This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a doctor from the Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General HospitalHepatic encephalopathy is a common complication of acute and chronic liver failure. Early detection and timely treatment of hepatic encephalopathy will help patients have a better prognosis. This article will provide the basic knowledge surrounding this pathology.
1. What is hepatic encephalopathy?
Hepatic encephalopathy or hepatic coma is a disorder of consciousness, behavior, and coma caused by liver dysfunction. The disease is caused by a metabolic disorder of the central nervous system due to toxins that are not metabolized and eliminated by the liver because of impaired liver function. Hepatic encephalopathy is also a sign of liver failure.2. Causes of hepatic encephalopathy
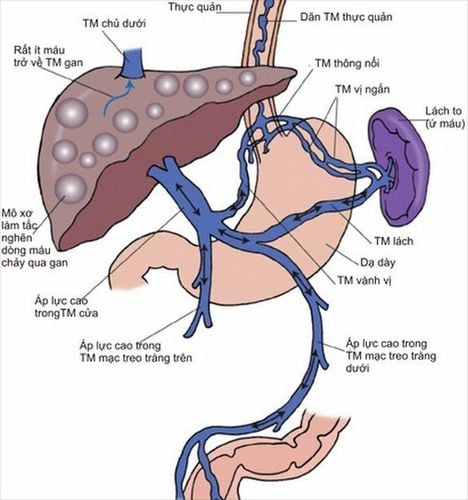
Pathogenesis of encephalopathy - liver is not yet fully understood. It has been suggested that the pathophysiological basis of hepatic encephalopathy is hepatocellular failure and portal-host disease either surgically or spontaneously from collateral circulation. Many toxic substances from the blood of the digestive system that are not metabolized and eliminated by the liver enter the circulatory system and penetrate the blood-brain barrier to the brain, causing brain dysfunction.
Hepatic encephalopathy is the result of many factors, such as proteins including protein, amino acids, ammonia, mercaptan, metabolic disturbances, and accumulation of inhibitory neurotransmitters due to failure of the liver. Metabolism can play an important role.
3. Stages of hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is divided into 5 stages according to the West Haven classification system:Stage 0: Changes in personality, behavior Changes in memory, impaired concentration, impaired intellectual function and coordination . Stage 1: Insignificant cognitive deficit Shortening of attention span Insomnia Depression, irritability. There may be postural dyskinesia.

Mất ngủ trầm trọng
4. Clinical symptoms
Clinical symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy vary according to each stage:Stage 1: Prognostic stage Patient has slight personality changes and behavioral disturbances. The patient's answer is still correct, but the pronunciation is not clear and quite slow, there may be tremor also known as liver tremor. This stage usually lasts a few days or weeks, symptoms are sometimes not obvious, easy to miss.
Stage 2: Pre-coma The patient has signs of confusion of consciousness, sleep and behavior disturbances. There are symptoms of disorientation and decreased understanding. Slurred speech, writing disorder, patients have abnormal behaviors, sleep during the day, even hallucinations, fear. Important neurological signs in this phase: hyperreflexia, increased muscle tone, leg muscle stiffness, and Babinski's sign (+).
Stage 3: Sleep stage Mental confusion, a series of neurological signs that persist or increase most of the time. The patient is comatose, but can be awakened. The patient can answer questions but is often confused and hallucinating. Tremor is still a common symptom.
Stage 4: Coma stage The patient falls into a state of complete loss of consciousness, unable to wake up when stimulated, uncomfortable with the position of the stimulus, pain and reaction, tendon and muscle reflexes increase. Deep coma, altered reflexes, hypotonia, possibly paroxysmal seizures, nystagmus, and hyperventilation.
Severe liver damage often markedly jaundiced, gastrointestinal bleeding, and breath odor of liver. The disease will be complicated by a series of infectious complications, hepatorenal syndrome and cerebral edema.
5. Diagnostic test for hepatic encephalopathy
Xét nghiệm nồng độ amoniac máu
Vinmec International General Hospital is the leading prestigious hospital in the diagnosis and treatment of liver diseases. Patients will be examined and diagnosed with the most modern methods today, with the support of high-tech machines for accurate results. The treatment also ensures thorough, minimizes the possible risks in case of liver disease with serious complications such as hepatic encephalopathy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.