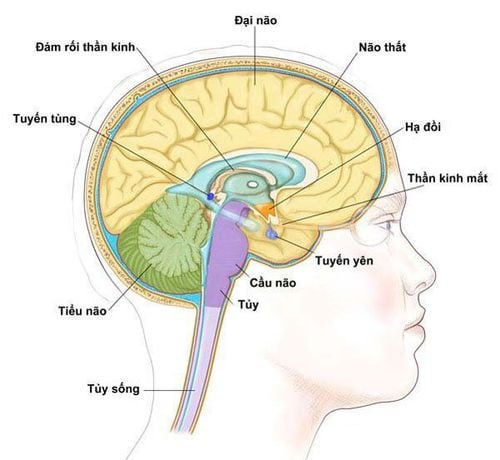
Tuyến tùng tiết ra melatonin là một loại hormone giúp điều chỉnh nhịp sinh học
3. The function of the pineal gland
Some of the functions of the pineal gland include:
Biological clock The pineal gland acts like a clock in the human body to recognize any changes in sunlight amount from day to night or between other seasons thereby regulating circadian rhythms in the body. When the night clock strikes, the pineal gland secretes melatonin, which induces sleep.
Bone metabolism Changes in pineal gland function can affect bone metabolism, and postmenopausal women are significantly more susceptible to osteoporosis than other groups. The function of the pineal gland tends to decline with age. Oral melatonin supplements that increase bone mass may be used in the future to protect against postmenopausal osteoporosis.
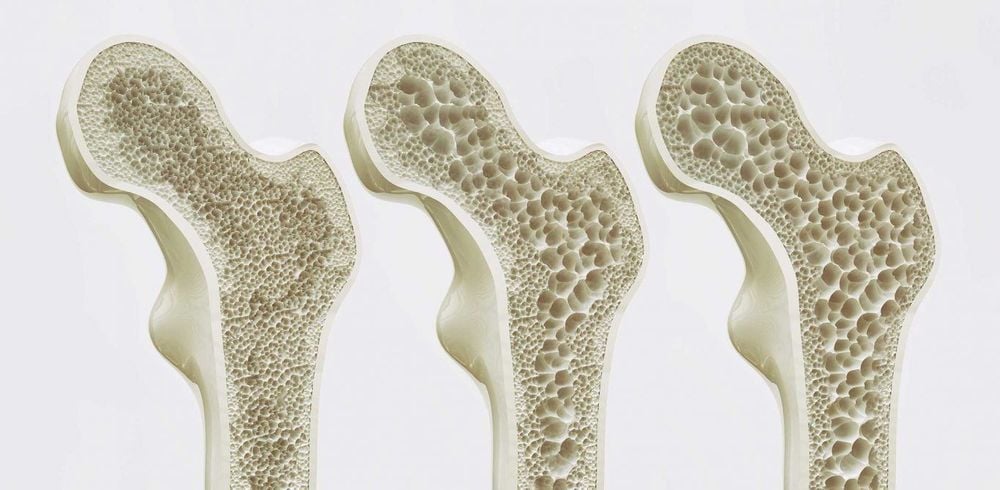
Chuyển hóa xương có sự liên quan với melatonin
Mental health Sleep and mental health are closely related. Certain mental health disorders can also make it harder to sleep. A mental state that has been shown to be closely related to light. Seasonal affective disorder is a form of depression that affects a person's mood and tends to occur when light levels are low. This may be due to changes in the pineal gland that secretes melatonin. However, recent studies show that melatonin does not have any effect on mood disorders.
Regulates pituitary function The pituitary gland is a gland in the hypothalamus that regulates hormones, including growth and thyroid function. Recent research has shown that the pineal gland can alter the functioning of the pituitary gland. Melatonin secreted by the pineal gland can prevent the pituitary gland from secreting hormones that play an essential role in the development of the ovaries and testes and regulate functions such as the menstrual cycle.

Chức năng của tuyến tùng có ảnh hưởng đến chu kỳ kinh nguyệt
Drug metabolism Certain medications, including psychostimulants and therapeutics, can alter pineal gland function and pineal gland melatonin production.
Aging As the body ages, the pineal gland tends to secrete less melatonin. Although melatonin is not the only cause of age-related changes, reduced melatonin levels have a significant effect on the body's normal functioning and metabolism. Melatonin may be a contributor to the fact that older adults sleep less and may have more difficulty falling asleep.

Chức năng của tuyến tùng ảnh hưởng đến sự lão hóa
Sense of orientation People with impaired pineal gland function due to damage to this gland affect the person's perception, spatial and temporal orientation.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE
Role of growth hormone (GH) test Growth hormone excess GH What do prolactin hormone test results say?