This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Specialist II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalIsolated rectal ulcer syndrome is a rare disorder associated with bowel discomfort and sometimes bloody, mucus-based bowel movements. The cause is ischemic lesions or prolapse of the rectal mucosa. The diagnosis of this pathology is clinical and confirmed by endoscopy with biopsy.
1. What is a solitary rectal ulcer?
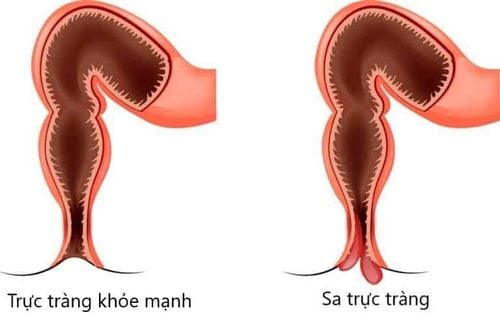
Isolated rectal ulcer syndrome is a rare benign disorder with an estimated annual prevalence of 1 in 100,000 people. The disease occurs most commonly around the age of 30 in men and at the age of 40 in women, but men and women are equally affected. In addition, some cases have been recorded in children and the elderly.The name “solitary rectal ulcer” is a reference to the ulceration observed in 40% of patients. The location of a solitary ulcer on the rectum is usually in the anterior wall of the anorectal canal, about 7-10 cm from the anus.
However, the ulcer may be closer to the anus, deeper inside, or in the lateral or posterior wall of the rectum. The remaining patients had various types of lesions in shape and size, ranging from edematous and congested intestinal mucosa to extensive multi-polyposis lesions. Therefore, the name "alone" can be misleading as there can be more than one ulcer; At the same time, the patient also had observable mucosal lesions that had not progressed to a true ulcer.
The underlying cause of solitary ulcerative colitis is thought to be related to the habit of straining too much during defecation. Due to the overactive anal sphincter during defecation, the patient has to push the stool out more, leading to increased pressure in the abdomen and in the rectum. The result is mucosal damage. The intestinal mucosa is repeatedly compressed, lack of local blood supply can cause tissue to swell, necrosis and form ulcers. Other predisposing factors for rectal ulceration, both repeated frictional trauma and dry, hard stools may also contribute.

Nguyên nhân cơ bản của viêm loét trực tràng đơn độc được cho là có liên quan đến thói quen rặn quá nhiều khi đại tiện
2. What are the manifestations of solitary rectal ulcer?
Signs and symptoms of isolated rectal ulcer syndrome include:Constipation Bleeding from the rectum A bowel movement with mucus Difficult or painful bowel movements Incomplete bowel movements Pain or a feeling of fullness Pelvic abdominal pain Perianal-rectal pain However, some people with isolated rectal ulcer syndrome may have no symptoms.
3. How is a solitary rectal ulcer diagnosed?
Because the symptoms reported by the patient are often nonspecific, and the abdominal examination or physical examination is not abnormal, the doctor may need to order some of the following tests to diagnose the syndrome: Solitary rectal ulcer:anorectal endoscopy: In this procedure, the doctor will use a thin, flexible tube with a very small camera attached, inserted into the rectal lumen to view the lining of the rectum. and part of the colon. If damage is found, the doctor will take a tissue sample for testing. Lesions in solitary ulcerative proctitis are always benign in nature. Abdominal ultrasound: This imaging technique uses sound waves to create images. Physicians need ultrasound to help distinguish isolated rectal ulcer syndrome from other abdominal conditions that can cause similar discomfort. Other imaging tools: Your doctor may order an imaging test called a contrast-enhanced colonoscopy. During this procedure, a small amount of solution containing barite is inserted into the rectum. After that, the patient will pass out the same way as when having a bowel movement. Rectal-anal view showing clear barite content on x-ray may indicate rectal mucosal prolapse or problems with muscle function or coordination of the rectal muscles in expulsion. feces.
