This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi An - Pediatrician - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Prolonged jaundice is a common medical condition in premature babies. To deal with this situation, parents should do from simple daily habits such as: sunbathing properly enough hours, keeping children warm...
1. Jaundice in babies
Neonatal jaundice is common in premature babies, making the metabolism of excess bilirubin unable to occur, leading to jaundice. The more excess bilirubin, the longer the jaundice process in the baby. This is a common condition, especially in premature babies.For newborns, red blood cells are always created and lost, the loss is more or the rupture of red blood cells after birth, when red blood cells are broken, hemoglobin is released, This substance will be converted to bilirubin. From here, bilirubin will be metabolized in the baby's liver and excreted through feces and urine.
However, because the newborn's liver is still weak, this bilirubin excretion is not effective, causing hyperbilirubinemia in the blood, causing jaundice in newborns. According to the medical literature this is called physiological neonatal jaundice.
1.1 Jaundice in infants The first manifestation of jaundice is yellowing in the skin and eyes of the baby. Yellow color can begin within 2 to 4 days after birth and can start on the face before spreading down the body. Bilirubin levels usually peak between 3 and 7 days after birth. When gently pressing a baby's skin with a finger, causing the area to turn yellow, it could be a sign of jaundice.
Most cases of jaundice are normal, but sometimes jaundice can indicate other conditions. Severe jaundice also increases the risk of bilirubin entering the brain, which can cause permanent brain damage.
1.2 Causes of Jaundice in Newborns It is usually caused by a baby's liver not yet mature enough to remove bilirubin from the blood – a yellow pigment produced when red blood cells are destroyed. While in the womb, the mother's liver takes care of this process, but after birth the baby's body has to take care of it while the newborn's body produces a large number of blood cells and is relatively degraded. fast. This phenomenon is called physiological jaundice.
1.3 Progression to prolonged jaundice In many cases, the physiological jaundice in children will go away on its own as the child's liver develops and when the child begins to eat, helping to remove bilirubin from the body. In most cases, jaundice will go away within 2 to 3 weeks after birth. In addition, there is still pathological jaundice, which is cases of jaundice lasting more than three weeks or children with too high levels of indirect bilirubin in the blood beyond the physiological threshold called persistent jaundice.
For children with high levels of bilirubin can put the child at risk of deafness, cerebral palsy or other forms of brain damage. Therefore, experts always recommend that all newborns be checked for jaundice (or at least 8 to 12 hours) before discharge and a few days after discharge.
Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
2. What is prolonged jaundice? How to quickly detect prolonged jaundice in children
Persistent jaundice is a condition in which an infant has jaundice for more than 1 week (even if the baby is born at full term) or for more than 2 to 3 weeks (for babies born prematurely before 37 weeks of gestation).Experts believe that prolonged jaundice is caused by high levels of bilirubin in the body, which causes the skin and sclera (in the eyes) to turn yellow.
Thus, when the liver or bile ducts are inflamed or there are other abnormalities of hepatocytes and bile ducts (including the gallbladder), the amount of bile pigments in the blood increases, causing skin and mucous membranes. The conjunctiva (including the conjunctiva of the eye) are stained yellow with bile pigments, giving them a yellow color.
Babies at high risk for persistent jaundice are:
Premature babies: Babies born before 37 weeks have a higher risk of physiological jaundice, because the liver is not able to process bilirubin as quickly as babies full-term birth. Baby bruises during delivery: During labor and natural delivery or also cesarean section, some babies have bruises on their body. Many studies have shown that infants with bruises are at increased risk of over-normal levels of bilirubin from the breakdown of red blood cells. Blood group factors: Mothers with blood group O or Rh blood group also have a higher chance of being born prematurely with jaundice. Babies whose blood type is incompatible with their mother's can develop antibodies that can destroy red blood cells and cause a sudden increase in bilirubin levels. Breastfeeding: Breastfed babies have a higher risk of jaundice. However, the benefits that breast milk brings far outweigh the disadvantages that jaundice can cause, so experts still recommend that mothers should breastfeed from birth. Other causes of persistent jaundice in newborns include:
Infection Enzyme deficiency Abnormalities in the baby's red blood cells. How to quickly detect persistent jaundice in a baby:
Perform a quick test in a well-lit room, gently touching the baby's nose or forehead with your index finger. If the skin is still yellow where you just released your finger, you should consult a doctor. If the baby has dark gray skin, try checking the yellow color in the whites of the eyes or in the gums. You may also notice that your baby has very pale stools.
