This is an automatically translated article.
The monospot test or mononucleosis test is a tool to confirm this condition. Based on signs of disease and suspicion, a monospot test checks your blood for specialized antibodies your body makes to fight a viral infection. Although not always accurate, it is still an essential tool for initial screening for Epstein Barr virus infection.
1. What is a monospot test?
Mononucleosis is an infectious disease, commonly known as mono, caused by the causative agent of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). A monospot test is a test that detects a protein in the blood that serves as a heterogeneous antibody produced by the immune system in response to an EBV infection.
Mononucleosis is characterized by a distinctive set of symptoms that most often affect adolescents. People with this disease often have fever, sore throat, swollen glands, and fatigue. Some people will feel a fullness in the abdomen due to an enlarged liver or an enlarged spleen. Symptoms of the infection usually arise about a month after the initial viral infection and can last for several weeks. However, the feeling of fatigue sometimes persists for several months. Even so, in the majority of cases, mononucleosis is self-limited and symptoms sometimes resolve on their own without specific treatment.
Epstein-Barr virus is very common and very contagious. According to community statistics, most people will contract this virus at least once in their lifetime. At the same time, the saliva of an infected person is also an easy source of person-to-person transmission through close contact such as kissing and through sharing personal utensils including cups.
Bạch cầu đơn nhân
Usually, infection with EBV occurs during childhood and may cause few or no symptoms. However, the virus can still cause symptoms of mononucleosis in about 25% of adolescents and young adults as adults. Not only that, the disease can affect anyone at any age, but its prevalence is highest in populations that are young people, such as students in high school or in military settings. team.
The monospot test has an accuracy of 71% to 90% and can be used as the initial test for the diagnosis of mononucleosis. However, the test has a false-negative rate of 25% because some people infected with EBV do not produce the antibodies the test is designed to detect. Therefore, if the monospot test is negative, the possibility of suspicion of disease is still high.
In addition, other agents that can cause mono include:
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Hepatitis A, B or C HIV Rubella Toxin

HIV có thể là nguyên nhân gây bệnh mono
2. What is the role of the monospot test?
The monospot test or mononucleosis test is used to help determine if a person with symptoms of mononucleosis has the disease. This test is used to detect proteins in the blood that are essentially antibodies produced by the immune system in response to infection with the Epstein-Barr virus, the most common cause of mononucleosis.
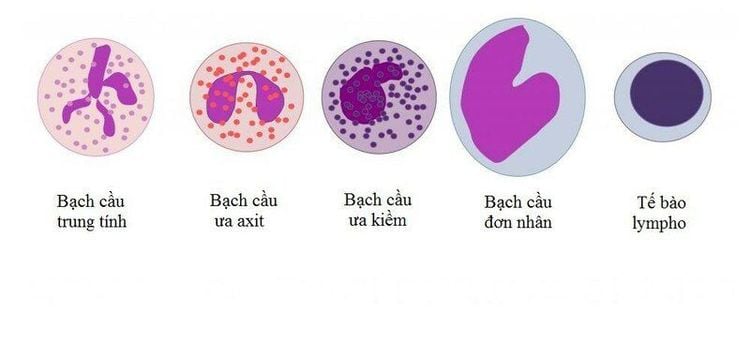
Monospot testing is often ordered at the same time as a complete blood count analysis. Thereby, the number of white blood cells will be examined whether there is an increase and whether there is a significant increase in the number of reactive lymphocytes. Therefore, mono is characterized by the presence of predominantly atypical white blood cells.
If the initial monospot test is negative but the clinician still suspects the disease, a repeat monospot test should be done after a week or so to determine if antibodies have been detected. production or not. If the monospot test remains persistently negative, a specific test for EBV antibodies may be used instead to help confirm or rule out the presence of EBV infection. A streptococcus test may also be ordered at the same time as a monospot test to determine if a patient's sore throat is a strep throat (group A strep infection) substituting for or superimposed on leukemia. single demand.

