This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Gastroenterology - Endoscopy, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a common, recurrent disease with a high risk of complications if not detected and treated aggressively. Gastroesophageal reflux disease is classified into many levels to facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of the disease more effectively..
1. What is Gastroesophageal Reflux?
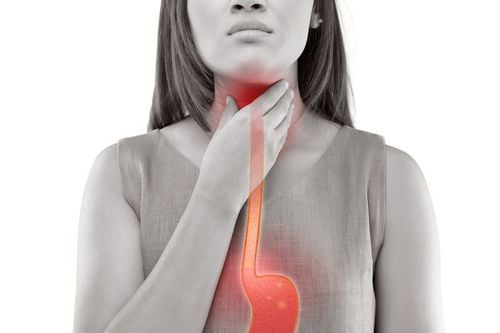
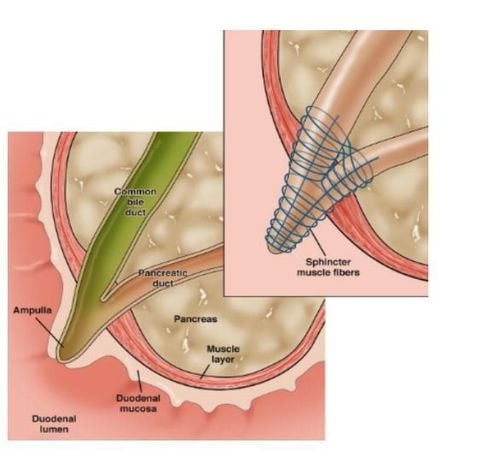
Gastroesophageal reflux is a condition in which gastric juice flows back from the stomach into the esophagus. Common signs of acid reflux are belching, heartburn, burning pain in the epigastrium, difficulty swallowing, discomfort in the chest, burning neck, stomach cramps, feeling bitter liquid flowing into the mouth. ,... If gastric juice gets into the airway, the patient may experience hoarseness, loss of voice, cough, even difficulty breathing.
Risk factors for the disease include: Eating certain foods causes the lower esophageal muscles to relax causing reflux; or complications of acute or chronic gastritis.
Gastroesophageal reflux can lead to unpredictable complications such as: Chronic esophagitis, esophageal cancer (the most dangerous complication), esophageal tumor and loss of voice,... Therefore, the diagnosis is developed. Early detection and aggressive treatment are effective methods to control gastric reflux, avoiding the risk of dangerous complications.
2. How many levels of gastroesophageal reflux?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease progresses in different levels. The division of levels helps to specifically assess the patient's condition and have a more effective treatment plan. Accordingly, the disease is usually classified into 5 levels:
Gastroesophageal reflux, grade 0; Gastroesophageal reflux grade A; Gastroesophageal reflux grade B; Gastroesophageal reflux degree C; Gastroesophageal reflux grade D.

3. Characteristics of each grade of gastroesophageal reflux
3.1 Level 0 At level 0, gastric acid reflux with little frequency, not much impact on the esophagus, does not cause esophagitis. Patients may present with symptoms such as belching, heartburn infrequently, easily confused with normal physiological phenomena.
3.2 Grade A This is a new stage of disease, the esophageal mucosa has shown signs of damage but the level is still mild. Grade A gastroesophageal reflux disease is the most common grade that patients find out. About 90% of patients are diagnosed at this stage.
Patients with grade A gastroesophageal reflux have symptoms: Burning behind the sternum, choking behind the breastbone and heartburn. Although it is possible to choke, it is perfectly normal to drink water or swallow food.
With proper treatment, the disease can improve quickly. In the absence of detection and treatment, the patient will have more sour mouth feeling, burning in the oropharynx, accompanied by symptoms of cough, difficulty breathing and bronchial edema due to inhaling a lot of refluxed gastric juice. .
3.3 Grade B At this level, gastric reflux has appeared inflammation, mucosal erosions with a length of more than 5mm, which may converge close together or scattered in the gastric mucosa, food manage. Patients in this stage present with pain when swallowing. At the same time, because the frequency of contact between the refluxed acid and the esophageal mucosa is very large and frequent, the ulcers are painful, difficult to swallow, and create a feeling of entanglement and choking when eating. The patient's feeling of difficulty in swallowing will gradually increase because the esophageal mucosa is edematous, which when healed will leave scars, narrowing the esophagus and increasing the sensation of difficulty swallowing, even with soft foods and causing burning pain. neck. In addition, the patient also has a dull pain in the abdomen (above the navel), the pain occurs both when hungry and when full.

3.4 Grade C At grade C, gastroesophageal reflux causes Barrett's esophagus. This is a condition in which the color and composition of the cells lining the lower part of the esophagus are changed due to repeated exposure to refluxed stomach acid. Erosions on the lining of the stomach and esophagus concentrate into larger ulcers. Patients with Barrett's esophagus often have heartburn, difficulty swallowing, abdominal burning, nausea, vomiting blood, chest pain, black stools, ... This condition usually occurs in the elderly but It can occur at any age and men are at higher risk of Barrett's esophagus than women.
3.5 Grade D This is the most dangerous grade of GERD. At this level, Barrett's esophagus metaplasias into a collection of scars and deep ulcers with extensive damage. Patients have symptoms of heartburn, heartburn, nausea, ... constantly and often tired, sluggish. At this stage, the risk of cancer is very high and it is necessary to do tissue tests to get an accurate conclusion.
4. Note when treating gastric reflux
Depending on the patient's condition and the stage of disease development, each patient will have an appropriate treatment plan. Specifically, gastroesophageal reflux disease at stage 0 is often difficult to detect, easily confused with other diseases, so it is not promptly treated. Therefore, the best treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease will be at grade A. At this stage, the damage caused by the disease is not much because the disease has just started, so the thorough treatment is not too difficult. It is important that patients need to go to reputable medical facilities to be examined and have an appropriate treatment plan.
Note when performing gastric reflux treatment:
Follow the doctor's treatment regimen, take prescription drugs, do not arbitrarily use drugs without consulting the treating doctor and do not self-medicate. increase or decrease the dose as well as the duration of drug use; Have a scientific diet, prioritize foods that are good for the stomach and limit foods that can irritate the stomach; Exercise regularly, build a healthy lifestyle and avoid using stimulants such as alcohol, beer or tobacco.
Gastroesophageal reflux can be completely treated if detected early and intervened in time. Therefore, when there are warning symptoms of this pathology, the patient should go to the doctor soon for an accurate diagnosis and a positive and effective treatment plan.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.