This is an automatically translated article.
The article is advised by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Nhat - Infectious Diseases - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalHistamine is a substance that exists in the body and plays an important role in the production of a number of body reactions such as allergies, anaphylaxis, increased secretion of tears, nasal discharge...etc. Through this article, let's learn about the formation of Histamine as well as its mechanism of action and impact on the human body.
1. What is Histamine?
Histamine is one of the substances that is closely related to anaphylaxis, inflammatory reactions, allergies, nerve conduction and gastric secretion. Histamine is detected in all tissues in the body with uneven distribution density, mainly in lung, intestinal, and skin tissues.2. Conditions for the formation of histamine
Histamine formation begins from the decarboxylation of Histidine under the catalysis of decarboxylase. Under electrostatic attraction, Histamine with a positive charge easily binds Heparin with a negative charge to form a Histamine - Heparin complex that has neither activity nor biological effects. This complex is stored in granules in mast cells, gastric mucosal cells, intestines, nerve cells... and only when affected by external factors such as cold, air dust, chemicals. substances, cells containing this complex are stimulated to release free histamine. If the amount of this histamine exceeds the allowable threshold of the body, it can cause an allergic reaction, which is often seen in people with sensitive terrain. Some bacteria and viruses that cause dangerous diseases when infected in the intestinal tract can also produce histamine.
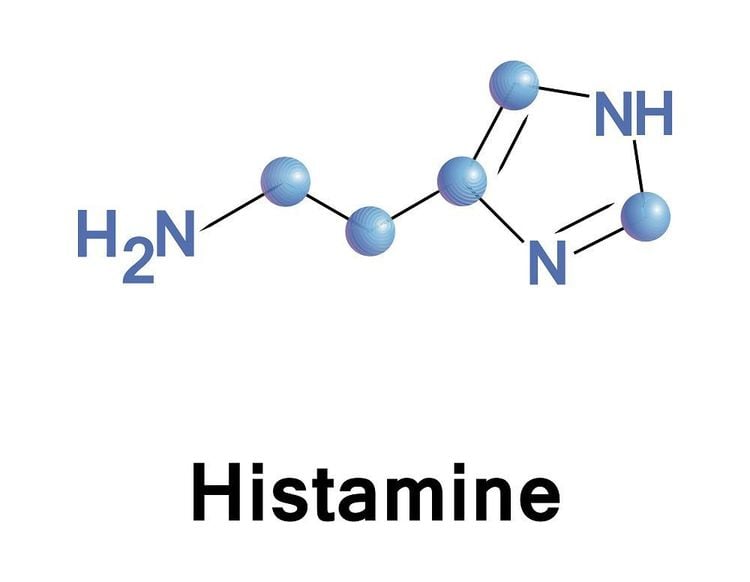
Sự hình thành Histamin bắt đầu từ sự khử carboxyl của Histidin dưới sự xúc tác của decarboxylase
3. Histamine's mechanism of action
When the human body is affected by agents such as drugs, chemicals, pollen, dust, etc., for people with sensitive terrain, the body will release Histamine. As mentioned above, Histamine is always latent in the human body in skin tissues, stomach, lungs, oral mucosa.
When in a normal state, cells containing Histamine are usually inactive because they exist in a complex with proteins. When the body is allergic, tends to be sensitive to drugs, chemicals or other external agents, the antigens will act on this protein complex and release free histamine, causing reactions. Allergic reactions from mild to severe such as: rash, skin redness, swelling, difficulty breathing, itching, cough, nausea, anaphylaxis ... For cases of complicated allergies, patients Antihistamines may be required for treatment. Antihistamines are all effective in the treatment of acute allergic reactions, which are known to have symptoms such as runny nose, red rash, connective tissue inflammation, dermatitis, ciliary inflammation. allergic circuit,... Antihistamines have many active ingredients and are usually classified by generation or by chemical structure.
Phát ban do histamin
4. The effect of Histamine on the body
As mentioned above, if the amount of Histamine in the body exceeds the allowable threshold, it can lead to allergic reactions such as:
For the respiratory system: Causes runny nose, asthma due to the influence of inflammation, edema and tracheal constriction. For the digestive system: Causes excessive secretion of HCl and pepsin leading to diarrhea due to intestinal spasms, increasing peristalsis and secretion of intestinal juices. For the excretory system: Histamine contributes to increased secretion of tears, nasal secretions, saliva, pancreatic juice. Effects on the eyes: Inflammation and redness of the conjunctiva of the eye. Skin reactions: Rash, urticaria, eczema, itching, swelling on the skin. For the cardiovascular system: lowering blood pressure, causing cardiac constriction, vasodilation. Histamine also has a direct effect on the myocardium and internal nerves, increasing contractility of both atria and ventricles, slow atrioventricular conduction and slow depolarization of the sinus node. For the nervous system: Histamine stimulates the peripheral nerve fibers to cause itching and pain. On the central nervous system Histamine also causes hypothermia, insomnia, loss of appetite, increased secretion of ADH. For smooth muscles: In humans, Histamine increases uterine smooth muscle contraction (bladder, gallbladder, and urethra smooth muscles are less affected).

Histamin tăng cao gây hen suyễn
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
MORE:
Commonly used H1 antihistamines Using antihistamines for pregnant and lactating women Some common allergies in children