This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalGastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also known as reflux esophagitis, is a disease that occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus (the digestive tube that connects the mouth to the stomach), which can cause serious problems. heartburn or other symptoms.
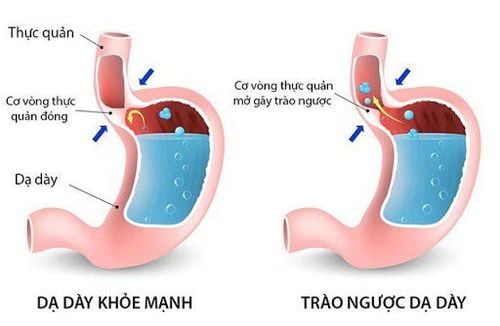
1. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (reflux esophagitis)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also known as reflux esophagitis, is a disease that occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus (the digestive tube connecting the mouth to the stomach). cause heartburn or other symptoms. Reflux episodes usually occur after meals, are short-lived, are not accompanied by symptoms, and rarely occur during sleep. However, these normal bouts of reflux become GERD when symptoms occur frequently (about 2 to 3 times per week) or damage the esophagus.
2. Causes of Resistant GERD
There are many potential causes of refractory GERD, which vary in incidence, clinical importance, and symptom severity and frequency. Compliance and poor compliance should first be assessed before continuing with the assessment. The most common mechanisms of resistant GERD include bowel dysfunction, weak acid reflux, and excess acid. Factors related to metabolism and bioavailability play a limited role in PPI treatment failure. GERD-like symptoms can also result from a variety of other disorders, such as eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), drug-induced esophagitis, infectious esophagitis, and achalasia, which should be considered. when differential diagnosis with patients whose symptoms do not improve.
3. Causes of Resistant GERD
Adherence to treatment and adherence to medication PPIs (PPIs are proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) – The main effect is a prolonged decrease in gastric juice production.Esophageal dysfunction: functional heartburn. Functional, Esophageal Hypersensitivity, IBS Weak Acidic or Acid Reflux: Weak Acid Reflux, Gastroduodenal Reflux
Residual Acidity: Nocturnal Acidity (NAB), Acid Pockets Slow gastric emptying Thickness Rapid PPI metabolism Eosinophilic esophagitis Causes unrelated to GERD
4. Treatment of refractory reflux esophagitis
There are countless potential therapies that vary in effectiveness, invasiveness, and accessibility. Most treatment strategies for refractory reflux esophagitis target one or more of the underlying mechanisms mentioned above
Methods used in the treatment of refractory reflux esophagitis include:
Change Lifestyle changes: Weight loss, diet Medication use: Antacids, motility drugs, antidepressants, reflux inhibitors Interventional procedures: Transverse gastric aneurysm or lateral gastric aneurysm Extragastric bypass through endoscopic ultrasound Surgery: Gastric aneurysm reconstruction Alternative and complementary therapies: Acupuncture, herbal treatment
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious address trusted by many patients in performing diagnostic and treatment techniques for reflux esophagitis, refractory reflux esophagitis, and gastritis. .. Along with that, at Vinmec Hospital, the diagnosis through colonoscopy with the Olympus CV 190 endoscope, with the NBI function (Narrow Banding Imaging - endoscopy with narrow light frequency band) gives results. The results of the analysis of mucosal pathology are clearer than conventional endoscopy, detecting ulcerative lesions, reflux in the esophagus, stomach, Barrett's transformed lesions, and cancer lesions in the early stages. early stage....
Vinmec Hospital with modern facilities and equipment and a team of experienced experts who are always dedicated in medical examination and treatment, customers can rest assured with internal services. colonoscopy at Vinmec International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
Mermelstein J, Mermelstein AC, Chait MM. Proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of patients with erosive esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: current evidence and safety of dexlansoprazole. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2016;9:163–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Scarpellini E, Ang D, Pauwels A, De Santis A, Vanuytsel T, Tack J. Management of refractory typical GERD symptoms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(5):281–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Horn J. The proton-pump inhibitors: similarities and differences. Clin Ther. 2000;22(3):266–280. discussion 265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Chiba N, De Gara CJ, Wilkinson JM, Hunt RH. Speed of healing and symptom relief in grade II to IV gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 1997;112(6):1798-1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Joseph Mermelstein, Alanna Chait Mermelstein, and Maxwell M Chait. Gastroesophageal reflux disease resistant to proton pump inhibitors: challenges and solutions. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2018; 11: 119–134.