This is an automatically translated article.
Clinical medicine or clinical in medicine is a very popular form of medicine, where the clinician's responsibility to the patient is demonstrated through two main tasks including: Giving treatment and understanding Get the patient's health problems to accurately diagnose and treat the disease. Therefore, understanding clinical medicine has an important role in the study of general health. So what is clinical in medicine?
1. What is clinical in medicine?
In the word "clinical" there is clinical means approaching, in a certain situation: such as in danger, in labor (a pregnant woman about to give birth), ill, dying (general = the end, coming to the end of life. life, death). “Sieve” means the bed, here referring to the patient's bed.
Clinical is the word we used to translate the French word “clinique” back in the day, when medical schools taught in French. It was not until the 1960s, under Prime Minister Nguyen Cao Ky in the South, that the Saigon Medical School began to partially teach in Vietnamese. Hue University Medical School has been teaching in Vietnamese since its opening (1957) with the faculty being Doctor Le Khac Quyen, a person with a more radical tendency and left-wing political activity than the professors of Hue University. Saigon Medical School. When medical school switched to teaching in Vietnamese, one of the first words learned was “clinical”. Most current Vietnamese or English Vietnamese dictionaries define "clinical" incorrectly with the use of the word "clinical" in medicine/medical today. The word was not found in dictionaries prior to 1970, and dictionaries that translated "clinic" were either incomplete or misleading.Perhaps the lexicographers did not clearly understand the organization of the medical profession.
French, “clinique” and English “clinical” refer to what happens at the bedside of the sick person, simply speaking, during the examination. From the Ancient Greek word “kline” means bed. Hippocrates (460-377 TTC) . that we see, hear, touch and smell. Hippocrates was influenced by the philosophy of Pythagoras (Greek mathematician), according to which "Nature" consists of 5 elements: water, earth, wind and fire, hence the theory of the time that our bodies are composed of five different fluids or humors: black bile, yellow bile, phlegm (viscous) and blood. establish a balance between these fluids. Perhaps similar, but probably not as detailed as the Eastern side, wanting between the balance between yin and yang, the six palaces (Tieu Truong, Dai Truong, Dom, Vy, Bang Quang, Tam Tieu) and the five organs (heart, liver, spleen, waste, kidney).

Hippocrate là ông tổ ngành Tây Y tiên phong
However, the important point here is that reasoning is based on observations of sick people, as opposed to healing based on religious beliefs, or magic. Hippocratic antiquity medicine and science were lost after the decline of Greek and Roman civilization. Through the Middle Ages, healing was religious and dogmatic. Clinical medicine only re-evolved after the Renaissance), with the rediscovery of the "classical" knowledge of antiquity, the rejection of the notions of epidemics ("humors") and mechanical disciplines. anatomy, chemistry, and surgery were developed. Through the 17th century, knowledge of physiology (how the body is governed) expanded, and more emphasis was placed on bedside clinical practice, that is, Observe the manifestations of the disease, use the knowledge of anatomy, physiology to consider the origin of the disease.
We can talk a little more about the "clinical" work of the oriental medicine doctors in Cochinchina (of Lord Nguyen) in the 17th century by priest Alexandre de Rhodes, the pioneer who created the word. write the national language, narrate. Their "clinical" method is different from the Western method: the doctor "takes the pulse" and then diagnoses first, not letting the patient declare the disease first as in Western medicine. The physician was educated in a hereditary way and had many esoteric books. The doctor takes the pulse with 3 fingers (for 3 parts of the body: head, stomach and abdomen), takes about 15 minutes to think, and then reveals to the patient what symptoms he has, how sick . If the doctor says something wrong, he/she will be kicked out and won't pay because the patient no longer trusts. According to Alexandre de Rhodes' personal experience, Vietnamese doctors at that time were not inferior to those in Europe.
After several thousand years, Hippocratic medicine transformed and developed into present day Western medicine, on the basis of observation, inference, experiment, and the important role of biomedical sciences. .
Now what is directly related to the patient is called clinical. For example, the doctor asks a story about the disease (medical history, history), records the symptoms (symptoms) such as fatigue, headache, nausea, is subjective, and examines the patient's body to detecting objective signs such as acne-prone skin, arrhythmia, and tumors in the abdomen are objectively recorded by people who are not patients. These signs are called clinical signs. Diagnosis of the disease based on the examination process is called clinical diagnosis. However, the physician may also have the means to learn more about the patient.
