This is an automatically translated article.
Cysts and tumors are both growth cells. They may be similar in appearance, but the cause of the disease is completely different. To get the most accurate results, patients need to go to the hospital to be tested and diagnosed.1. What is a cyst?
Cysts are sac-like structures filled with liquid, are semi-solid or gaseous, and occur in most tissues of the body.
Cysts have different sizes, small and form anywhere on the body, be it bone, soft tissue. Internal organs can be displaced by cysts, but most cysts are not cancerous.
The most common types of cysts are:
Breast cysts: These are fluid-filled sacs inside the breast that can easily move under the skin and are usually benign. You may have one or more breast cysts on one or both sides; Epidermoid cyst: A fluid-filled bump located just below the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. Epithelial cysts can appear in many locations such as: on the neck, chest, upper back, and scrotum. Ovarian cysts: Occur around the time of ovulation harmlessly. The cysts contain fluid-filled sacs on the inside or on the surface of the ovary. Usually, ovarian cysts cause no specific symptoms, with occasional pelvic pain, back pain, and bloating. Brain Cysts: Brain tumors can be brain cysts, but these cysts are located in the brain but are not “brain tumours” because they do not arise from brain tissue. Liver Cysts: Liver cysts that develop in the liver. Sebaceous cysts: These form in the cells at the bottom of the hair follicle, which usually develop on the scalp. Kidney cyst: Grows in the kidney. There are also other types of cysts that are less common. Usually, the cysts are benign, rarely turning malignant. However, people should not be complacent because most cancers produce cysts.
Nang gan là một loại u nang
2. What is a tumor?
Tumors include benign and malignant tumors: An abnormal growth of cells, a solid mass of tissue.If it is a malignant tumor that will grow uncontrollably and invade other parts of the body; Invasion, metastasis to healthy tissues; invades from where it started to other parts of the body, more likely to lead to cancer.
If it is a benign tumor, the tumor will not spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Benign tumors can form anywhere. Benign tumors are usually slow-growing and not life-threatening, however, with a small probability, they can become malignant, and should be monitored if surgical removal is not performed.
Common tumors such as:
Adenoma: Like colon polyps, bile duct adenomas and liver adenomas are usually benign. These tumors are of glandular epithelial tissue origin, covering organs and glands. Fibroids: Fibroids that grow on connective tissue or fibers most often develop in, on, or around the uterus. This is a benign tumor, not dangerous. Lipoma: People over the age of 40 are prone to this fat cell tumor. Lipomas are usually soft and located just below the skin. Malignant tumors: On the human body, any location can get them. Connective tissue is the site where sarcomas develop like bone marrow. Another common type of malignancy is carcinoma, another common type of malignancy, that develops from epithelial cells in the colon, liver, or prostate. With malignant tumors, large tumors, the doctor will appoint the patient to have surgery to remove it. These tumors affect the health and life of the patient because it compresses the organs, causes pain and other symptoms.
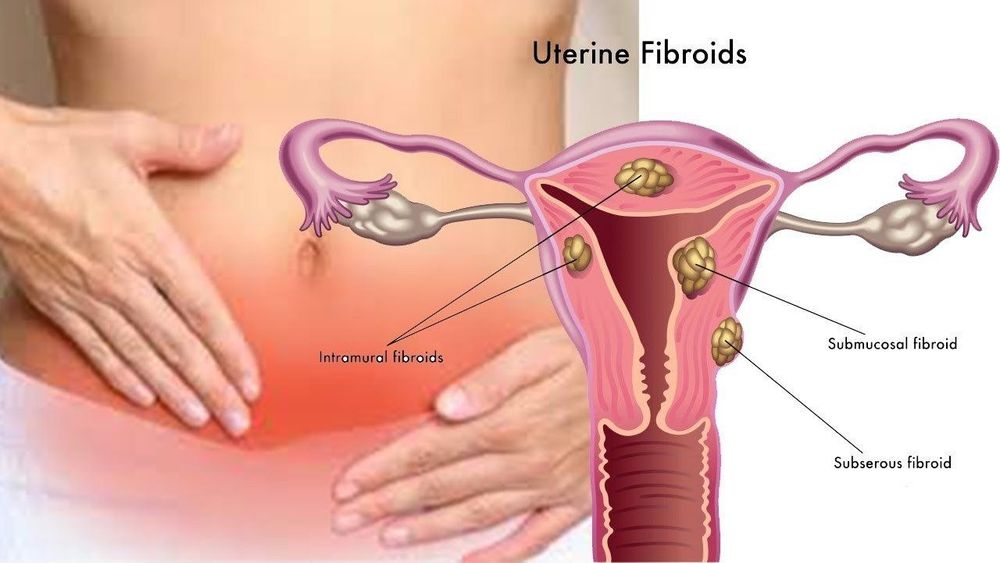
Các khối u xơ thường là u lành tính
3. Diagnosis of Cysts and Tumors
When you find out you have a tumor, it is advisable to go to the hospital for an examination to get the most accurate results, whether it is a cyst, a benign tumor or a malignant tumor.Some measures, doctors appoint to diagnose tumors such as
Ask about the patient's history Ask about the onset of symptoms, the most prominent symptoms. Ultrasound Biopsy Request
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist as well as customers wishing to examine and diagnose diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the Health System Vinmec nationwide or register online HERE.