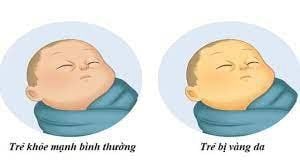
3. Is prolonged jaundice dangerous?
Jaundice in premature infants is particularly dangerous and progresses rapidly. If not detected or treated early, the child will be neurotoxic, causing death or severe sequelae.When the child has signs of prolonged jaundice that does not stop or the child's body is abnormally yellow, it may be light yellow, dark yellow, brownish yellow... it is best to visit a health care provider to have a diagnosis. Determine the exact cause of jaundice. Because the resistance of newborns is very poor, they need to be protected and cared for more than anything. Jaundice should not be allowed to last for a long time or use unfounded folk remedies and remedies that will not only not cure the disease but may hinder the treatment process later on.
3.1 Dangerous complications from prolonged jaundice Newborns with prolonged jaundice may experience dangerous complications such as:
Acute cerebral palsy: If the mother detects that the child has jaundice, there are signs Other symptoms such as lethargy, inability to concentrate, crying a lot, refusing to breastfeed and high fever should immediately consider acute cerebral palsy. According to doctors, bilirubin is very toxic to the cells of the brain. Severe jaundice has the potential for bilirubin to get into the brain and cause serious complications. Nuclear jaundice: When bilirubin exceeds the allowable limit, the liver can't excrete it in time, there is a risk of seeping into the brain, ie the child has nuclear jaundice. This causes irreversible brain damage. Therefore, if pathological jaundice is identified, it must be treated before 7 days after birth to prevent brain damage. 3.2 When to see a doctor? Parents should take their child to see a doctor as soon as they see the following symptoms:
Jaundice appears before 24 hours of age The degree of jaundice becomes more and more obvious, the whole body yellows The rate of jaundice increases rapidly Jaundice lasts for more than 1 week (despite term birth) or more than 2 weeks (for premature infants) Jaundice accompanied by any other abnormality such as: chalky white stools, vomiting, poor feeding, abdominal distension, apnea, tachypnea, bradycardia, hypothermia, weight loss, pallor, purpura, lethargy, rigidity, convulsions, coma...
4. How does a newborn have persistent jaundice?

The doctor may give the child a blood test to check the bilirubin level. More severe jaundice may require other treatments. Phototherapy is a common and highly effective treatment that uses light to break down bilirubin in a child's body. There are two types of phototherapy:
Conventional irradiation Ultraviolet light while the child is in bed. The light helps break down the bilirubin so it doesn't put pressure on the liver. The light will stop every 3-4 hours for the mother to feed the baby.
Optical fiber treatment The child is wrapped in a blanket containing a special optical fiber, which radiates light directly onto the child's skin. The mother can still hold and breastfeed the baby as usual.
Note:
In very severe cases, an exchange transfusion may be necessary. Your baby will receive a small amount of blood from a donor or blood bank, which helps to replace damaged blood with healthy red blood cells. This also increases the baby's red blood cell count and lowers bilirubin levels.
4.2. Caring for a child with prolonged jaundice Make sure the baby gets enough nutrition through breast milk If the mother is breastfeeding, the baby should be breastfed often. This helps to brighten young skin. No need to use formula or water instead. Mothers should wake the baby up to feed the baby even when the baby is sleeping If the mother cannot breastfeed her baby because there is no milk in time, she can choose formula milk to feed the baby. Should consult with a doctor, if you are concerned that your baby is using too little or too much formula, you should keep your baby warm every day. At the same time, mothers should pay attention to taking care of the navel and body hygiene for children. Mothers should pay attention to sunbathing properly, enough hours for children in the early morning and late afternoon, when the sun is soft, it is very good for yellow disease. skin. Sunbathing cannot cure the disease, but it will be an agent to stop prolonged and worsening jaundice. To ensure the accuracy of the newborn's health status as well as know whether the baby has jaundice or not, the mother should register for a screening test for premature babies. Because if left untreated, jaundice can lead to dangerous complications. Consequences of not detecting and treating jaundice in time will lead to nuclear jaundice and the sequelae that can be lifelong cerebral palsy, even death.
Pediatrics Department - Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining newborn diseases, including jaundice. At Vinmec, it is equipped with a safe and easy-to-implement lighting system, babies can still breastfeed when under lights, can be combined with 10% Glucose infusion. There are many types of illuminator suitable for each jaundiced object that needs to be illuminated: crib light (child lying directly on top, double lamp with upper and lower projection (used in cases where positive light is required), lamp form blankets, bags wrapped around the young (very convenient for mothers to take care of the baby: just pick it up to breastfeed and light up)
If the treatment for severe jaundice is not effective, or the child is yellow If the skin is severe to late, there is too much bilirubin in the blood, the doctor will prescribe the use of a blood transfusion as a last resort. to reduce bilirubin in the blood and thereby also reduce bilirubin outside the organization. Currently, he is a Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Department of Neonatology at Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
5 week old baby still has jaundice, does it affect anything? What is nuclear jaundice? Distinguish between physiological neonatal jaundice and pathological jaundice