This is an automatically translated article.
Bladder prolapse at first onset often makes patients feel pain, fatigue and discomfort, depression. The disease, if not detected and treated properly, will cause urinary retention, urinary tract infections and reduce kidney function, affect physiological function, reduce fertility and complications of all kinds. other diseases that threaten the patient's life.
1. What is bladder prolapse?
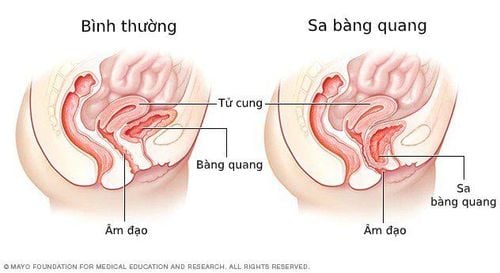
Bệnh sa bàng quang
Bladder prolapse (bladder prolapse) is a weakening or damage to the connective tissue system of the anterior wall of the vagina that causes the bladder to bulge and prolapse. Bladder prolapse is divided into 4 grades based on the condition of the bladder prolapsed from the vagina:
Grade 1: This is mild, only a small part of the bladder prolapses into the vagina. Grade 2: This is a moderate degree, the bladder prolapse can reach the vaginal opening. Grade 3: This is severe, the bladder protrudes from the vagina. Grade 4: This degree is the degree of complete prolapse through the vaginal opening, often associated with other forms of pelvic organ prolapse such as uterine prolapse, rectal prolapse. Bladder prolapse at first onset often causes patients to feel pain, fatigue, discomfort, and depression. If the disease is not controlled, it will cause sexual dysfunction.
Bladder prolapse also causes stagnation of urine, urinary tract infections and reduced kidney function. If not detected and treated properly, it will affect the physiological function, reduce the ability to conceive. More dangerous, complications of other diseases threaten the patient's life.
2. Causes of bladder prolapse
The main causes of bladder prolapse are:
Obesity: When the body weight is too heavy, it will increase the pressure on the pelvic floor muscles, causing bladder prolapse. Menopause: The main reason why menopausal women often experience bladder prolapse is due to a decrease in hormone levels, a gradual loss of elastic and firm function of the vaginal muscles, unable to support. bladder. Carrying heavy objects or stress, excessive stress: The cause of bladder prolapse often occurs in women who often carry heavy objects, stress. Pregnancy and childbirth: During pregnancy, the pelvic muscles are stretched, leading to a gradual loss of bladder function. There are also risk factors for the disease during childbirth. The cause of bladder prolapse can also be due to prolonged constipation, genetics, chronic cough, ... due to weakened muscles and connective tissue between the vagina and bladder.

Sa bàng quang do béo phì
3. Symptoms of bladder prolapse
Symptoms of bladder prolapse are often confused with some other pathology. However, most of the time, the patient will experience the following symptoms:
Pain and discomfort in the pelvic area: Always feel like something is coming out of the vagina; pain in the vaginal, pelvic and lower abdomen. Pain increases when the sick person sneezes, coughs, or exerts himself. Urinary tract disorders: Bladder prolapse often causes painful urination, dysuria, urinary retention, urinary frequency, urinary incontinence. This condition needs immediate treatment, because it can easily cause urinary tract or bladder infections, which is dangerous to the patient's health. Low back pain: Low back pain can be a warning symptom of bladder prolapse, but it's often confused with other conditions, so it's easy to ignore. Pain during sex: When the bladder falls into the vagina, it will cause pain and discomfort in the sex life. There is a tumor in the vagina: In severe bladder prolapse (grade 3 or higher), the patient feels like sitting on an egg, because the entire bladder has been completely prolapsed. If you lie down or stand, this symptom will go away.
4. Bladder prolapse treatment
Treatment depends on the extent of bladder prolapse. Specifically:
Mild prolapse: If there are few or no obvious symptoms that usually don't need treatment, the patient should take care of themselves at home such as pelvic floor strengthening exercises and regular checkups. . Severe prolapse: Use a vaginal lift to insert into the vagina to support the bladder; Estrogen therapy (vaginal cream, suppository, or ring) is used during menopause to help keep pelvic muscles strong. Severity: If the prolapse becomes more severe, and the above measures do not work, the patient must have surgery to lift the bladder back to the correct position, remove excess tissue, and tighten the muscles. , ligaments of the pelvic floor.
Phẫu thuật điều trị bệnh sa bàng quang nặng
5. Measures to prevent bladder prolapse
To prevent bladder prolapse, you should do the following methods:
Avoid lifting heavy objects: If not necessary, you should not lift heavy objects but ask others for help, in case you have to lift heavy objects, you should lift them. Correct posture, use strength in legs instead of waist or back. Cough control: If you have a cough, you need to treat it and give up smoking. Moderate weight: The body should not be overweight or obese because it can increase the possibility of bladder prolapse. If you are overweight, you need to have a plan to lose weight accordingly. Do Kegel exercises: These Kegel exercises are intended to help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, especially women after childbirth. Constipation treatment: Constipation is the cause of bladder prolapse, so you should follow a diet to treat and limit the risk of constipation by eating foods rich in fiber to help you not be constipated. , reduce bladder prolapse. Do not give birth prematurely, excessively and thickly; giving birth in a place with safe medical conditions, delivering birth with proper technique; do not let labor prolong; Obstetric procedures follow indications and techniques, avoiding trauma to the vagina and perineum. In particular, after giving birth, you should not do heavy labor too soon, rest and eat in moderation.