This is an automatically translated article.
The endocrine system is a collection of glands that produce hormones, which regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep and mood.
1. What is the hormone and the endocrine system?
What are hormones? What is endocrine gland?...is a question many people are interested in. Hormones are substances produced by your endocrine glands that have tremendous effects on body processes. They affect growth and development, mood, sexual function, reproduction, and metabolism.
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones that help control many important bodily functions, including the body's ability to change calories into energy for cells and muscles. The endocrine system affects heart, bone and tissue development, and even the ability to bear children. It plays an important role in the development of diabetes, thyroid disease, growth disorders, sexual dysfunction, and a host of other hormone-related disorders.
2. Major endocrine glands
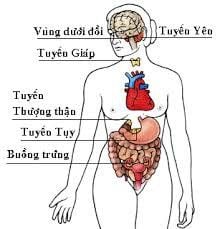
Các tuyến nội tiết
Each gland of the endocrine system secretes specific hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones travel through the bloodstream to other cells and help control or coordinate many body processes. The adrenal glands are two glands that sit on top of the kidneys and release the hormone cortisol. The hypothalamus is the part of the lower midbrain that tells the pituitary gland when to release hormones. The ovaries are female reproductive organs that release eggs and produce sex hormones Islet cells are the cells in the pancreas that control the release of the hormone insulin, and the parathyroid glands are four small glands in the neck that play a role in Development of Bones The pineal gland is found near the center of the brain and may be linked to sleep patterns. The pituitary gland is found at the base of the brain behind the sinuses. It is often called the "master gland" because it affects many other glands, especially the thyroid. Problems with the pituitary gland can affect bone growth, a woman's menstrual cycle, and the release of breast milk. The testicles are the male reproductive glands that produce sperm and sex hormones. The thymus is a gland in the upper chest that helps develop the body's immune system early on. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck that controls metabolism.
3. Function of endocrine glands
The function of the endocrine glands is completely different. Even the slightest malfunction with the function of one or more endocrine glands can upset the delicate balance of hormones in your body and lead to an endocrine disorder, or endocrine disease.
Endocrine disorders are generally grouped into two categories: Endocrine diseases caused when a gland produces too much or too little endocrine hormone, known as hormonal imbalance, or endocrine disease caused by the development of Lesions (such as nodules or tumors) in the endocrine system, which may or may not affect hormone levels.
4. What is the role of the endocrine feedback system?
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, chemicals produced in the body that regulate the functioning of cells or organs. These hormones regulate growth, body metabolism (physical and chemical processes), and sexual development and function. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and can affect one or several organs throughout the body.
The endocrine feedback system helps control the balance of hormones in the blood. If your body has too much or too little of a certain hormone, the feedback system signals to the appropriate gland or glands to correct the problem. Hormonal imbalances can occur if this feedback system has trouble keeping the right levels of hormones in the blood or if the body doesn't remove them from the blood properly.
Increased or decreased levels of endocrine hormones can be caused by: A problem with the epidemic endocrine feedback system Failure of one gland to stimulate another gland to release hormones (for example, a problem with hypothalamus can disrupt hormone production in the pituitary gland) An inherited disorder, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) or congenital hypothyroidism. Infection Damage to an endocrine gland Tumor of an endocrine gland
5. Problems related to the endocrine system
Suy tuyến yên là mốt trong các vấn đề liên quan đến hệ nội tiết
Endocrine tumors: Most endocrine tumors and nodules (tumors) are noncancerous. They usually do not spread to other parts of the body. However, a tumor or nodule on the gland can interfere with the gland's hormone production. Adrenal insufficiency: Adrenal insufficiency is when the adrenal glands secrete too little of the hormone cortisol and sometimes, aldosterone. Symptoms include fatigue, upset stomach, dehydration, and skin changes. Addison's disease is a type of adrenal insufficiency Gigantism: This is a growth hormone problem. If the pituitary gland produces too much hormone, hyperthyroidism: Hyperthyroidism is when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, resulting in weight loss, rapid heart rate, sweating, and nervousness. The most common cause for an overactive thyroid is an autoimmune disorder called Grave's disease. Hypothyroidism is when the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone, leading to fatigue, constipation, dry skin, and depression. Underactive glands can cause growth retardation in children. Some types of hypothyroidism are present at birth. Insufficient thyroid hormone can cause many body functions to slow down or stop working altogether. Hypopituitarism is when the pituitary gland secretes little or no hormone. It can be caused by a number of different diseases. Women with this condition may stop getting their periods. Multiple endocrine glands I and II are rare genetic conditions that are passed down through families. They cause tumors of the parathyroid glands, adrenal glands and thyroid gland, leading to overproduction of hormones. Polycystic ovary syndrome is when the overproduction of androgens interferes with the development of eggs and their release from the female ovaries. It is a leading cause of infertility. Precocious puberty is abnormally early puberty that occurs when the glands tell the body to release sex hormones too early in life.
6. Diseases of the endocrine system
Hormone levels that are too high or too low indicate a problem with the endocrine system. Hormonal disease also occurs if the body does not respond to hormones in the proper ways. Stress, infections, and changes in fluid and electrolyte balance in the blood can also affect hormone levels.
The most common endocrine disease in the US is diabetes, a condition in which the body does not properly process glucose, a simple sugar. This happens because of a lack of insulin or, if the body that produces insulin is not working properly. Diabetes is treated with medication or insulin injections.
Thyroid cancer begins in the thyroid gland and begins when the cells in the thyroid gland change, grow out of control and eventually form a tumor. Tumors - both benign and cancerous - can also disrupt the functions of the endocrine system.
7. Endocrine disorders

Khi bị rối loạn nội tiết thường cảm thấy mệt mọi và suy nhược
Management of other endocrine disorders often involves stabilizing hormone levels with medication or, if a tumor is causing an overproduction of hormones, removing the tumor.
Symptoms of endocrine disorders vary widely and depend on the specific gland involved. However, most endocrinologists complain of fatigue and weakness.
Blood and urine tests to check hormone levels can help your doctor determine if you have an endocrine disorder. Imaging tests may be done to help locate or identify a nodule or tumor.
Treatment of endocrine disorders can be complex and needs to be approached very carefully and individually because a change in one hormone level can eliminate another. Hormonal imbalances can have a significant impact on the reproductive system, especially in women.
Your doctor or specialist may order routine blood work to check for problems or to determine if your medication or treatment plan needs to be adjusted. For more information, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
Reference source: webmd.com; emedicinehealth.com
MORE:
Female hormone disorders: What to check? Health problems related to the endocrine system as you age Common endocrine diseases