This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Resident Doctor, Master Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalLymph node TB is a mild form of tuberculosis, which is less dangerous to the patient's life and has good treatment results if it is diagnosed early, treated promptly and on principle, leaving no sequelae.
1. What is lymph node tuberculosis?
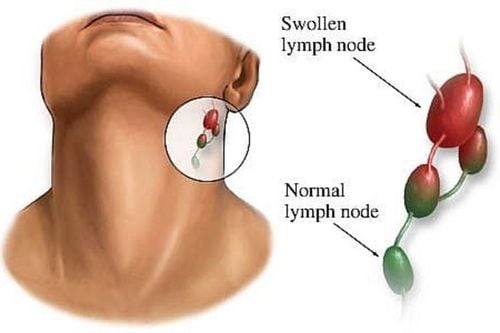
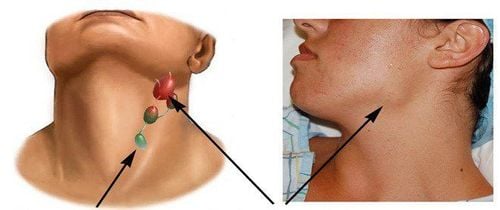
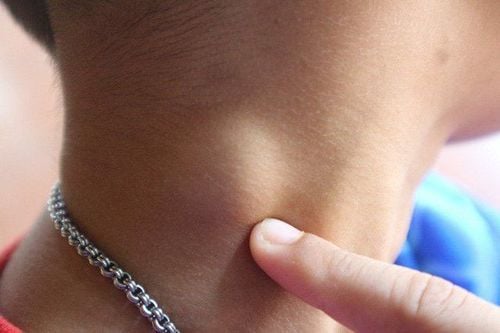
Lymph node tuberculosis is a fairly common type of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually occurs in the neck, armpits, and groin. The cause of the disease is caused by tuberculosis bacteria entering through the pharynx, Amydal disease spreading to the lymph nodes, or TB bacteria spreading to the lymph nodes from a tuberculosis cluster from the primary stage through blood, lymphatic routes, or access routes. There are many types of lymph node TB such as:Tuberculosis of the bean: The most common form Tuberculoma: A solitary, large, dense, painless, sclerotic tuberculous tuberculoma. Inflammation of many lymph nodes: Common in people with HIV/AIDS with inflammation of many lymph nodes in the whole body. Tuberculosis associated with tuberculosis in other organs: Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes can be associated with primary infection, membranous tuberculosis or pulmonary tuberculosis... Symptoms of lymph node tuberculosis are usually gradually enlarged, painless, density is slightly firm, The face is smooth, not hot, the lymph nodes are swollen, the skin is not red. Often there are many swollen lymph nodes, gathered in a chain, but sometimes only a single lymph node is swollen and painless. However, TB lymph nodes can develop through the following stages:
First stage: The lymph nodes begin to swell, the lymph nodes are irregularly large and small, not yet attached to each other and mobile. Later stage: The lymph nodes can stick together to form plaques, or stick to the skin and surrounding tissues, restricting mobility. The stage of molting: The lymph nodes will gradually soften, the skin of the lymph nodes will be red, not hot and painless. In case of purulent lymphadenitis, it is easy to rupture. In people infected with HIV/AIDS, if they have tuberculosis, they will have symptoms of systemic lymphadenopathy accompanied by prolonged diarrhea, candidiasis, shingles, .. in the skin.
2. What diagnostic methods should be done when lymph node tuberculosis is suspected?
When lymph node tuberculosis is suspected, the patient will need to do the following methods to diagnose lymph node TB:Lymph node aspiration : This is the first test in diagnosing peripheral TB. Cases of large peripheral lymph nodes need to aspirate lymph nodes for testing. Diagnosis of peripheral lymph node tuberculosis through fine needle aspiration gives 70-90% accuracy. In addition, TB bacteria can also be found in lymph node aspiration specimens by culture or direct endoscopy. Lymph node biopsy: This is an important test in the diagnosis of lymph node tuberculosis. The lymph node biopsy showed a typical tuberculous cyst. However, lymph node biopsy is a complicated technique, so using this method when aspiration lymph nodes does not give diagnostic results. Mantoux reaction: In lymph node tuberculosis, the Mantoux reaction is often strongly positive, so it is an important sign in the diagnosis of lymph node tuberculosis and in differential diagnosis with Hodgkin's disease, lymphoma... Lymph node tuberculosis is secondary TB, so a chest x-ray is required to detect lesions. Lymph node ultrasound: This method is used to assess the nature of the lymph nodes, the size and size of the lymph nodes.... Immunoassay: The tests commonly used to diagnose tuberculosis are the lymphocyte transformation reaction and the suppression reaction. macrophage migration mechanism. Screening or culture: Look for TB bacteria by direct smear or culture through lymph node aspiration or lymph node biopsy.
3. Treatment of lymph node tuberculosis

Medical treatment:
Combination of anti-TB drugs, at least 3 drugs or more. The attack phase should use a combination of 3 to 4 anti-TB drugs, the maintenance phase should use 2 anti-TB drugs. The duration of treatment for lymph node tuberculosis must last 9-12 months because of the recurrence or recurrence of lymph node tuberculosis. In case of nodal TB in HIV/AIDS patients, it is recommended to use a combination of 4 anti-TB drugs RHZE in the active phase, then 2 anti-TB drugs should be used in the consolidation phase. The total duration of treatment lasts from 9 to 12 months to prevent recurrence of lymph node tuberculosis. Surgical treatment:
If the lymph nodes are swollen, purulent and likely to burst, pus should be extracted to avoid bad scars. After the incision and curettage, combined with local treatment by sprinkling isoniazid powder or 1% rifampicin solution daily until the wound is dry. widen the fistula, drain the pus and treat it locally and combine anti-tuberculosis drugs as above. In case the lymph node is too large and puts pressure on surrounding tissues (blood vessels, nerves, etc.), it is necessary to remove the lymph nodes but not to damage blood vessels and nerves. Do not aspirate lymph nodes because it is easy to create a fistula along the needle line. In the case of lymph nodes enlarged, molten and leaking pus, treatment should be combined with anti-tuberculosis drugs with corticosteroids, combined with drainage of pus. Lymph node TB is a mild form of tuberculosis, less life-threatening to the patient and treatment has a high cure rate of over 90%. However, it is difficult to predict the course of tuberculous lymphadenopathy because lymph nodes continue to enlarge or appear new nodes despite treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment of lymph node tuberculosis at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.