This is an automatically translated article.
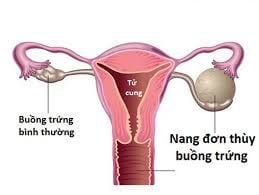
Ovaries are important endocrine organs in women. The ovaries produce eggs, which then meet the sperm to fertilize them. So any abnormal growth in the ovary will lead to the formation of a tumor in the ovary, most commonly an ovarian cyst.
1. Ovarian cyst pathology
Ovarian cyst disease occurs with a frequency of 12.8/100 000 women, of all ages from girls to postmenopausal women. Most ovarian cysts are benign if they develop during reproductive age, but the risk of developing a malignancy increases with age. Ovarian cysts account for about 80% of the diseases that cause tumors in the ovaries in general. When detecting pathology, patients should treat ovarian cysts early to avoid missed cases of ovarian cancer - one of the risk factors for death in women.
2. Common types of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cyst pathology has many different forms, including:
2.1. Functional ovarian cyst pathology The cause of cystic tumors is due to endocrine disorders of the ovaries. However, the pathophysiology of the ovary was still normal, there was no change. Functional ovarian cysts include 2 types:
Ovarian cyst: The follicle develops but does not burst and does not ovulate. Then they continue to grow (maybe over 10cm) and continue to secrete oestrogen, causing the patient to delay menstruation. In some cases, ruptured ovarian cyst can cause massive intra-abdominal bleeding that requires emergency surgery; Thyroid cyst: This is a common type of cyst in patients with ovulatory pregnancy, glioblastoma, multiple pregnancy or being treated for infertility. 2.2.Physical ovarian cyst pathology These are tumors with histological changes in the ovaries, so they have a risk of cancer, including the following types:
Ovarian water cysts : The most common form, accounting for about 40%. Cases on the surface of the cyst with comb-shaped proliferative blood vessels or the appearance of superficial/intraluminal papillae are signs suggesting progression to cancer; Ovarian mucinous cyst: This type accounts for about 20% of organic ovarian cysts. Mucous cysts are often large in size, can weigh up to several tens of kilograms and often stick to surrounding tissues; Ovarian dermoid cyst: Found in 25% of cases, of which the most common are teratomas with a very special organizational structure. The tumor wall has a structure similar to the skin, has a horny structure or a sebaceous gland... The inside of the cyst usually contains tissues such as hair, teeth, bean residue... MORE: Learn about robotic endoscopic surgery. ovarian cyst at Vinmec

U nang nước buồng trứng là bệnh lý u nang buồng trứng thường gặp
3. Symptoms of ovarian cyst disease
Symptoms of ovarian cysts often progress silently and most of the time there are no specific symptoms, so most are discovered when the patient has regular gynecological examination or visits for other reasons.
However, in cases when the cysts are large, the patient may appear the following signs:
Dull abdominal pain in the lower abdomen or pain when performing special activities. The pain of cysts is often misunderstood due to a number of other gynecological diseases such as cervicitis, uterine fibroids... May disrupt the menstrual cycle; Signs caused by cysts pressing on nearby organs such as difficulty urinating or constipation...; In case the cyst grows quickly, the patient may have symptoms such as abdominal distension, weight loss, loss of appetite, fatigue... and these are signs suggesting malignancy.
4. Points to note when treating ovarian cysts
4.1. Complications of ovarian cyst disease if not treated Ovarian cyst complications vary from patient to patient, appearing sooner or later. Many complications appear as signs to diagnose the disease:
Torsion of the cyst: Occurs with any type of cyst. In which, it is easiest to twist when the tumor is small, the stalk is long, and it is not sticky. When the tumor is twisted, the patient will have severe, continuous abdominal pain, which may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting and sometimes shock due to pain. On examination, the doctor can note abdominal distension, pain in the lower abdomen and 2 pelvises, positive abdominal wall reaction. Direct vaginal examination revealed the tumor was very tight, less mobile, and painful when pressed; Cyst rupture: Sudden, continuous abdominal pain in the hypogastrium and 2 iliac fossa, with abdominal wall reaction. Some patients rupture the cyst causing intra-abdominal bleeding and even hemorrhagic shock. Vaginal examination is more difficult to identify the tumor, painful uterine mobility is increased, and the posterior is full; Compression of surrounding organs: this is a late complication, when the tumor has grown before and is large in size (for example, the tumor presses on the bladder causing urinary urgency / burning, the tumor compresses the rectum causing constipation. , tumor compresses the ureter causing hydronephrosis). Rarely, very large ovarian cysts compress the inferior vena cava causing collateral circulation, edema of the legs or ascites... 4.2. Note when having ovarian cyst disease during pregnancy Pregnant women with ovarian cyst disease are mainly diagnosed through routine antenatal check-ups or ultrasound. Women can develop any type of ovarian cyst, but the highest rates are corpus luteum or dermoid cysts, and in very few cases the cysts are malignant. Treatment of ovarian cysts in women should be considered surgery at 13 weeks of gestation or more because at this time, the fetus has secreted enough hormones to nourish the fetus. In case ovarian tumors in pregnant women are corpus luteum cysts, after 13 weeks of age they will decrease in size or stop growing, so sometimes surgery is not needed but only pathological surgery to monitor. In the case of ovarian cysts that enlarge during the second trimester of pregnancy, immediate surgery is required.

Cần thăm khám kỹ lương khi điều trị u nang buồng trứng khi mang thai
5. Ovarian Cyst Treatment
Treatment of ovarian cysts depends on the differential diagnosis of functional cysts and organic cysts because the management attitude of the two types is very different.
Functional cysts usually do not need treatment, disappearing on their own after a few menstrual cycles. Some patients may be prescribed combined oral contraceptives by their doctor, but the effectiveness has not been clearly proven. In the case of functional ovarian cysts with complications such as cyst torsion, cyst rupture, bleeding... emergency surgical treatment may be indicated but very rarely.
For organic cysts, surgical treatment should be performed as soon as possible to avoid dangerous complications. The treatment regimen for ovarian water cysts as well as other types of organic cysts will depend on the size, nature of the tumor and the patient's desire to have children.
The surgeon can remove the entire tumor and the ovary on the same side or remove only the tumor and keep the healthy ovary. However, the disadvantage of ablation therapy is the increased risk of pathological recurrence of ovarian cysts.
Depending on the preoperative assessment, the treating doctor advises the patient to choose the appropriate surgical method such as laparoscopic or open surgery, removing ovarian cysts or removing both appendages and uterus. especially in patients with comorbidities requiring treatment).
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is applying the method of removing ovarian cysts with a robotic arm. This is a modern surgical method with low risk of infection, short hospital stay and quick recovery time. Under the direction and implementation of a team of experienced and skilled medical staff and doctors, patients will be operated with high safety and efficiency.
With the most modern equipment in Vietnam such as anesthesia machine in the operating room. The world's most modern Hybrid operating room system, which integrates the operating room and advanced imaging equipment, helps to reduce surgery time and bring the best surgical efficiency to the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.