This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Ta Que Phuong - Department of Gastroenterology - Vinmec Times City International HospitalA diet rich in fiber has many potential health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. That's because fiber can help lower cholesterol and help control blood sugar levels. blood sugar.
Fiber can help you have softer and more regular bowel movements. Adding fiber to your diet can help with problems like constipation, hemorrhoids, and diarrhea. Fiber is commonly found in beans, whole grains, vegetables, and fruits. However, most people don't eat as much fiber as recommended.
>>> Types of fiber and their health benefits
1. What is fiber?
Traditionally, fiber has been thought of as a substance found in the outer layer of grains or plants and not digested in the intestines. Wheat bran, the outer layer of the wheat grain, fits this pattern. We now know that "fiber" actually consists of several different substances. The term "dietary fiber" includes all of these substances and is now considered a better term than just "fiber".Most of the fiber in food is not digested or absorbed, so it stays in the intestines, where it regulates the digestion of other foods and affects stool consistency. There are two types of fiber, each believed to have its own benefits:
Soluble fiber consists of a group of substances made up of carbohydrates and dissolved in water. Examples of foods that contain soluble fiber include fruits, oats, barley, and legumes such as peas and other legumes. Insoluble fiber comes from plant cell walls and is insoluble in water. Examples of foods containing insoluble fiber include wheat, rye, and other grains. The traditional fiber, wheat bran, is an insoluble fiber. Fiber is a combination of all soluble and insoluble fiber.

2. Benefits of a High-Fiber Diet
The health effects of high fiber may depend to some extent on the type of fiber eaten. However, the difference between the health effects of the two types of fiber is not so clear and can vary between individuals, so many providers encourage fiber supplements in whatever way is easiest. for patients.There are several potential benefits of eating a high fiber diet:
Insoluble fiber (wheat bran, and some fruits and vegetables) has been recommended for treatment Digestive problems such as constipation, hemorrhoids, chronic diarrhea and urinary incontinence. Fiber swells stools, making them softer and easier to pass. Fiber helps with regular bowel movements, although it is not a laxative. Soluble fiber (psyllium, pectin, wheat dextrin, and oat products) may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke by 40 to 50% (compared to a low-fiber diet) Soluble may also reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In people with diabetes (types 1 and 2), soluble fiber can help control blood sugar levels. It's not clear whether a high-fiber diet is beneficial for people with irritable bowel syndrome or diverticulitis. Fiber may be helpful for some people with these diagnoses while it may worsen symptoms in others. >>> Eating more fiber from fruits and vegetables reduces the risk of being hospitalized for diverticulosis
3. Daily fiber needs
The recommended amount of fiber is 20 to 35 grams per day. By reading nutrition labels on packaged foods, the number of grams of fiber per serving can be determined (Figure 1).
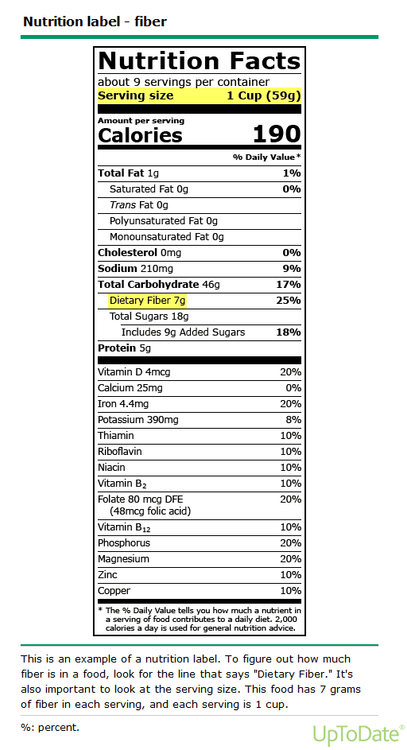
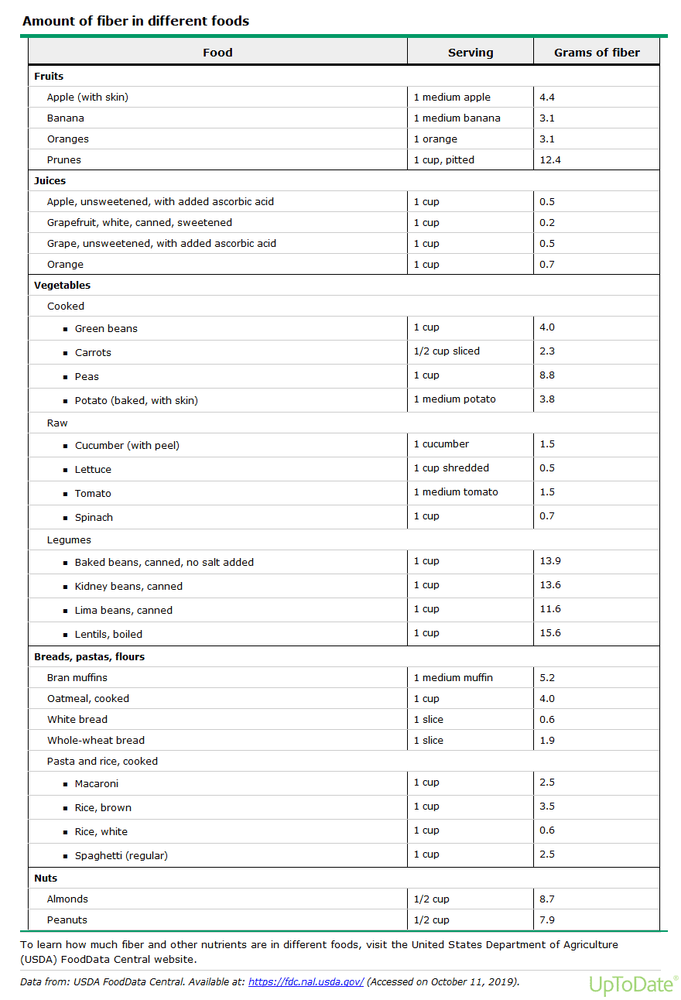
Sources of dietary fiber: The fiber content of many foods, including fruits and vegetables, is available in the table (Table 1). Breakfast cereals can be a good source of fiber. Certain fruits and vegetables are especially helpful in treating constipation, such as prunes and prunes juice.
Other sources of fiber
For those who don't like high fiber foods like fruits, beans, vegetables, a good source of fiber is unprocessed wheat bran; One to two scoops can be mixed with food. One tablespoon of wheat bran contains about 1.6 grams of fiber.
Additionally, several fiber supplements are available. Examples include psyllium, methylcellulose, wheat dextrin and calcium polycarbophil. The dose of fiber supplements should be increased slowly to prevent bloating and cramping, and fluid intake should be adequate. The fiber in these supplements is mostly soluble.
>>> Some notes when using dietary fiber supplements
4. Effects of eating a lot of fiber
Adding fiber to the diet can have some side effects, such as bloating or gas. This can sometimes be minimized by starting with a small amount and gradually increasing until the stools become softer and more frequent.
However, many people, including those with irritable bowel syndrome, cannot tolerate fiber supplements and do better by not increasing fiber in their diets.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Update.com













