This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by - Master, Resident, Specialist I Trinh Le Hong Minh - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a large magnet and radio waves to evaluate organs and structures inside the body. MRI scans help doctors diagnose many conditions of the body, especially problems with the brain and spinal cord.
1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that creates 3D anatomical images of tissues and organs in the body. This is a modern method, which is being used popularly around the world because of its safety and effectiveness.
MRI uses large magnets to create a strong magnetic field wave, the nuclei of protons in the body align in a straight line with that magnetic field. A radio wave is then passed through the patient, stimulating and causing the protons to move out of equilibrium to counteract the attraction of the magnetic field. After the radio source is switched off, sensors in the magnetic resonance imaging machine can detect the energy released when the protons align together in the direction of the magnetic field. The time it takes for the protons to move as well as the amount of energy released depends on the chemical nature and environment of the nuclei. Through the obtained data, the computer will analyze and produce images of tissues and organs that are taken with magnetic resonance imaging.
Magnetic resonance imaging is especially suitable for imaging soft tissues of the body or non-bone parts. Magnetic resonance imaging differs from computed tomography in that it does not use x-ray damaging ionizing radiation. The brain, spinal cord, and nerves, as well as muscles, tendons, and ligaments are all present. can be shown with MRI much more clearly than with conventional X-rays and computed tomography. For this reason, magnetic resonance imaging is used extensively in the diagnosis of knee or shoulder injuries.
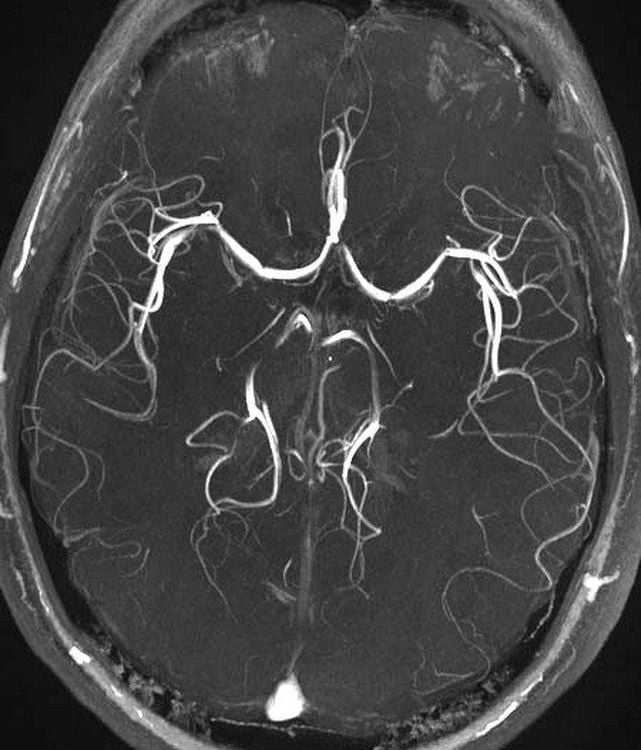
Chụp MRI não sẽ cho kết quả rõ ràng hợp chụp cắt lớp vi tính
In brain imaging, MRI can clearly distinguish the white and gray matter parts of the brain and can be used to diagnose aneurysms and detect the presence of tumors. Because magnetic resonance imaging does not use candle ionizing radiation, this is the diagnostic method of choice when it is necessary to regularly monitor images of the brain during treatment. However, the cost of magnetic resonance imaging is much higher than that of X-rays or computed tomography.
A specialized type of MRI is functional magnetic resonance imaging. This technique is used to observe the structures of the brain and determine how regions of the brain behave in proportion to their features in order to further study the brain and provide criteria for assessing the condition of the brain. status as well as determine the risk of needing neurosurgery.
Although magnetic resonance imaging does not use ionizing radiation that is harmful to the body, the magnetic fields they generate are often very strong and can affect patients who are implanted with metal devices. metal. Following are the notes when taking MRI:
Patients with metal implants in the body such as nails (to fix broken bones), pacemakers, defibrillators, insulin pumps, hearing aids, ... need to be carefully evaluated by a specialist doctor about the possibility of having an MRI scan or not, on a case-by-case basis. Noise: Sometimes the radio waves used in magnetic resonance imaging can have a sound intensity of up to 120dB so the patient should be protected to avoid ear damage. The constantly changing magnetic field during the scan can also cause the patient to become irritated or develop a mild convulsion (very rare). For patients on hemodialysis, there may be some substances in the blood that contain gadolinium, such as gadodiamide. These substances change the contrast of the images, making it impossible for MRI to get accurate results, so these patients should have dialysis before the scan.

