This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Phi Tung - Intensive Care Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Anti-thrombin is a protein with anticoagulant properties, however, anticoagulant activity is weak and slow when it exists alone. By combining with anti-thrombin on a specific site, heparin increases the anticoagulant activity of anti-thrombin by 1000-4000-fold.
1. What is Anti-Thrombin?
Mechanism of action of heparin is indirectly through anti-thrombin (also known as anti-thrombin III). Anti-thrombin is a protein with anticoagulant properties, however, the anticoagulant activity is weak and slow when it exists alone. By combining with anti-thrombin on a specific site, heparin increases the anticoagulant activity of anti-thrombin by 1000-4000-fold.
2. Principle of Anti-Thrombin
Test principle is to remove excess factor Xa of known concentration into the patient's blood, factor Xa will combine with anti-thrombin complex and heparin available in the patient's blood, the excess factor Xa will be quantified. by optical methods to calculate. Then, based on the normalized curve, infer the amount of factor Xa that has combined with antithrombin-heparin complex in the patient's blood. Therefore, anti-Factor Xa quantification is actually measuring the concentration of antithrombin-heparin complex in the patient's blood, which reflects both the concentration and effectiveness of heparin in the patient's blood in the absence of antithrombin reduction.
Because the rate of reduction in antithrombin in the general population is so small, that the test is independent of reagents, anti-Xa is considered the most reliable test in monitoring the effectiveness of heparin anticoagulants. However, the rate of anti-thrombin reduction in some special populations is very high, as in the ECMO population, according to the study of the author, more than 50% have decreased anti-thrombin, especially the rate This is higher the longer ECMO is performed, reducing the accuracy of the test.
3. Aim of Anti-Xa
Lovenox (LMWH) and unfractionated heparin (UFH) differ in their ability to combine with factor Xa and IIa, the goal also depends on the intended use: therapeutic or prophylactic.
Treatment goal:
Lovenox: 0.5-1.2 UI/ml UFH: 0.3-0.7 UI/ml Thrombosis prevention goal:
Lovenox: 0.2 – 0.5 UI/ml (steady state, sample taken from 4- 6 hours after injection of Lovenox and after the first 3-4 doses) Note: Because anti-Xa is calculated indirectly based on the standard curve. This standard curve is different for different types of heparin. Therefore, it should be noted that the anti-Xa test is titrated to which type of heparin (LMWH, UFH or rivaroxaban..), otherwise it is often implicitly titrated to UFH or LMWH.
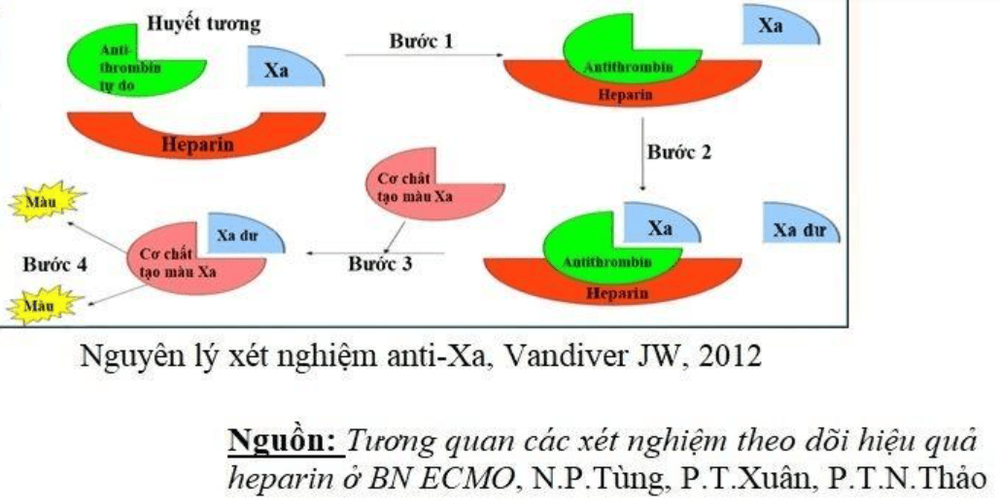
Nguyên lý xét nghiệm Anti-Xa, Vandiver 2012
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
REFERENCES:
Tung Phi Nguyen, Xuan Thi Phan, Dai Quang Huynh, Ha Thi Viet Truong, Yen Nguyen Hai Le, Tuan Manh Nguyen, Quan Quoc Minh Du, Thao Phuong Le, Hai Ngoc Truong, Thi Thi Ho, Thao Thi Ngoc Pham, "Monitoring Unfractionated Heparin in Adult Patients Undergoing Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO): ACT, APTT, or ANTI-XA?", Critical Care Research and Practice, vol. 2021, Article ID 5579936, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5579936