Article by MSc, Dr. Mai Vien Phuong – Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Doctor, Department of General Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Central Park International Hospital
Nausea can be accompanied by hypersalivation and appetite loss to certain types of food. While these symptoms are generally not dangerous when occurring occasionally, frequent episodes may indicate an underlying medical condition. So, how can nausea and hypersalivation be managed?
1. What causes salivation and nausea?
Several medical conditions can cause nausea and hypersalivation. Some require immediate medical attention, while others can be addressed through routine medical consultations.
1.1 Constipation
Constipation is a digestive condition characterized by infrequent and painful bowel movements. Common symptoms include painful defecation, hard stools, and a sensation of incomplete evacuation.
Studies have shown that nausea is a common symptom of chronic constipation. Other related symptoms include heartburn and difficulty swallowing, both of which can trigger increased salivation.
1.2 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome refers to a group of gastrointestinal symptoms leading to chronic abdominal discomfort. This condition may result in chronic constipation, diarrhea, or both. Research indicates that nausea, often accompanied by excessive salivation, is a common symptom, along with bloating and abdominal distension.
1.3 Food Poisoning
Food poisoning is a bacterial infection affecting the gastrointestinal tract. Nausea is one of the earliest symptoms of food poisoning. Other symptoms include fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. Patients with food poisoning must seek immediate medical care.
1.4 Gastritis
Gastritis refers to acute or chronic inflammation of the stomach lining. Nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain are the primary symptoms of this condition. Frequent episodes of nausea and vomiting can lead to increased salivatio
1.5 Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers refer to sores that form in the stomach, esophagus, or intestines. They often cause a burning pain ranging from mild to severe across the chest and abdomen. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, indigestion, and blood in the stool. Similar to other gastrointestinal conditions, nausea can lead to hypersalivation.
1.6 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Acid reflux can cause nausea, difficulty swallowing, and hypersalivation. Other symptoms include heartburn, a bitter taste in the mouth, and regurgitation of food or fluids.
1.7 Esophagiti
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus, the tube connecting the mouth to the stomach. In esophagitis, inflammation may make swallowing difficult, leading to drooling or hypersalivation
Several causes of esophagitis, including GERD, medications, or infections, can result in nausea and hypersalivation. Untreated esophagitis may require medical intervention.
1.8 Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a condition causing difficulty swallowing. Hypersalivation is a common symptom of dysphagia. Other symptoms include pain or discomfort while eating. Some medical causes of dysphagia may trigger nausea, worsening hypersalivation. If dysphagia leads to choking or breathing difficulties, immediate medical care is necessary.
1.9 Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious diabetes complication that occurs when the body breaks down fat into ketones for energy due to insulin deficiency.
DKA requires immediate medical care. Visit the nearest emergency room if you experience nausea and vomiting accompanied by:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Rapid breathing
- Elevated blood glucose and ketone levels
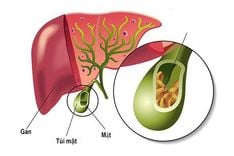
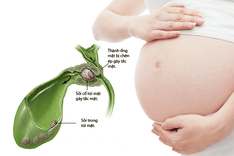
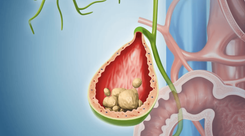
- Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits formed in the gallbladder due to excess cholesterol in bile. Untreated gallstones may cause acute cholecystitis, leading to nausea and vomiting.
1.10 Mumps
Mumps is a viral infection that affects the salivary glands, causing them to swell. Mumps can make swallowing difficult, leading to hypersalivation. The condition may also cause pancreatitis, leading to nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Other symptoms include fever and body aches
1.11 Stroke
A stroke is a life-threatening condition where blood flow to the brain is obstructed. Stroke can cause hypersalivation, making it one of its possible symptoms.
Seek emergency medical care immediately if you notice stroke symptoms such as:
- Drooping eyelids, numbness, or weakness on one side of the body
- Slurred speech
- Nausea
- Headache
- Dizziness
1.12 Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer can arise from two types of cells in the pancreas. Nausea is a common symptom of pancreatic cancer, which can also increase gastric acid secretion, leading to hypersalivation.
Other symptoms include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
1.13 Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety can lead to several gastrointestinal symptoms. Nausea is a common symptom of anxiety. Other associated symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Indigestion
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
Excessive anxiety can also contribute to IBS or stress-induced ulcers, both of which may cause hypersalivation.

1.14 Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas produced during fuel combustion. Carbon monoxide poisoning can be fatal. Common symptoms include:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Vomiting
Carbon monoxide can cause neurological damage, potentially triggering hypersalivation.
1.15 Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance occurs when the body lacks lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose. Symptoms typically appear shortly after lactose consumption and include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Bloating
- Gas
1.16 Prescription Medications
Research shows that nausea and hypersalivation are potential side effects of many medications. Treatment for hypersalivation and nausea depends on the underlying cause. Some conditions require emergency care, others can be managed at a doctor’s office, while some may be treated at home.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, carbon monoxide poisoning, stroke, and gallstones are all serious conditions that require immediate medical attention. If you or someone else experiences nausea, hypersalivation, and other common symptoms of these conditions, call emergency services immediately.

2. Comprehensive Treatment for Nausea and Hypersalivation
For gastrointestinal infections such as food poisoning, gastroenteritis, and certain peptic ulcers, antibiotics may be prescribed. Conditions such as gastritis, GERD, and esophagitis can be managed through a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications.
- Dysphagia is commonly seen in elderly individuals who require round-the-clock care.
- Mumps, caused by a viral infection, necessitates rest, hydration, and supportive care.
- Pancreatic cancer requires specialized medical approaches from a team of healthcare professionals, while generalized anxiety disorder may need intervention from mental health specialists.
If hypersalivation and nausea impair your quality of life, consult a physician. Various diagnostic tests can help determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment.
In reality, numerous causes can lead to hypersalivation and nausea. In most cases, hypersalivation is triggered by nausea rather than being a standalone condition. However, some neurological or physical conditions affecting the oral cavity may also present with nausea.
If nausea and hypersalivation persist for an extended period, patients should seek medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and tailored advice. Self-medication is strongly discouraged, as it may cause unwanted side effects and exacerbate the condition.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a trusted healthcare facility with highly skilled doctors and modern equipment. For any health concerns, patients are encouraged to visit the hospital for comprehensive care.
For more health, nutrition, and beauty tips, visit Vinmec International General Hospital to safeguard the health of yourself and your loved ones.
To schedule an appointment at the hospital, please contact the HOTLINE or book directly HERE. Download the MyVinmec App to manage, track, and schedule appointments conveniently anytime, anywhere.