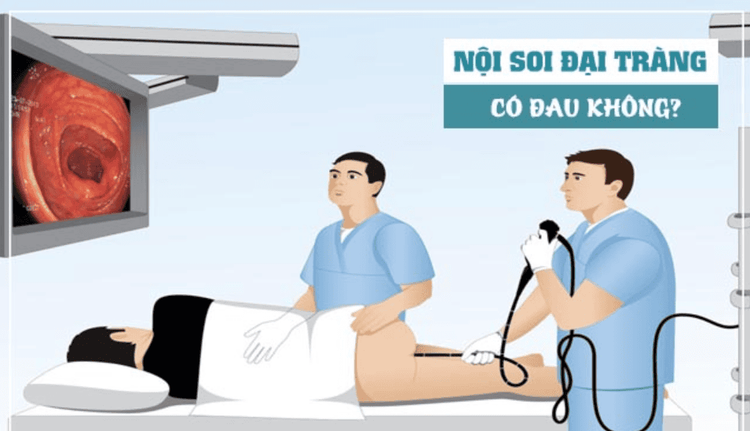
Nội soi ống hậu môn - trực tràng là một trong sô những thủ thuật bác sĩ sẽ yêu cầu bệnh nhân thực hiện để chẩn đoán bệnh
4. How to treat solitary rectal ulcer?
Treatment of isolated rectal ulcer syndrome depends on the severity of the clinical manifestations. Patients with mild signs and symptoms may improve on their own through aggressive lifestyle measures. Conversely, patients with more severe signs and symptoms will require medical treatment or sometimes surgery.Non-pharmacological treatment includes:
Dietary changes to relieve constipation, the patient may be instructed to increase the amount of fiber in each daily meal. Behavioral defecation therapy if the patient often feels strained to go to the toilet. These therapies will help you learn to relax your pelvic muscles during bowel movements, recognizing this activity as a routine that needs to be done every day. Drug therapy:
Mainly treatments such as topical steroids, sulfasalazine enemas, and onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) can help alleviate rectal ulcer symptoms. However, these treatments are not always effective for everyone and some are still being tested.
Surgical interventions are applied in the treatment of isolated rectal ulcer syndrome:
Rectal mucosal resection: when the patient has rectal prolapse causing symptoms. Surgery to remove the rectum: when the patient's symptoms do not improve with other treatments. At this point, the surgeon will connect the colon to an opening in the abdominal wall, called an ostomy, for the patient to pass stool.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
5. How to live with solitary rectal ulcer at home
Every person can make daily lifestyle changes to help improve symptoms of solitary rectal ulcer disease as well as proactively prevent it. These changes include:Increasing the amount of fiber in the diet, while also making it a habit to read nutrition labels on food packages that list the amount of fiber in a serving. The best sources of fiber are fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Eat fruits and vegetables with their skins on instead of drinking juice. If you eat bread, you should choose whole wheat bread with ingredients of wheat, oats. Use laxatives and stool softeners for constipation. These drugs will increase the absorption of fluid in the intestinal lumen and will make the stool softer, helping to trigger peristalsis, increasing the frequency of contractions and pushing the stool out. However, these drugs should be taken with a large amount of water for optimal effect. Drink enough water during the day. The habit of drinking enough water and fluids in general not only makes bowel movements softer and easier, but also helps the functioning of metabolic processes in the body take place better. To increase the amount of water you drink, you should make a variety of drinks, such as adding lemon juice, orange juice to the water to create a delicious taste. Also, try other non-carbonated, caffeinated or alcoholic beverages such as vegetable juices, fruit juices, especially prune juice, which can be helpful because of their natural laxative effects.

Thói quen uống đủ nước và các loại chất lỏng nói chung không chỉ giúp đi tiêu mềm và dễ hơn mà còn giúp hoạt động của các quá trình chuyển hóa trong cơ thể diễn ra tốt hơn
Articles refer to sources: mayoclinic.org, NCBI, msdmanuals.com