This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Cardiologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Arrhythmia is a general term for a number of conditions in which the heart's electrical activity is active. These activities may be subject to unusual disturbances: faster or slower than normal electrical activity.
1. What is bradycardia?
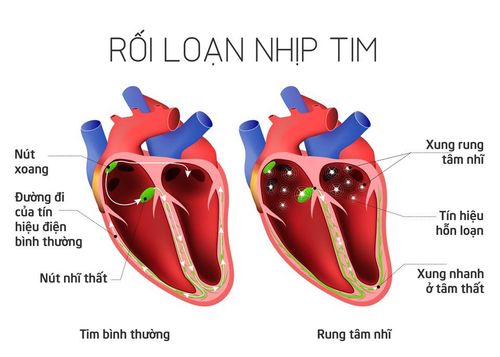
The heart is like a pump, the heart contracts to supply blood to the organs and maintain life. However, the heart contracts either by electrical impulses and controlled by a pacemaker node called the sinus node, which sends out impulses that stimulate the heart to contract. In a normal person, the sinus node generates a rhythm of 60-80 times/minute, during exertion (exercise, sports...) the sinus node will respond faster to the body's needs.Bradycardia can be physiological as in athletes, sports people or in normal people if there are no symptoms. When you have bradycardia, your heart beats slower than normal, for example: Less than 50 times/minute, less than 40 times/minute, even less than 30 times/minute, or sometimes prolonged cardiac arrest. When the heart rate is slow, important organs such as the heart, brain and kidneys will lack blood supply, at this time the patient will have symptoms such as fatigue, inability to exercise, dizziness, dizziness, severe cases can be severe. may lead to fainting due to cerebral ischemia, sometimes sudden cardiac arrest.
2. Causes of bradycardia arrhythmia
There are many causes of bradycardia:Ischemic heart disease Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy Congenital heart disease Conduction system degeneration Acute myocardial infarction Myocarditis Inflammation of the vagus due to certain drugs: digoxin , beta sympathomimetic... Poisoning of some plants and herbs Metabolic disorders: acidosis, hyperkalemia, hypothyroidism, hypothermia, hypoxemia...
Nguyên nhân có thể là do dùng thuốc gây nhịp chậm
3. Some common bradycardia arrhythmias
3.1. Sinus node insufficiency syndrome Sinus node insufficiency syndrome is a condition in which the sinus node is weakened, leading to the heart not able to generate a heart rate that is not suitable for the body's physiological needs. Clinically, there may be manifestations: sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, tachycardia - bradycardia syndrome, sinus arrest, sinoatrial block.Symptoms of sinus node failure syndrome: syncope or presyncope (fainting) are noticeable symptoms, dizziness, dizziness, shortness of breath... For patients with tachycardia - bradycardia syndrome can have palpitations.
Patients may have a temporary pacemaker inserted when there is no improvement with medication. Indications for implantation of a pacemaker apply to all patients with sinus node failure who have had symptoms (syncope, fainting...) or are still required to take drugs to slow the heart rate. For patients with tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, a pacemaker should be inserted to treat episodes of bradycardia and medication to treat tachyarrhythmias.
3.2. Atrioventricular conduction disorder (AV block) Atrioventricular block is the slowing or stopping of electrical impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles. Atrioventricular block is usually divided into 3 degrees:
1st degree atrioventricular block (delayed conduction from the atria to the ventricles) 2nd degree atrioventricular block 3rd degree atrioventricular block or complete atrioventricular block The most severe condition is when the conduction pathway from the atria to the ventricles is completely blocked, the atria will beat to the rhythm of the excitatory sinus node and the ventricles will beat in its own rhythm) If the ventricular rate is only mildly slow, there may be no symptoms. If the heart rate is too slow, the blood flow from the heart to the organs, including the brain, is reduced, the patient may experience lightheadedness, loss of balance, sometimes fainting or fainting. When fainting occurs, the patient loses consciousness, his limbs twitch, foaming at the mouth... Heard the heart rate slow (30 - 40 cycles/min) and is regular.
First-degree or second-degree atrioventricular block (Mobitz type I) usually requires no specific treatment. With persistent second-degree (Mobitz II) or third-degree AV block, pacemaker implantation is often required.
4. How to detect bradycardia?
When there are signs of fatigue, dizziness, inability to exercise, or fainting, it is necessary to seek medical attention immediately to screen for bradyarrhythmias. It is necessary to have annual medical examination, because bradyarrhythmias are often unclear, sometimes manifest as debilitating diseases, vestibular disorders, sometimes without symptoms.Some cases of bradyarrhythmias in the form of "Tachycardia - bradycardia syndrome" - sometimes the heart beats very slowly, causing dizziness, alternating periods of very fast uncontrollable heartbeat causing palpitations, if If you have these symptoms, you need to see a cardiologist immediately. Attention should not be used to treat tachycardia in this case because there is a possibility of causing severe bradycardia.
5. Methods of treating bradycardia
Phương pháp điều trị rối loạn nhịp tim chậm là gì?
The doctor will implant a pacemaker under the skin of the patient's chest, the electrode wire is threaded through the blood vessels into the heart chamber, fixed in the heart chamber. If the patient's heart rate is normal, the machine will be in standby state, if the patient's heart rate is slow, the device will beat to make the heart contract. Today's modern pacemakers have a rhythm response function, when the patient is stressed, has a fever... the machine will create a faster pace to meet the body's needs.
Vinmec International General Hospital has routinely deployed pacemaker implantation technique. With modern equipment, the Hybrid operating room system is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment such as DSA angiography machine, anesthesia machine with the most closely integrated patient hemodynamic monitoring software (PiCCO system, entropy. ..). Therefore, the Hybrid operating room can meet the requirements of surgery and intervention for pacemaker implantation, dilation, coronary stenting, aortic stent graft, open heart surgery, heart valve replacement for congenital heart diseases with advanced technology. Modern techniques are the least invasive, safe, and help patients recover quickly.
Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec International General Hospital owns a team of experts including Professors, Doctors, Specialist 2 doctors, Masters with experience and great reputation in the field of internal treatment. science, surgery, interventional cardiac catheterization and application of advanced techniques in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. In particular, the Center has modern equipment, on par with the most prestigious hospitals in the world.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.