Phụ nữ mang thai cần cân nhắc khi chụp MRI
Pregnant women: Although it is considered safe for the body, MRI should be avoided in pregnant women to prevent possible consequences, especially in the first 3 months of pregnancy when The fetal organs are immature and some contrast agents may be present in the blood. People with claustrophobia may experience discomfort or even respiratory disturbances during the scan. To overcome this situation, the patient can be gradually familiar with the machine as well as the steps of taking or using sedation or anesthesia. Currently, magnetic resonance imaging machines are designed in an open direction at both ends to help reduce discomfort for patients with claustrophobia.
2. How to use magnetic resonance imaging
To obtain magnetic resonance imaging images, the patient will be placed in a large magnetic field created by the surrounding magnet blocks and lie still during the scan to obtain the best image.
Contrast agents can be given intravenously to the patient to speed up proton movement. The faster the protons move, the sharper the image obtained.
The magnetic resonance imaging process can be summarized in the following steps:
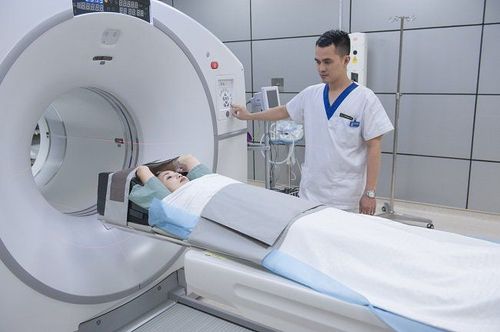
First, the patient is placed on a bed that can be moved along the axis of the machine. Depending on the part of the body that needs to be scanned, the patient will be gradually moved into the machine from the head or the front legs. All machines for magnetic resonance imaging are operated by a technician via a computer in another room next to the imaging room to avoid the influence of the magnetic field generated by the machine. However, the patient can still communicate with the technician in charge of the machine through the intercom system in the room. There are 2 times during the imaging process when the machine emits a loud noise, which can reach 120dB, is when the current in the coil is turned on and off, so before taking the picture the patient will be informed about that as well as used. tool to cover the ear. Most importantly, the patient needs to keep their body as still as possible during the operation of the MRI scanner. Typically, an MRI scan lasts between 15 and 90 minutes depending on the size of the area to be scanned and the quantity and quality of images captured.
Bệnh nhân cần giữ yên cơ thể ở mức tối đa trong khi máy quét MRI hoạt động
To obtain magnetic resonance imaging images, the patient will be placed in a large magnetic field created by the surrounding magnet blocks and lie still during the scan to obtain the best image.
Contrast agents can be given intravenously to speed up proton movement. The faster the protons move, the sharper the image obtained.
The magnetic resonance imaging process can be summarized in the following steps:
First, the patient is placed on a bed that can be moved along the axis of the machine. Depending on the part of the body that needs to be scanned, the patient will be gradually moved into the machine from the head or the front legs. All machines for magnetic resonance imaging are operated by a technician via a computer in another room next to the imaging room to avoid the influence of the magnetic field generated by the machine. However, the patient can still communicate with the technician in charge of the machine through the intercom system in the room. There are 2 times during the imaging process when the machine emits a loud noise, which can reach 120dB, is when the current in the coil is turned on and off, so before taking the picture the patient will be informed about that as well as used. tool to cover the ears. Most importantly, the patient needs to keep their body as still as possible during the operation of the MRI scanner. Typically, an MRI scan lasts between 15 and 90 minutes depending on the size of the area to be scanned and the quantity and quality of images captured.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a non-invasive imaging method, based on the action of magnetic waves to capture images of tissues and organs in the body for diagnosis and treatment of diseases. During the scan, the patient needs to stay as still as possible. Only in this way can you get clear, good quality images.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the first unit to put into use a 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging machine with Silent technology (noise reduction), bringing outstanding advantages. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at Vinmec will have the following outstanding advantages:
High imaging technology, first-class safety by accuracy, non-invasiveness and no radiation. High image quality, allowing doctors to comprehensively evaluate, not miss even the smallest lesions in organs Minimize noise, create the most comfort for patients when taking pictures, reduce stress, this helps better image quality and shortens the maximum scanning time. MRI with Silent technology is especially suitable for the elderly and children, people with weak health, and patients undergoing surgery. .. MRI scan at Vinmec can take 3-D vascular reconstruction without contrast injection, can reconstruct and handle the patient's motion artifacts
Before taking a job at National General Hospital Medical Center Vinmec Central Park, the position of Doctor of Imaging Department since February 2018, Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh used to work as a resident in the Department of Radiology at hospitals: Cho Ray, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Oncology, Gia Dinh People, Trung Vuong...from 2012-2015. Officially working at Cho Ray Hospital from 2015-2016, City International Hospital since 2016.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, customers can call the Hotline at: hospital or register online HERE.