This is an automatically translated article.
Pap smear or Pap test is the simplest way to screen for cervical cancer. Through smears and observations, a woman can be detected early and increase her chances of treatment. An abnormal Pap test result tells you a lot about your risk of cervical cancer.
1. What is a Pap test?
A Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, is a test that doctors use to screen for cervical cancer in women. Through the Pap smear, the doctor can observe changes in the cells of the cervix, predicting the risk of turning into actual cancer later on.
The Pap test is quite simple, done as an outpatient at the gynecologist's office, it only takes about 10 to 20 minutes and then you can go home.
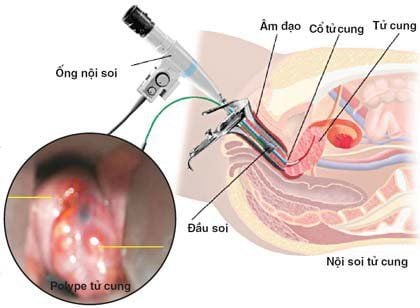
To do the Pap test, the patient is instructed to lie on a table with their legs apart, firmly resting on the stirrups. The vagina needs to be enlarged with a special metal instrument called a "speculum". Through it, the doctor can observe the cervix and use a cotton swab to take a local cell sample. The specimen will be placed in a small vial, containing a preservative, and sent to a laboratory for analysis under a microscope.
Pap test has absolutely no complications or harm to the patient. However, in some women who are overly sensitive, the PAP test can sometimes cause mild discomfort or a little stress. Therefore, it is extremely necessary to explain how this test is performed and the necessary meaning of this test to the patient before performing it.

Xét nghiệm Pap là một kiểm tra mà bác sĩ sử dụng để tầm soát ung thư cổ tử cung ở phụ nữ
2. What is an abnormal Pap test result?
Pap test results will be sent back within a few days, either negative or positive.
With a negative result, this is actually a good thing. This means that the doctor did not find any foreign cells in the smears on your cervix. You can rest easy until your next Pap test is scheduled.
With a positive result, this does not mean you have cancer. Depending on the grade, the results of the Pap test will be analyzed differently. Patients need to be specifically explained by the doctor for each case as well as a follow-up plan.
2.1. Abnormal Low-Risk Pap Test The most common cause of an abnormal low-risk Pap test is an HPV infection. This is a very common sexually transmitted virus. Up to 8 out of 10 people contract this germ in their lifetime without even knowing it.
The time when you may have been infected with the virus is as recently as many months or years ago. However, if you are completely healthy, you will be able to clear the infection and your Pap smear will return to normal. In fact, most women clear the HPV infection in one to two years. However, in a very small number of women, the HPV infection is not cleared and remains in the cervix. In these subjects, there is an increased risk of abnormal progression to cancer in the following years if left untreated. Therefore, you should be followed up with a repeat Pap smear to make sure an infection has been ruled out. If the results are still abnormal, you will be advised to have more advanced testing than colposcopy.
Colposcopy is in principle the same as a Pap smear through the placement of a speculum. However, this technique needs to be performed by a gynecologist and uses a colposcope.
Colposcopy is the next step of the Pap smear to confirm if the result is indeed a low-risk abnormality. If that's the case, you won't need any treatment and will continue to be monitored every year until your Pap smear results come back normal.
However, although rare, colposcopy sometimes reveals high-risk abnormalities. At this point, you may need to have a biopsy and/or start the right treatment.
2.2. High-risk abnormal Pap test This result doesn't mean you have cancer, but it's important, because it's very likely that you've had HPV for a long time and developed cancer in subsequent years if Untreated.
The next best thing to do is to have a colposcopy. If colposcopy results still confirm that high-risk abnormal cells are present, a cervical biopsy is the next step. And this is also the last test to do, the "gold standard" of cancer diagnosis.
Conversely, if colposcopy shows only low-risk abnormal cells, you will not need a biopsy.
2.3. Pap Test Abnormal Gland and Squamous Cells The glandular cells of the cervix are located mainly in the cervical canal while squamous cells are located on the outside of the cervix. As with changes in cervical cells in general, abnormalities in glandular and squamous cells are primarily caused by HPV infection and are associated with an increased risk of progression to cancer. Therefore, in these women, treatment should be initiated to prevent malignancy.
However, prior confirmation is also required by colposcopy and/or biopsy.
3. Who should get a Pap test?

Hầu hết các phụ nữ trong độ tuổi từ 21 đến 65 đã lập gia đình hay đã có hoạt động tình dục nên được xét nghiệm Pap mỗi 3 năm/lần
Most women between the ages of 21 and 65 who are married or sexually active should have a Pap test every 3 years.
You may need more frequent screening if:
Have an immediate family member with cervical cancer or cancers in general Ever had an abnormal Pap test result Immunocompromised or positive HIV Your mother used diethylstilbestrol (a synthetic estrogen) while pregnant with you. During pregnancy, a woman can still have a Pap test, and even have a colposcopy if indicated. There is no risk of harm to the fetus, but if the results are abnormal and require treatment, it will be delayed until the baby is born.
In summary, cervical cancer is a very common cancer in women. To screen for this disease, it is necessary to have regular Pap tests combined with a general examination. This is the simplest way to help detect the disease early and treat it promptly, preventing disease progression from becoming complicated.
Besides, the proactive vaccination against cervical cancer also helps women reduce the risk of the best disease.
Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, there are two vaccines against HPV virus that cause cervical cancer in women, including Gardasil 0.5ml (provided by MSD-USA) and Cervarix (provided). issued by GSK-Belgium). These two vaccines are given in 3 doses over 6 months for each patient.
The examination and vaccination process at Vinmec is always performed by a team of experienced doctors and medical staff. Along with that is the quality of vaccines and medical services, so customers can completely trust and feel secure.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.