This is an automatically translated article.
Pathologically, non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a form of lymphoma. So what are the symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma? Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is common in which population?1. Overview of non-Hodgkin lymphoma pathology
Pathologic non-Hodgkin lymphoma (the disease is called non-Hodgkin lymphoma), is a type of cancer of the lymphatic system. In the body, the lymphatic system is responsible for protecting and fighting against pathogens and infections.With non-Hodgkin lymphoma, the tumor develops from lymphocytes (lymphocytes that exist in the lymph nodes, spleen, and other organs of the immune system). With this feature, the tumor can originate from any location in the body and spread to other parts.
Malignant non-Hodgkin lymphoma can arise from 1 of 2 types of cells:
B lymphocytes: The job of B cells is to produce antibodies to neutralize foreign agents that cause infection. Most non-Hodgkin lymphomas start from B cells. T lymphocytes: The job of T cells is to destroy foreign agents that directly invade the body and cause disease. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas very rarely arise from T cells.
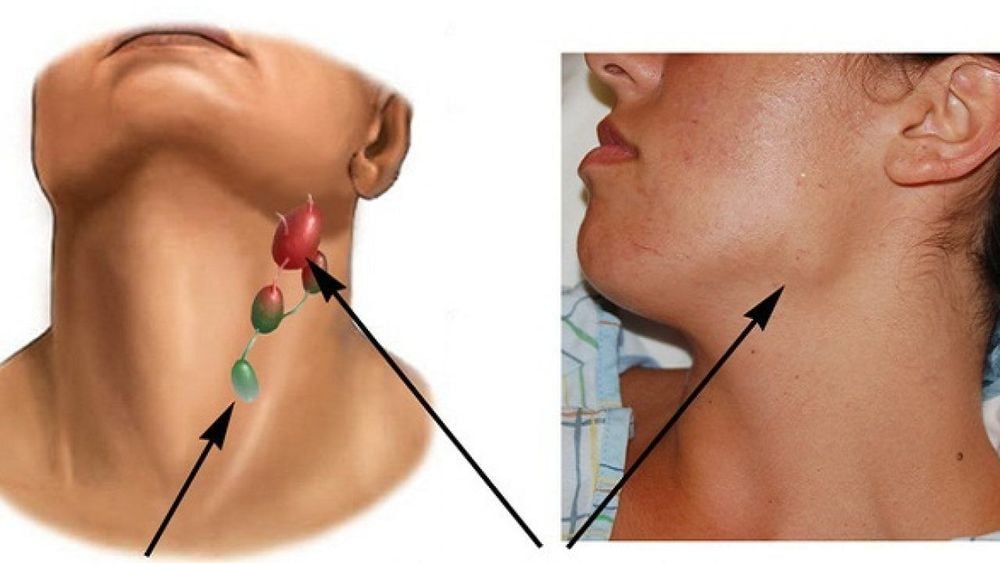
U lympho ác tính không Hodgkin vùng cổ
2. What causes non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
To date, the cause of non-Hodgkin lymphoma remains unknown. The origin of the disease is when the body occurs abnormally overproduction of lymphocytes. However, researchers suggest that people with weakened immune systems (after transplant surgery, or infected with the HIV virus) have an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma.3. What are the signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma usually causes the following signs:The lymph nodes (in the neck, armpit or groin area) are enlarged but do not cause pain. Abdominal pain (also abdominal distension), chest pain. Often has a fever and often has headaches and fatigue. Sweating, especially at night. Lose, lose weight. Difficulty breathing, dry cough. Eating is not appetizing. Nausea or vomiting. Constipation. There may be convulsions.
4. Who is at risk for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?

Người lớn tuổi trên 60 tuổi có nguy cơ mắc u lympho không hodgkin cao hơn bình thường
Have a weakened immune system after being treated for another disease with an organ transplant; or weakened immune system due to infection with certain bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori, HIV virus, Epstein-Barr. Elderly (over 60 years old). Men have a higher risk of getting the disease than women.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE:
Hodgkin: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Diagnosis of lymphoma with ultrasound Can treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma be delayed?