This is an automatically translated article.
Increased intracranial pressure is a potentially life-threatening condition. For patients with brain damage due to severe trauma and ICP below 20 mmHg, the mortality rate is about 20%. Intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure provide important information for physicians in the monitoring and treatment of traumatic brain injury.
1. What is intracranial pressure?
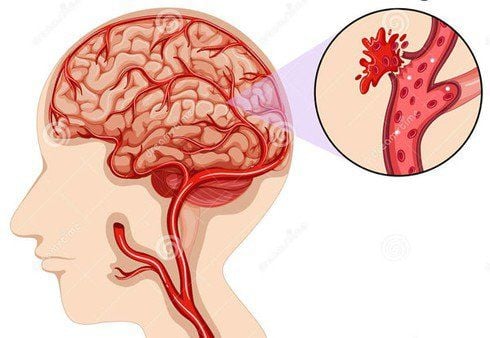
IntraCranial Pressure (ICP)) is the result of pressure specific to each area: brain parenchyma (88% volume), cerebrospinal fluid (9% volume) and blood vessels (accounting for volume). 3% by volume). Normally, the average intracranial pressure is around 10-12cmH2O. In practice, it is acceptable to measure intracranial pressure through normal CSF pressure of 7 - 20cmH2O when lying down or lumbar puncture. When the cerebrospinal fluid pressure reaches 25cmH2O or when the intracranial pressure is above 12mmHg, it is called Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP).
Increased intracranial pressure can be caused by increased fluid around the brain (increased natural CSF volume, bleeding into the brain due to trauma or a ruptured tumor). In addition, increased intracranial pressure can also be caused by brain tissue swelling on its own, injury or disease (epilepsy),...
Increased intracranial pressure is a potentially life-threatening condition. For patients with brain damage due to severe trauma and ICP below 20 mmHg, the mortality rate is about 20%. For patients with ICP above 20 mmHg, mortality reaches approximately 50%. Patients with brain damage due to severe trauma, intracranial pressure above 40 mmHg, the mortality rate is up to 75%. And in the case of patients with ICP above 60 mmHg, the mortality rate is almost 100%.
Tăng áp lực nội sọ cần được điều trị sớm
2. What is cerebral perfusion pressure?
Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) is closely related to intracranial pressure. Cerebral perfusion pressure was defined as the difference between mean arterial pressure (MAP) and intracranial pressure (ICP). That means: CPP = MAP - ICP. Mean arterial pressure is the mean pressure in the carotid artery. MAP = (systolic pressure + 2 diastolic pressure)/3. The cerebral perfusion pressure in a normal person is above 50 mmHg. Cerebral perfusion pressure should be maintained at 70-80 mmHg and intracranial pressure at less than 15 mmHg.Increased intracranial pressure leads to decreased cerebral perfusion pressure and cerebral blood flow, which is the main cause of death in patients with traumatic brain injury. Therefore, maintaining cerebral perfusion pressure at an appropriate value in the fastest time is one of the key factors in intensive care for patients, avoiding brain necrosis in patients with cerebral palsy. Increased intracranial pressure, especially in people with traumatic brain injury, is common in traffic accidents.

Người bệnh nên gặp bác sĩ để được thăm khám và điều trị sớm
Monitoring the level of intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure allows accurate assessment of changes in pressure and blood flow in the brain, best serving the diagnosis and treatment process in trauma patients. severe brain injury, coma,...
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
MORE:
Function of cerebrospinal fluid Treatment in patients with cerebral hematoma due to traumatic brain injury Traumatic brain injury: How to recognize and treat?