This is an automatically translated article.
HIV is an infectious disease that affects the body's immune system, making patients susceptible to opportunistic infections due to immunosuppression. HIV develops through several stages, each with different characteristics. Recognizing HIV stage 1 disease helps to treat and prevent HIV infection more effectively.1. HIV exposure stage
HIV exposure stage is the period when newly exposed to an infectious source, at risk of getting HIV such as:
Unprotected sex: Through anal or vaginal without using condoms, orally do not use protective equipment (oral protection) with people infected with HIV, sexually assaulted... Sharing needles or equipment if injecting drugs. People who work in professions that may come into contact with infectious sources such as police, medical staff, etc. Get splashed with blood or body fluids of an HIV-infected person on damaged skin or on the body. into mucous membranes such as eyes, nose, throat... What to do when exposed to HIV?
If the body has bleeding wounds, it is necessary to immediately wash the wound under running water, let the wound bleed for a short time, then repair it thoroughly with soap, disinfect with antiseptic solutions for at least a short time. is 5 minutes.
If exposed through contact with mucous membranes: Flush with distilled water or 0.9% NaCL saline continuously for 5 minutes.
Through the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose: Wash with distilled water or 0.9% NaCL saline and rinse your mouth with 0.9% physiological saline several times.
Contact medical facility for anti-exposure treatment. Taking medicine immediately after exposure is important because it can prevent HIV infection. Post-exposure prophylaxis has been improved with success rates up to 95-99%. The effectiveness of treatment is highest in the first few hours after exposure, diminishes over time, and may not be effective after 72 hours of exposure.
Not every exposure to HIV (sexual or blood-to-blood contact with an HIV-infected person) will lead to HIV. Therefore, during this period, it is necessary to contact them to use post-exposure prophylaxis to reduce the risk of chronic HIV infection.
2. HIV stage 1
Stage 1, also known as the acute phase of the disease, symptoms occur about 2-4 weeks after exposure to the HIV virus. Stage 1: The HIV virus is multiplying and destroying the body's immune system.
Virus HIV đang nhân lên và phá hủy hệ thống miễn dịch của cơ thể
Symptoms may be mild, which the person may not notice. At this stage the virus is multiplying and spreading throughout the body. The possibility of HIV transmission during this time is highest because the amount of virus in the blood is very high. Signs of HIV disease stage 1: Symptoms can be easily confused with common viral infections.
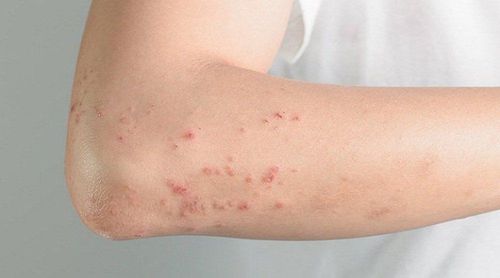
Fever and chills: Patient Mild fever from 37o5 to 38o, accompanied by chills is one of the most common HIV symptoms. Tired, sleepy. Body aches, headaches, joint pain. Sore throat: Pharyngitis causes difficulty swallowing and sore throat. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpit and groin. Red skin rash: The most common symptom of HIV infection within 2 to 3 weeks of being infected with the virus. Nausea, diarrhea Less common symptoms at this stage include: unexplained weight loss, thrush, thrush or infection, menstrual disorders in women.
3. HIV disease stage 2
This stage, also known as the latent stage, is the period when there are no symptoms.
Features of stage 2:
This stage can last for years without any symptoms. It is also possible that in some people there are limited symptoms associated with HIV infection during this period. During this stage the virus is in the body but does not attack the immune system, treatment during this stage is very important. At this stage, the disease is still contagious.
4. HIV disease stage 3
Or called end stage hiv disease, at this time the patient has AIDS ((Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)
This stage has the following characteristics:
Usually occurs many years after being infected When you have AIDS, your immune response is very weak and you lose the ability to fight infections. Symptoms in this stage are very different, mainly showing opportunistic infections... Treatment in this stage The disease is more difficult, but there is still a cure. The main treatment is antiviral and opportunistic diseases. At this stage, the patient can still infect others. End stage disease related to immunodeficiency and opportunistic diseases, may have the following manifestations:
The patient has prolonged fever, swollen lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss. mouth ulcers, oral thrush, respiratory infections, tuberculosis, meningitis, encephalitis caused by microorganisms... Chronic diarrhea Skin rash, folliculitis... Fatigue, difficulty concentrating ,
5. How to prevent HIV?

Phòng ngừa HIV bằng giáo dục tình dục lành mạnh, tình yêu chung thuỷ, hạn chế số lượng bạn tình
Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases
Healthy sex education, faithful love, limiting the number of sexual partners. Practice safe sex, use a condom, or a mouthguard when having vaginal, oral, or anal sex. Blood-borne prevention
HIV testing of all transfused blood samples using the most reliable technique. Blood products are subject to rigorous HIV testing. Organizations selling blood products must have a certificate that the product has been tested for HIV. Do not use shared syringes. Complying with the principle of sterilization in medical practice, needles and syringes are used only once. Educate and prescribe the principles of sterilization for professional tools such as tattooing, ear piercing. Test and carefully screen the donor of semen and organs. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission
Antiviral drug treatment for mothers Prophylaxis for children after birth It is recommended to have a cesarean section and not breastfeed after birth. Treating HIV in its early stages brings many benefits to patients. Above are the characteristics and symptoms of each stage of HIV disease. If there are signs or there is a risk of exposure to HIV, it is advisable to proactively do early screening tests to give patients the opportunity to prolong life.
Package of Social Diseases Examination and Screening of Vinmec International General Hospital helps customers to screen for social diseases in order to detect diseases early for effective treatment and avoid complications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.