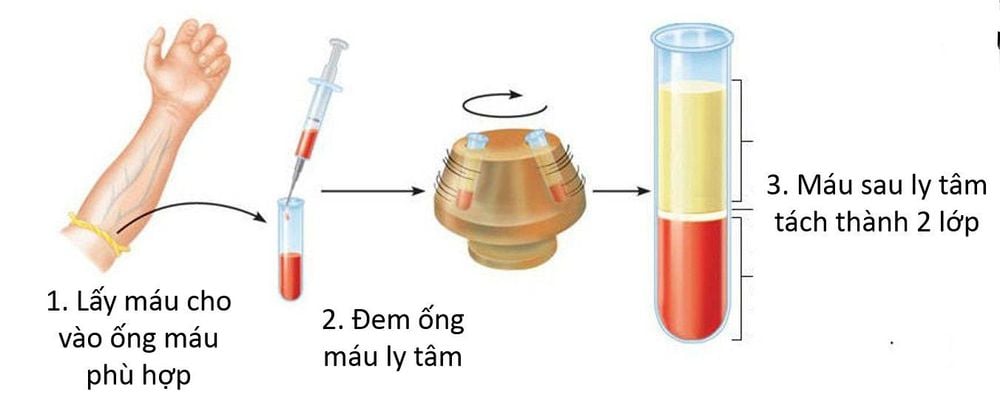
Máy ly tâm để quan sát cặn nước tiểu qua kính hiển vi
Several decades ago, the doctor's office could have simple facilities such as: a centrifuge to observe the urine sediment through a microscope, take sputum and mucus to stain and look for germs or bacteria in it. no, or there is an x-ray machine, eg to see if a patient has melasma, etc. and often those tests are done by a doctor or nurse, near where the patient lies, so the noise France calls those test results “paraclinique” (do:para=next, clinique=hospital bed). We translate it as "sub-clinical". However, in English, the word "paraclinical" is rarely used.
In the US, people usually use the word paraclinical less often. Younger doctors tend to cut back on asking questions, examine patients directly, and focus more (according to some, too much) on "subclinical" results, which are much more expensive than before. Doctors often refer to "subclinical" disciplines such as: "lab work" = blood testing, microbiological testing (eg blood culture [blood culture] for bacteria growth), genetic testing, genetic testing, etc. biopsy (biopsy).
"Pathology" (the branch of pathology, finding the changes caused by the disease on tissues and cells observed with a microscope, formerly in Saigon called "ana-path", because the French word anatomie pathologique = muscle
Activities such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, are grouped in the department of "medical imaging". Films and images, which do not "touch" the patient, may also have clinical operations; for example, an interventional radiologist may use CT, ultrasound-guided puncture of the patient's chest or abdomen.
One of the methods of medical teaching is the "conference clinical and pathology" (French: confrontation clinico pathologique). The resident presents clinical observations and recommends a diagnosis inferred from those observations, and the pathologist then presents the clinic's findings. Laboratory tests such as biopsy (biopsy) or autopsy results (autopsy) mean that the answer to the initial question is what disease the patient has, what causes the clinical symptoms.
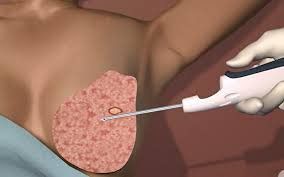
Sinh thiết vú tìm nguyên nhân gây u tuyến vú
2. Some commonly used words
Clinical death, the patient's heart stops beating (cardiac arrest), the patient stops breathing. However, with current methods of resuscitation, it is possible to reverse "clinical death" in some cases (CPR: cardiopulmonary resuscitation).
Clinic: private clinic, outpatient room of a hospital. Sometimes a clinic is a large organization that includes many hospitals, clinics, and laboratories, for example the Mayo Clinic opened by Dr. William Mayo and his sons in Rochester, Minnesota in the late 19th century, and today is one of the world's largest medical research and treatment systems, staffed by over 50,000 people and nearly 4,000 physicians from all walks of life. Cleveland Clinic in Cleveland, Ohio is a great medical education hospital, earning nearly 10 billion dollars a year, and branches in many states of the US, Canada and the Middle East. At first, it was just a private practice of a surgeon at the end of the 19th century.
In a broad sense, clinic is also used in a number of non-medical areas: as "legal clinic" refers to offices that deal with treatment. resolution and advice on legal issues.
