This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by BSCKI Truong Nghia Binh - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec International Hospital Da Nang.Pelvic inflammatory disease is a serious complication in women caused by sexually transmitted diseases. The disease is quite common but completely treatable. Early treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease reduces the risk of associated complications.
1. Pelvic inflammatory disease in women
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs). This is a common disease. Each year in the United States more than one million women are diagnosed with pelvic inflammatory disease.Pelvic inflammatory disease occurs when bacteria from the vagina and cervix move into the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes. These bacteria can cause abscesses in the fallopian tubes or ovaries. If left untreated, it can lead to long-term complications.
2. Causes of pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease is caused by two common sexually transmitted diseases, gonorrhea and chlamydia. Symptoms of these two diseases in women may be subtle or even asymptomatic. When a woman is infected with gonorrhea or chlamydia but is left untreated, it can lead to complications from pelvic inflammatory disease in a few days or weeks. It can also be caused by non-sexually transmitted infections, such as bacterial vaginosis.3. Is pelvic inflammatory disease dangerous?
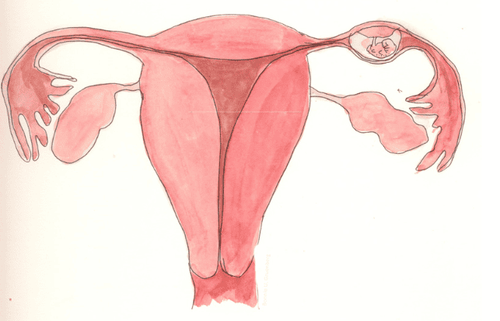
Pelvic inflammatory disease in women can lead to serious and long-lasting problems, including:Infertility : One in 10 women with pelvic inflammatory disease is infertile. This is because the disease can leave scars on the fallopian tubes. This scar will most likely block the fallopian tubes and prevent fertilization. Ectopic pregnancy: Once the egg is fertilized, its way into the uterus is likely to be blocked by scarring caused by pelvic inflammatory disease. As a result, the fertilized egg will begin to develop right in the fallopian tube. This condition, called an ectopic pregnancy, is very dangerous for pregnant women. Accordingly, the fallopian tube can burst due to the pressure developing from the fetus, causing bleeding into the abdominal cavity and pelvis, threatening the mother's life. If an ectopic pregnancy is not diagnosed early enough, emergency surgery may be required. Chronic pelvic pain: It can lead to pelvic pain that lasts for years.
4. Subjects often have pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease can occur in women of any age, after sexual activity. However, the disease occurs most commonly in young women. Especially women under the age of 25 are more likely to get the disease. Women with the following risk factors are also at increased risk for pelvic inflammatory disease:Sexually transmitted infections, most commonly gonorrhea or Chlamydia. Having sex with different sex partners (the more sex partners, the greater the risk of contracting the disease). The risk of infection from a partner who is having sex with many other people. Have had pelvic inflammatory disease before. Some studies show that women who douche regularly are more likely to develop pelvic inflammatory disease. Vaginal douching is the agent that not only makes it easy for pathogenic bacteria to grow, but also accidentally pushes bacteria from the vagina into the uterus and fallopian tubes. Therefore, douching is often not recommended by doctors.
5. Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Most women with PID have only mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. Because the symptoms are often quite subtle, many cases of the disease go undetected by clinical signs. Here are the most common symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease:Abnormal vaginal discharge. Pain in the lower abdomen (usually mild). Right upper abdomen pain. Menstrual bleeding is abnormal. Fever and chills. Pain when urinating. Nausea and vomiting. Pain during sex. Just because you notice one of the above symptoms does not mean you have pelvic inflammatory disease. It could be a sign of something more serious, such as appendicitis or an ectopic pregnancy. You should see your gynecologist if you notice any of these symptoms.
6. Diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease
To determine if you have pelvic inflammatory disease, your doctor will first ask about your medical history and related issues, including your sexual habits and birth control methods you're using. If you're experiencing symptoms, you'll need to have a pelvic exam to determine if there's a problem with your reproductive organs. Your doctor will take a sample of discharge from your cervix to check for the possibility of gonorrhea and chlamydia. In addition, you may have blood tests, ultrasound, endometrial biopsy, and even a laparoscopy.
7. Treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease is completely treatable. However, treatment will not be able to reverse the scar caused during the infection. On the other hand, with an untreated condition, the longer it goes on, the greater the risk of other problems, such as infertility.To treat pelvic inflammatory disease, the doctor will first prescribe oral or intravenous antibiotic treatment. Antibiotics alone are likely to resolve the infection. However, your doctor may prescribe a combination of two or more antibiotics at the same time. Usually, patients need to be re-examined after 2-3 days to check the effectiveness of treatment. Sometimes the symptoms will go away before the infection is cured. At that time, you should still use all the medicine prescribed by your doctor.
Some cases of pelvic inflammatory disease require hospital treatment:
There is no clear diagnosis. Pregnant. Intravenous antibiotics must be used. Bad prognosis. Nausea and vomiting. High fever. Abscess in a fallopian tube or ovary. In certain situations, such as when an abscess is found, surgery may be needed.
In addition, the patient's sexual partner must also be treated. Women with pelvic inflammatory disease are more likely to have sexual partners with gonorrhea or chlamydia, even if there are no signs of the disease.
8. Prevents Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
To prevent the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease, keep the following in mind:Use a condom every time you have sex to prevent the risk of STIs. Condoms should still be used even if other methods of birth control are available. Have sex only with a partner who does not have the disease and who does not have promiscuous sex. Limit the number of sexual partners to limit the possibility of infection. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has implemented the Basic Gynecological Examination and Screening Package to help women detect inflammatory diseases early, including pelvic inflammatory disease, and help treat easy, inexpensive. In addition, screening for early detection of gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) is also performed.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Acog.org