Viêm họng do liên cầu khuẩn (nhiễm trùng liên cầu nhóm A)
3. When is a monospot test indicated?
Monospot testing is ordered primarily when a person, especially an adolescent or young adult, has symptoms that the examining physician suspects is due to mono. Symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for a cold or flu infection. Some common signs and symptoms of mononucleosis include:
Fever Headache Sore throat Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits General muscle weakness or fatigue Some people may experience signs Other signs and symptoms such as:
Abdominal pain Enlarged liver Spleen Enlarged Rash

Người bệnh xuất hiện các cơn đau đầu
4. What do monospot test results mean?
A positive monospot test along with an elevated white blood cell and reactive lymphocyte count on the smear as well as the presence of symptoms associated with mononucleosis suggests diagnostic potential. This diagnosis is quite high.
In contrast, a negative test requires more careful interpretation. If the patient has symptoms and a reactive lymphocytosis but the monospot test is negative, it may still be too early to detect antibodies. Another explanation could be due to encountering one in a very small percentage of people who do not make antibodies. Even so, this test may be repeated afterwards and/or a specific test for EBV antibodies may be performed to help confirm or rule out the diagnosis of mononucleosis.
The truth is that most infants and young children are not yet able to synthesize antibodies. Therefore, the monospot test on these subjects would be negative even with EBV infection. This population is rarely tested, however, because they often have no symptoms of mononucleosis.

Kiểm tra sức khỏe định kỳ là việc làm cần thiết
Persons with a negative monospot test and few or no reactive lymphocytes should be alerted to the possibility that the condition may be infected by another microorganism that causes similar symptoms, such as sepsis. cytomegalovirus or toxoplasmosis. If an infection occurs during pregnancy, it is important to determine the cause because several other infections are associated with pregnancy complications and damage to the fetus. In addition, strep throat should also be identified for prompt antibiotic treatment. Because EBV is a virus, it cannot be treated with antibiotics.
On the other hand, the monospot test, although quick and easy to perform, is specific for antibodies in general rather than for EBV. Accordingly, this test may also be positive in people with lymphoma, lupus erythematosus, and some gastrointestinal cancers, although it is not used as a diagnostic or screening tool for these conditions. this state.
Furthermore, when the monospot test is negative and the physician cannot rule out EBV infection, repeat tests or in combination with specific testing for EBV antibodies should be indicated. These tests can show whether a person has EBV because of a recent infection, has been infected with EBV in the past, or has had a reactivated EBV infection. At the same time, the number of antibodies will decrease after the sixth week of illness and the monospot test will become negative when the infection is resolved.
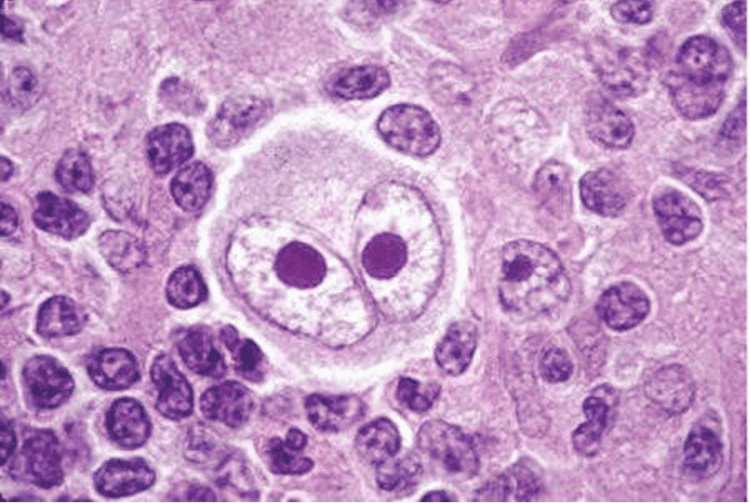
Ung thư hạch có thể làm xét nghiệm monospot dương tính
In summary, the symptoms of mononucleosis can still be resolved with supportive measures, such as rest and plenty of fluids, to improve the overall condition in one to four months. However, the monospot test to confirm the disease is extremely necessary to not only confirm the disease, provide active supportive treatment, prevent complications, but also help raise awareness to prevent spread to those around. around.
References: medlineplus.gov
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
MORE:
Diagnosis and treatment of EBV virus What disease does EBV virus cause? How to classify white blood cells?