This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Assoc. Dr. Dr. Huynh Thoai Loan - Head of Pediatrics - Neonatology Department, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.VA appears in children from birth, to 6 months of age, gradually developing according to the immune task. From 9-10 years old, the VA gradually atrophies and only traces are left in puberty. However, in many cases, children are exposed to too many pathogenic bacteria in the respiratory tract, causing VA to work too hard, which will lead to VA. What causes VA and what are the symptoms of acute and chronic VA?
1. What is VA?
VA is an acronym for the French Végétations Adénoides, which is an organization made up of many white blood cells. When breathing, air enters the nose, through the VA and then into the lungs. Normally, the VA is only about 4-5mm thick, does not obstruct the airway. The job of the VA is to recognize the bacteria to produce antibodies. Kill bacteria when they re-infest. These include: VA, tubal tonsils, pharyngeal tonsils, and tonsils of the tongue (called Waldeyer's ring), which surrounds the airways and the alimentary canal. All bacteria entering the nose and mouth must pass through the Waldeyer ring.White blood cells at the VA are responsible for waiting and "catching" bacteria. Cells have the ability to recognize and make antibodies. This antibody is replicated and spread everywhere, mostly in the nasopharynx. When bacteria re-enter, they will automatically neutralize the bacteria and kill it immediately.
2. Manifestations of acute and chronic VA
2.1. Acute VA usually occurs in children 6-7 months to 4 years of age, but can also occur in older children.VA disease develops acutely with the following symptoms:
Children have a fever, 38 - 39 degrees Celsius, sometimes fevers as high as 40 degrees Celsius. Nasal congestion, gradually worsening, stuffy on one side and then on both sides. Children have difficulty breathing, often have to open their mouth to breathe, snort, cry or speak in a closed voice... Children may stop sucking or suckle intermittently because they cannot breathe through their nose. Runny nose anteriorly and down the throat: runny nose at first clear then cloudy. Cough: usually appears later, on the second or third day. Children cough due to dry mouth because they often breathe through their mouth or because fluid flows down from the nasopharynx, causing sore throat. Children are tired, anorexia, fussy, bad breath. Possible digestive disorders: vomiting, diarrhea. Children can't hear.
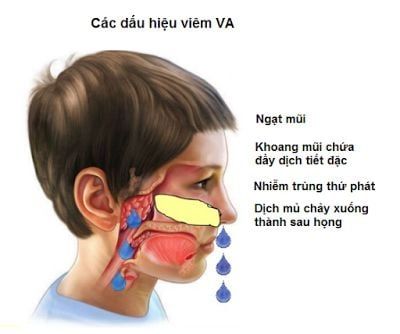
Acute VA often leaves no complications and often has the following manifestations:
The nasal passages and nasal passages collect nasal secretions, and the nasal mucosa is reddened. The mucosa of the throat is red, the back of the throat has nasal discharge from the top of the roof. Swollen mandibular lymph nodes 2.2 Chronic VA The disease occurs at a similar age but is the result of multiple episodes of acute VA.
Chronic VA disease, VA tissues have been fibrosis after many times of acute inflammation. At this stage, there are usually only 2 signs of a runny nose and a chronic stuffy nose:
Children have a clear or runny nose, or a runny nose with pus (superinfection). Runny nose is usually long-lasting. Nasal congestion has many levels, at least it's only stuffy at night, many are stuffy all day, even completely blocked nose. The child must breathe through the mouth, speak or cry in a nasal voice. If the inflammation is prolonged, the child is prone to severe cerebral hypoxia and may have more severe manifestations such as:
Retardation of physical and mental development, sluggishness, and lack of activity. Difficulty sleeping, grinding teeth while sleeping, snoring, restless sleep, often startled, bed-wetting. In severe cases, there may be episodes of apnea during sleep. Facial bone mass development disorder: children often breathe through the mouth, the nose is rarely used, so over the years the tip of the nose becomes smaller, the nose is flat, the forehead is protruding. The face is long, the upper jaw is protruding, the upper teeth are jagged, the lower jaw is narrow, the mouth is always open, the face is less agile. That is the typical facial expression of children with VA, a consequence of prolonged mouth breathing during the period of facial development.
3. What are the consequences of VA?
Nasopharyngitis: Prolonged VA causes the VA volume to increase, causing the child to have a stuffy nose. If the nose is blocked for a long time, the symbiotic bacteria in the nose will become disease-causing bacteria. Otitis media: A common complication of V.A. There are usually two types: Acute purulent otitis media is a complication of acute viral hepatitis and otitis media with serous or purulent pus is a complication of chronic V.A. Sinusitis Inflammation of the larynx and trachea. Bronchitis : After a few days of fever, runny nose and cough, the child has a higher fever, coughs more intensely, wheezing and fast, if severe, there may be signs of difficulty breathing, cyanosis. IBD .
4. Measures to prevent VA
Limit bringing children to crowded places, fragrant cheeks, coughing near children. Children on the road should wear masks to prevent dust and polluted air. Children should be given solid foods after 6 months, supplemented with vitamins and minerals. Give your child enough water to drink, especially before and after exercise. Fully vaccinated and on schedule for children, dry vaccines can be used to prevent respiratory infections. Children with nasopharyngitis should be treated immediately and definitively, avoiding serious complications, avoiding arbitrarily using drugs and abusing antibiotics indiscriminately. If the child has a high frequency of cough and runny nose, the child should be examined for otolaryngoscopy to evaluate the condition of the tonsils and VA overgrowth. The pediatric department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children. ,....With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.