This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by doctors of Internal Oncology Department, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Treatment options and recommendations depend on factors including the type and stage of the cancer, possible side effects, the patient's wishes, and overall health. The first treatment is usually surgery to remove the testicle. This article provides information related to testicular cancer surgery.
1. Status of testicular cancer pathology
The incidence of testicular cancer is 1 in 250 men. The mean age of the disease was 33 years old. Testicular cancer is very rare before puberty. The disease is usually diagnosed in young and middle-aged men but can occur at any age, with 6% of cases being diagnosed in boys and adolescents and 8% of cases being diagnosed in men. 55 years and older.
In our country, although there are no exact statistics on the annual incidence of testicular cancer, we only know that this is not a common cancer in men. Therefore, early symptoms and signs of disease are also easy to ignore.
When a person is diagnosed with testicular cancer, many different specialists (called a multidisciplinary team) often work together to come up with an overall treatment plan for the patient, combining many treatments. For testicular cancer, this group includes urologists and oncologists.
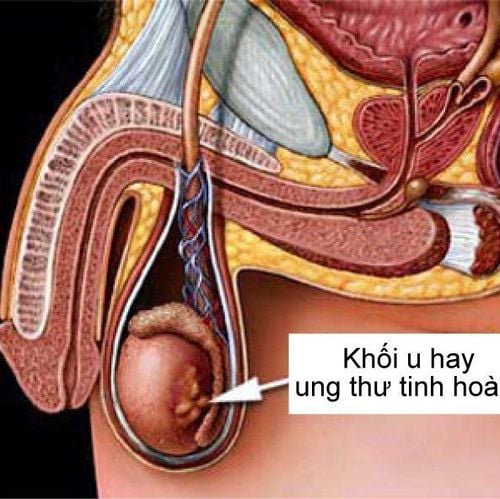
Các dấu hiệu bất thường thường bị bỏ qua dẫn đến nguy cơ mắc ung thư tinh hoàn càng cao
2. Testicular cancer surgery
Cancer surgery involves removing the tumor and sometimes some surrounding healthy tissue. Radical excision, also known as orchiectomy, is often the first line of treatment for testicular cancer. In addition to radical radical resection, other types of surgery may be performed for testicular cancer at different times in the treatment process. Before surgery, talk to your health care team about possible side effects from surgery.3. Removal of testicles
Treatment for testicular cancer usually begins with surgical removal of the testicle with cancer. This operation is done through an incision in the groin. During surgery, the entire testicle and most of the spermatic cord are removed. The spermatic cord contains the blood supply to the testicles and through which sperm travel from the testicles towards the penis. A person can develop cancer in both testicles at the same time or at different times, however, this only happens in about 2% of men with testicular cancer. At that time, both testicles had to be removed.Orchiectomy is used to treat both early and later stages of testicular cancer that can be diagnosed as a seminoma. For late-stage cancer, orchiectomy can sometimes be delayed after chemotherapy ends.
If the decision to remove the testicle is made, blood will be obtained prior to surgery to check the level of tumor markers in the serum for treatment planning and follow-up care. For example, elevated AFP or persistently high beta-hCG after surgery is a sign that the cancer has spread. At this point, patients often need chemotherapy even if metastases are not visible on imaging tests.
Điều trị ung thư tinh hoàn thường bắt đầu bằng phẫu thuật cắt bỏ tinh hoàn bị ung thư
4. What Happens After Orchectomy?
Removal of one testicle usually doesn't affect a man's testosterone levels if he still has one side of normal size. If a person's testosterone levels drop, symptoms can include depression or mood swings, fatigue, decreased sex drive, inability to achieve a normal erection, as well as decreased muscle and bone mass.
Removal of the testicle does not destroy the patient's ability to father children because the remaining testicle still produces sperm. However, about 25% of men with testicular cancer are infertile even before being diagnosed with the cancer. Sperm count usually improves after the cancerous testicle is removed.
If removal of both testicles is performed, the patient will no longer produce sperm or testosterone and cannot bear children. If your doctor recommends an orchiectomy in a patient with one testicle, the semen is usually analyzed twice before surgery to check that the patient's sperm is working properly. If the sperm is still functional, then depositing the sperm into a sperm bank will be encouraged, and the patient can still have children later if desired. In addition, for patients who have had both testicles removed, testosterone replacement therapy will be needed.
Liệu pháp thay thế testosterone được áp dụng cho người đã cắt bỏ 2 tinh hoàn
5. Reconstructive surgery after orchiectomy
If desired, men can have a prosthetic testicle implanted in the scrotum. A prosthetic testicle is usually a bit similar in weight and texture to a normal testicle, but not exactly the same. Some men find a prosthetic testicle uncomfortable, nor do they like having only one testicle. Each patient is encouraged to consult with his or her doctor about whether he wants to have it done and the best time for this transplant if he wants to. Some men wait until active treatment is over to make this option.6. Follow-up after orchiectomy
After radical surgical resection, for those diagnosed with stage I (for both histologically melanoma or mixed tumor, i.e. seminoma and non-seminoma) will also be followed up. closely and treat aggressively if the cancer recurs. This includes physical examination, blood tests, CT/scan and chest X-ray so that any recurrence can be detected at an early stage, especially in the case of AFP and beta- hCG was normal or returned to normal after the cancerous testicle was removed.
7. Physical, emotional and social effects of cancer

Hệ thống chăm sóc hỗ trợ giảm nhẹ tại Vinmec mang lại cảm giác yên tâm cho người bệnh
The 5-year survival rate for men with testicular cancer is 95%. This means that 95 out of 100 men diagnosed with testicular cancer will live at least 5 years after diagnosis. This rate is highly dependent on the stage of the disease.
Survival rates are higher for men diagnosed with early-stage cancer and lower for men with later-stage cancer. For people who have cancer but have not spread beyond the testicle (Stage 1), the survival rate is 99%. About 68% of men are diagnosed at this stage.
Cancer and its treatments cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social and economic effects. Managing all of these problems is called palliative supportive care. This is an important part of care along with cancer treatments.
Men with testicular cancer often worry about how treatment will affect their sexual health, fertility, and quality of life. Each patient should discuss these topics with their doctor before starting treatment because there will often be more than 1 treatment option. The final choice for a treatment plan depends on the specific condition of the individual patient. Patients should learn about all treatment options and uncertainties. It is necessary to sit down and discuss with the doctor to help the doctor choose a treatment method that is suitable for the patient's goals and wishes.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. The hospital always approaches and applies proven advanced techniques to help patients feel safe and reduce pain during surgery.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Source : Mescape 2019
MORE:
10 alarming reasons for testicular pain Risk of infertility in adults with undescended testicle Testicular cancer: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment