This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Van Quang - Ear, Nose Throat Doctor - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. BSCKI. Le Van Quang is an expert in the field of ENT with 15 years of experience.Earplugs occur when earwax builds up in the ear canal, cannot wash away naturally and causes a blockage. Although earwax is a natural physiological secretion and is useful to protect the body, if the blockage occurs due to earwax plugs, it becomes a really annoying problem, requiring the patient to get rid of it quickly. go out.
1. What is earwax?
Earwax is a secretion produced by glands located in the skin that cover the ear canal. Although scientists are still not sure why people get earwax, observations suggest that it is a substance that helps trap dirt and other small particles when accidentally falling into the ear canal. prevent them from reaching as well as damaging or infecting the eardrum. What's more, the growth of bacteria will also be more inhibited when earwax is in control.The characteristics of earwax depend on the location of each person with the amount, nature, color, and smell being genetically determined like hair color or height. Normally, earwax comes in a waxy form that, when dry, falls out of the ear on its own along with any trapped dirt or debris. However, some people have a habit of actively removing earwax when these things are completely unnecessary.
Even so, in cases where earwax is causing blockage or excessive buildup, intervention may become necessary if they cause undue effects.
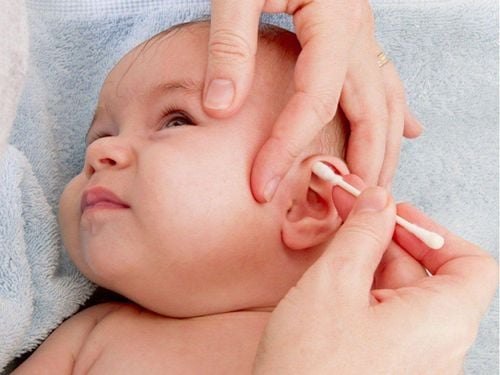
At this time, removing earwax requires a certain understanding and compliance. On the contrary, if you arbitrarily use sharp and pointed objects in the ear such as metal rods, hair pins, skewers, etc., it will push the wax down deeper and cause more severe blockages, even infection. infection and hearing loss.
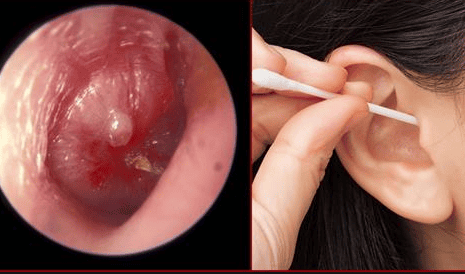
Không nên dùng tăm bông hay vật nhọn khi lấy ráy tai
2. Why get earplugs?
Earwax is a waxy substance in the ear, secreted by glands in the skin located on the outer half of the ear canal. Earwax and the tiny hairs in the ear canal act to prevent dust and other foreign matter from entering the ear canal, which can damage deeper structures, such as the eardrum.In most people, only a small amount of earwax is present in the ear canal, which often washes away or falls out as new secretions are released to replace it. However, if for any reason too much of this waxy substance is produced or if the earwax is not cleaned effectively, earwax can build up, forming a plug and clogging the ear canal.
Obstruction caused by earwax plugs often occurs if there is a habit or movement of trying to clean the ear by using non-standard tools such as cotton swabs or small, sharp sticks. This only causes the earwax to be pushed deeper instead of being able to clear it out naturally.
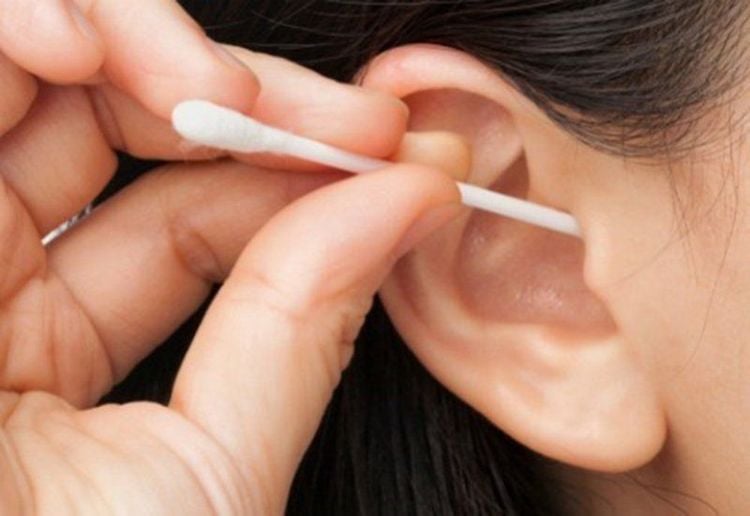
Nút ráy tai xảy ra khi cố gắng tự làm sạch tai bằng cách dụng cụ không đúng tiêu chuẩn
3. What are the symptoms of earwax plugs?
Symptoms of a blockage caused by earwax can include the following:Ear pain Feeling of fullness in the affected side ear Ù Hearing ringing or noises in the ear Hearing loss in the affected ear Effects Dizziness Dry cough due to irritation.

Ù tai là triệu chứng phổ biến của bệnh
4. What to do when you get earwax?
Your doctor can determine if you have an earwax blockage by looking at your ear canal with a bronchoscope and with a magnified image.If so, removal of earwax from the ear canal by an experienced otolaryngologist is a simple possible first step. In it, the doctor will use specialized tools of small size, curved or use a nozzle with suction force. If the earwax dries and forms a hard mass, a small amount of clean water can be injected to help soften the discharge.
However, care should be taken to use warm water, equal to body temperature to avoid irritating the ears. Thus, once the earwax is removed, the ear canal will be completely released and the symptoms caused by the blockage will disappear. On the other hand, if earwax buildup is a recurring problem, your doctor may prescribe medication to help limit discharge, such as carbamide peroxide. However, these substances can irritate the delicate skin of the eardrum and ear canal, use them only as directed.
Besides, patients can refer to simple measures to help overcome the formation of earwax or remove earwax at home as follows:
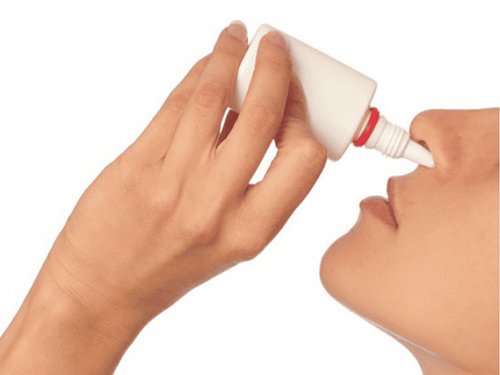
Soften earwax so that it can be released on its own: Use an empty eyedropper to inject a few drops of baby oil, mineral oil, glycerin, or hydrogen peroxide into the ear canal. Use warm water: After every day or two, use the syringe to gently squirt warm water into the ear canal to soften if dry, lumpy earwax is present. Tilt your head and pull the outer ear flap up to help straighten the ear canal and make it easier for secretions to drain. Finally, dry it or dry it with a hair dryer to make sure there is no stagnant water in the ear canal.
Sử dụng thuốc nhỏ mắt làm mềm ráy tai khắc phục sự hình thành của nút ráy tai
In this situation, each person needs to know how to properly and safely remove earwax; If this is not possible, seeking help from an ENT specialist would be the right alternative.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: mayoclinic.org, webmd.com, medicalnewstoday.com