This is an automatically translated article.
This article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Duc Hoang - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Forced vital capacity (FVC) is one of the indices performed to probe respiratory function. So what is the vital capacity, how is the vital capacity measured?
1. What is forced vital capacity?
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) is the amount of air that is exhaled quickly and forcefully after trying to breathe as deeply as possible. This is one of the indicators that allows the assessment of respiratory function, measured by spirometry.Stressed vital capacity is used to differentiate obstructive pulmonary diseases such as chronic pulmonary embolism or asthma from restrictive lung diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis.
In addition, forced vital capacity is also used to evaluate the progression of lung disease as well as the effectiveness of treatment.
2. Indications and contraindications for forced vital capacity measurement
Forced vital capacity is used to evaluate pulmonary ventilation function - one of the respiratory functions, by measuring the ability to inhale and exhale. Although FVC does not help identify specific lung disease, the results measured can help narrow the range of potential diagnoses and, along with other results, may help identify lung disease.
Forced vital capacity is indicated in the following cases:
Shortness of breath, wheezing or persistent cough. Assess respiratory function when blood oxygen levels are low. Assess respiratory function before performing surgery, especially lung surgery. Evaluation of breathing capacity in people with heart disease. Plan a pulmonary rehabilitation program.
Although safe, vital capacity is contraindicated in the following cases:
Coughing up blood of unknown cause: Performing FVC can make the cough worse. Recently diagnosed myocardial infarction, cardiovascular instability, or pulmonary embolism: Performing FVC may alter blood pressure and worsen angina. Recent eye surgery: Performing FVC can increase eyeball pressure.
3. Tests related to forced vital capacity
To evaluate respiratory function, specifically pulmonary ventilation function, the following parameters are taken along with the forced vital capacity (FVC):
Vital Capacity (VC for short) : Measures the maximum amount of air exhaled (under normal breathing conditions) with exertion of inspiration. Expiratory volume in one second (FEV1): Measures the amount of forced air exhaled during the first 1 second. Together with these indicators, forced vital capacity (FVC) and other pulmonary function tests will allow the status of pulmonary ventilation function to be determined by comparison with criteria based on age, sex, Height and weight.
4. How to measure forced vital capacity (FVC)
Measurement of forced vital capacity (FVC) is performed as follows:
The patient wears loose, loose clothing, sits on a chair, breathes normally, in a comfortable mood. Place the clip on the patient's nose. Insert the breathing tube into the patient's mouth and seal the lips to prevent air from escaping. The patient is asked to inhale as deeply as possible and exhale as forcefully as possible. Repeat this procedure at least 3 times for average and uniform values.
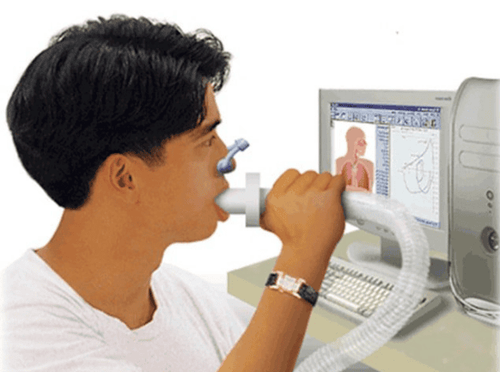
5. The result of the forced vital capacity measurement
Workforce vital capacity (FVC) results obtained, compared with standard FVC for age, sex, weight, and height. In addition, it is also compared with previous FVC values (if any) to determine the degree of lung progression or assess whether pulmonary ventilation function improves after treatment. FVC can also be expressed as a percentage of the predicted FVC.
The force vital capacity index (FVC) is expressed in two ways:
Absolute value in liters (L). Linear representation of expiratory dynamics. For adults, the normal FVC is in the 3 - 5 L range. For children, the standard FVC for 3 - 5 year old boys and girls is 1.16 L and 1.04 L, respectively.
Usually, the forced vital capacity (FVC) index is equal to the vital capacity (VC) of >80%. A gradual decrease in FVC is a sign of several respiratory conditions such as:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and bronchiectasis. Restrictive airway diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Structural restrictive airway diseases such as scoliosis and thoracic scarring. Other lung diseases such as sarcoidosis, pneumonia, asbestosis, silicosis, lung cancer. In addition, the forced vital capacity index was also compared with FEV1. The FEV1/FVC ratio is used to compare the amount of air exhaled in one second with the maximum amount of air exhaled. Normal values for this ratio are 70% - 80% or higher in adults and over 85% in children. This ratio may allow the determination of lung conditions to be obstructive (eg, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - COPD) or limited (eg, pulmonary fibrosis).

6. Notes when performing forced vital capacity measurement
To ensure safety as well as obtain accurate vital capacity measurement results, when performing the test, the patient should note the following information:
If using the meter at home, make sure it is cleaned. fully before use or do not come into contact with a possible source of infection. Do not share measuring equipment. Be sure to have medical supervision the first time you have this procedure. Make sure to use the meter correctly. When performing a vital capacity test, carry any medications you are taking, including an inhaler. Discuss with your doctor your current respiratory condition such as exposure to tobacco smoke, lung infection, etc. If you feel dizzy or short of breath, notify your healthcare provider for assistance in recovery. If symptoms persist or are severe, the person is tested for oxygen and supplemented with oxygen if needed. Forced vital capacity (FVC) is the amount of air that is exhaled forcefully when the patient is forced to inhale. This index is used to assess respiratory function, specifically lung ventilation function.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied the technique of measuring respiratory function to treat many respiratory diseases, including the overpowering vital capacity index. The respiratory function measurement technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and according to the standards of the process by a team of highly skilled medical doctors, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution. in disease diagnosis and staging.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.