This is an automatically translated article.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a common infectious virus. Cytomegalovirus infection can strike anyone, especially pregnant women, children, people with weakened immune systems, and weakened immune systems.1. What is cytomegalovirus?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a genus of viruses in the family Herpesviridae or Herpesviruses. The name cytomegalo comes from the Greek, meaning large cell. It is the most studied of all cytomegoliviruses.Cytomegalo virus belongs to the Betaherpesvirinae subfamily, which is related to other Herpesviruses in the Alphaherpesvirinae subfamily and the Gammaherpesvirinae subfamily including the Epstein-Barr virus. All these viruses can hide in the body for a long time. Although cytomegalovirus can be found anywhere in the body, CMV infections most often involve the salivary glands.
The cytomegalovirus is a double-stranded DNA virus and is part of the family Herpesviridae. Cytomegalo shares many attributions with other herpes viruses, including genome structure, virions, and can cause chronic and latent infections.
In the US, at least 60% of the population is exposed to CMV virus. In developing countries, most infections are acquired in young children; In developed countries, 50% of adults with serological results are diagnosed with CMV negative.
2. Cytomegalovirus causes what disease?
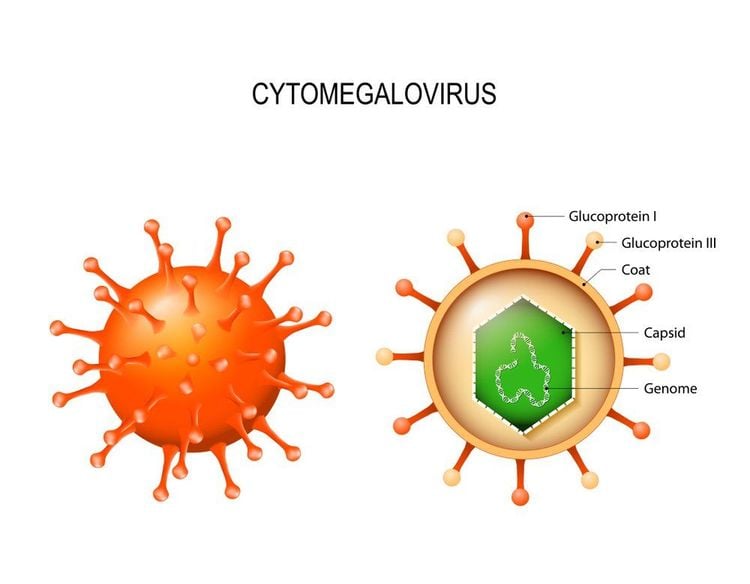
Virus cytomegalo gây ra tình trạng nhiễm trùng không triệu chứng, do đó thường rất khó phát hiện bệnh
Cytomegalovirus related to the virus that causes chickenpox, herpes simplex. In immunocompromised individuals, diseases caused by CMV often present as mononucleosis syndrome.
As mentioned, once the body is infected with CMV, it will stay in the body for life. The CMV cycle consists of a dormant phase and an active phase. When the body is healthy, CMV is mostly inactive. When the immune system is weakened, CMV can reactivate and cause disease in the body.
3. How is cytomegalovirus transmitted?
Cytomegalovirus infection can be transmitted from person to person through contact with an infected person's bodily fluids, including: blood, saliva, urine, milk, and semen.CMV can only be transmitted during an active virus phase. That is, if you come into contact with a person carrying the virus while the virus is asleep, you will not be contagious. Women who are pregnant and have an advanced CMV infection can pass the virus on to their baby.
Activities that can cause CMV infection include:
Touching your eyes, nostrils, mouth after coming into contact with the fluid of someone infected with the virus. This is the most common route of CMV transmission; Having sex without a condom with someone who has the virus; Transmitted from mother to child through breast milk. However, this case is very rare; Spread through blood transfusion, organ transplant; Transmitted from mother to child through the placenta.
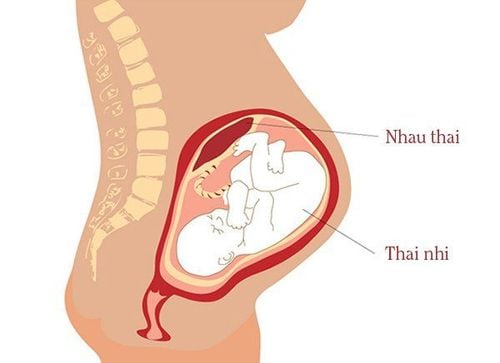
Cytomegalovirus lây truyền từ mẹ sang con thông qua nhau thai
4. Symptoms of cytomegalovirus infection
Newborns with congenital CMV infection (in the womb), infants with CMV infection during birth or after birth through breastfeeding, or with weakened immune systems are more likely to develop symptoms than healthy individuals.4.1. Symptoms of CMV infection in children Women infected with CMV before becoming pregnant can pass the virus on to their babies. If it is primary CMV infection, there is a higher risk of passing it on to the child than if it is a recurrent CMV infection. Infection usually occurs during the first 3 months of pregnancy.
Most babies infected with CMV during pregnancy have normal manifestations at birth. Symptoms will progress over time, taking months or even years. The most common symptom in infants infected with CMV soon after birth is hearing loss or progressive visual impairment.
Children with congenital CMV infection are usually very weak and tend to get weaker and weaker. Symptoms of CMV infection in children include:
Children with yellow eyes, jaundice; On the skin there are bruises, erythema; Babies born with low birth weight; Children with an enlarged spleen; Children with liver enlargement, poor liver function; The child has difficulty breathing; Convulsions. 4.2. Symptoms of cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompromised people Immunocompromised people infected with CMV often present as an infectious disease. This virus can also attack other organs in the body. Specific symptoms include:
Fever; Diarrhea ; Pneumonia; Hepatitis; Encephalitis; Ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract; Behavior change; Visual impairment, even blindness; Convulsions; Faint. 4.3. Symptoms of CMV infection in healthy people Most healthy people infected with CMV often have few specific symptoms. Symptoms are often similar to an infection and include: fever, body aches, and fatigue.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.