In the US, people who examine and treat patients are not always medical doctors: there are people who specialize in psychotherapy (psychologist), nurse practitioner; Nursing staff are trained in examination and treatment, often under the supervision of a medical doctor, a "physician assistant" (PA). The word "clinician" is sometimes used to include all groups of people with "clinical" tasks of medical examination and treatment at different levels and fields.
In American hospitals, medical students are allowed to practice examining patients in the last 2 years called clinical years (clinical rotations). After completing the first 2 years of basic science, called the 2 preclinical years (preclinical years). Doctors will volunteer to teach unpaid medical students and practicing doctors (interns, residents, fellows/ or doctors in training) were awarded the titles of clinical assistant professor, clinical associate professor, and clinical professor by the medical school. Clinical = "clinical" to distinguish it from the school's paid, full-time, regular track faculty, which are more research-intensive than teaching.
3. What is a clinical examination?
Clinical examination is an initial examination to monitor health status and detect abnormal signs through observation, hearing, touching, percussion... and without intervention by testing or imaging. .
Clinical examination is the first step in the medical examination process. This method is used when examining all diseases. Clinical examination helps doctors learn about factors that affect the patient such as environment, age or disease risk..., and at the same time assists doctors in appointing necessary paraclinical tests to take conclusions about the condition. This step shows the initial condition, the risk of disease and can find the cause of the disease.

Xét nghiệm cận lâm sàng giúp tìm ra nguyên nhân gây bệnh.
4. What is a paraclinical examination?
Subclinical health examination is a stage in the routine health examination process, it includes many techniques such as: X-ray, Ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (CT) MRI),... Subclinical medicine is an effective support for doctors in the process of diagnosing and treating diseases.
To be able to accurately diagnose the disease condition and treat it effectively, in addition to clinical examination, doctors must also combine tests with the use of subclinical medical techniques to diagnose the disease. , diagnosis to differentiate from other diseases, and at the same time help patients monitor progress, evaluate treatment effectiveness and disease prognosis.
Preclinical examination helps diagnose diseases accurately, including:
Blood tests: help doctors detect blood diseases; check and detect kidney and urinary diseases; liver diseases; detecting disorders of glucose metabolism, detecting and monitoring diabetes; detect hepatitis B virus; hepatitis C virus; HIV testing ; screening and monitoring gout; Check blood fat to detect dyslipidemia: hyperlipidemia, risk of atherosclerosis, hypertension, myocardial infarction. Urine test with 10 parameters: helps to detect diseases of the genitourinary system, urinary disease, kidney-urinary pathology. Fresh vaginal examination helps detect genital infections in women. Electrocardiogram: helps detect myocardial damage and arrhythmias. Diagnostic imaging: chest X-ray, abdominal ultrasound.
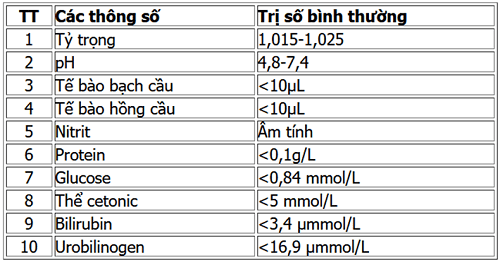
Xét nghiệm nước tiểu 10 thông số
If in the past, people used to only see a doctor when they were sick, nowadays, taking care of them, taking regular health checks, and proactively preventing diseases are becoming popular. This is because education levels have improved, quality of life has been improved and people have been empowered to have proactive access to their own health. At the same time, periodic medical examination and performing laboratory tests will sometimes help detect abnormalities that you have not noticed yourself. From there, people will have an early diagnosis, help with early treatment of diseases as well as receive medical advice on a healthy lifestyle, reducing the risk of common diseases. Thus, with medical services of periodic examination and testing, people will have the conditions and opportunities to live longer and healthier.
Because of the above benefits, with the goal of comprehensive health care, Vinmec International General Hospital System has launched general health checkup packages and performed paraclinical tests in accordance with each object. Customers will be directly taken by the doctor to take personal and family medical history, measure blood pressure, body mass index, physical examination, perform screening tests as well as advice in each situation.
With a team of professional, highly qualified and experienced doctors, modern facilities, advanced testing machinery system, Vinmec deserves to be a reliable, quality medical examination and treatment address. world-class quality of every person and of every family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.