This is an automatically translated article.
EBV virus (Epstein-Barr Virus) is one of the most common viruses in humans. This virus is the cause of mononucleosis and is associated with several types of cancer such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma, gastric cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, ...
1. Characteristics of the EBV . virus
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) also known as herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4). It is one of eight viruses in the Herpes group and one of the most common viruses in humans. Up to 90% of adults worldwide have been infected with the EBV virus and have antibodies to it.
EBV virus has a diameter of about 122 - 180 nm. EBV can infect immune system B lymphocytes and epithelial cells. During EBV infection, antibodies are formed. EBV antibody tests can be used to differentiate between unexposed and susceptible individuals to EBV infection from newly infected, former EBV infection or chronic recurrent EBV infection.
EBV virus is transmitted mainly through saliva (kissing, sharing toothbrushes, drinking cups,...). In addition, EBV can also be spread through blood and semen during sex, blood transfusion, or organ transplantation. Diagnosing EBV infection is often difficult because the symptoms are similar to many other diseases. Usually, your doctor will make a definitive diagnosis based on a blood test that detects antibodies.
The most common complication of EBV infection is a ruptured spleen. Other complications of EBV infection include: Difficulty breathing due to sore throat, rash, jaundice, pancreatitis, convulsions, encephalitis,...
Currently, there is no specific treatment for EBV, so treatment when infected with the EBV virus mainly at rest; drink a lot of water; treat symptoms (gargle with warm salt water to soothe the throat, take acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and pain) and avoid sports or heavy activity that can cause a ruptured spleen. There is also no vaccine to prevent EBV, so prevention is mainly to avoid contact with saliva and genital fluids of patients infected with EBV virus.

Cách điều trị virus EBV là uống nhiều nước và tánh tiếp xúc nước bọt với người bị nhiễm virus EBV
2. What disease does the EBV virus cause?
2.1 Mononucleosis
EBV virus is the cause of mononucleosis.
After being infected with the virus, children often have no symptoms. In adolescents and adults, there is about 30 to 50% of cases of mononucleosis, with symptoms appearing 4 to 6 weeks after infection with the virus. Common symptoms are: Fatigue, malaise, fever, sore throat, muscle weakness and pain, swollen lymph nodes in the neck and armpits, headache, swollen tonsils, rash, enlarged spleen, swollen liver, rash, .. Most patients get better after 2 - 4 weeks. However, some patients may feel tired after a few more weeks. Sometimes, symptoms of infectious mononucleosis can last for up to 6 months or longer.
There are some rare complications of mononucleosis. If the following symptoms are present, the patient should seek medical attention immediately:
Sudden sharp pain in the left side of the abdomen - there may be a problem with the spleen; Little urine - a sign of dehydration; Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
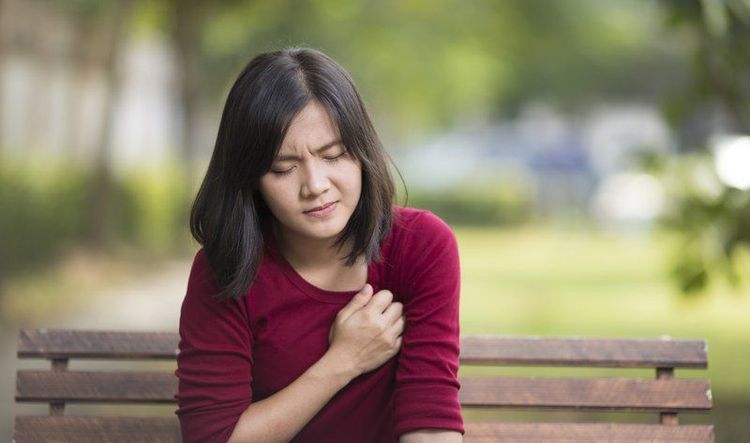

Bệnh bạch cầu đơn nhân gây triệu chứng khó thở cho người bệnh
2.2 Other diseases
In addition, in immunocompromised cases, EBV virus may be associated with some special forms of cancer such as: Burkitt lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, gastric cancer , lymphomas of the central nervous system, and HIV-associated conditions. In addition, EBV infection is associated with an increased risk of several autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatomyositis, Sjögren's syndrome, and multiple sclerosis. Ear infections and diarrhea in children, Guillain-Barre syndrome have also been associated with EBV infection. Statistics show that about 200,000 cases of cancer each year are related to EBV.Early diagnosis and treatment of EBV infection can prevent further progression of the disease. In particular, because EBV has no specific treatment, it is advised for each person to pay attention to prevent the risk of viral infection by avoiding contact with saliva and genital fluids of people who are carrying the virus.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE:
Signs of nasopharyngeal cancer in children What is chronic lymphocytic leukemia? What is Leukemia?