This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor Le Thu Huong - Rehabilitation Doctor, High-Tech Unit for Treatment of Cerebral Palsy and Autism - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Urinary incontinence is a part that greatly affects the quality of life of patients and their families. Urinary disturbances also lead to urinary tract infections, kidney failure, and may give rise to reflex sympathomimetic attacks (AD attacks) that lead to paroxysmal hypertension, decreased heart rate, and headaches, which can lead to to cerebrovascular accident in people with lesions D6 and above. Therefore, urinary control and urinary tract care are an important part of the care of patients with spinal cord injury.
1. Common urinary disorders
In the stage of spinal shock immediately after the injury, the bladder is reduced (loss of reflexes), after the shock exit, depending on the location of the injury, the extent of the injury, the bladder will have different manifestations of disorders:1.1. Symptoms related to urine storage (filling phase)
Urination Urgenturia Nocturia Frequent urination Sensory disturbances: decreased sensation, loss of sensation, increased sensation, urgency to urinate, bladder pain
1.2. Symptoms when urinating (ejection phase)
Hesitancy to urinate Weak stream Urinary frequency Intermittent Urination Difficulty urinating, urinary retention Long urination

Tiếu khó là triệu chứng của rối loạn tiểu tiện
1.3. Symptoms after urinating
Feeling of not emptying urine Drip after urinating Among these manifestations, urinary retention and urinary leakage, incomplete voiding are the most common symptoms.
2. Causes of urinary disorders
Normally, urine is produced from the kidneys, through the ureters 2 ureters down, stored in the bladder. A normal person has a bladder capacity of 400-600ml. When the bladder is full, the sensory endings that transmit sensory information along the S3 cord to the spinal cord and the sphincter in the bladder neck are opened.
Simultaneously, from the spinal cord signals to the pons, then to the cerebral cortex. If the environment is right (subject to individual preferences), the pons will send a signal to allow the external urethral sphincter to open and urination will take place smoothly.
In patients with spinal cord injury, due to loss of nerve signal transmission between the spinal cord and brain, or in some cases damage to the spinal cone (ponytail), the signal between the bladder and spinal cord is also impaired. affect, leading to the following 8 types of bladder and bladder sphincter disorders:
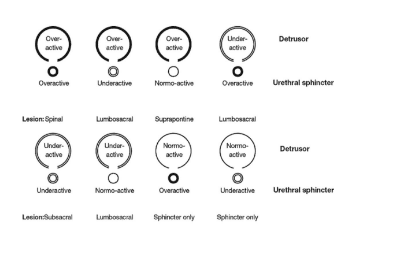
Nguồn ảnh: cambridge.org
3. Urinary tract care in patients with spinal cord injury
3.1. Urinary catheterization
After spinal cord injury, most patients can't urinate completely on their own, most of them have urinary retention, urinary leakage, and incomplete urination. And these patients often have indications for catheterization.
Commonly used catheters and pros and cons:
Urinary catheterization
This catheter is indicated in the acute period after trauma and should be removed as soon as possible after the patient is stable. In addition, catheterization is also used in the acute episode of urinary tract infection to drain urine continuously during this time. Urinary catheters cannot be placed for a long time due to the risks of urinary tract infections, pain, bladder bleeding during movement, bladder stones, and inconvenience in daily activities
Clean Intercontinental Catheterization (CIC)
An hourly catheter is used to collect urine with a clean catheter (usually a Nelaton catheter).
Advantages: Compared with catheterization, intermittent catheterization shows superiority in being independent in daily activities. Instead of constantly wearing catheters and urine bags like catheters, patients will use catheters at regular intervals, just like the average person goes to the bathroom every hour. Intermittent urinary catheterization helps to get all the urine in the bladder in the most physiological way like a normal person, limiting urine leakage, being proactive in daily activities, not causing the bladder to shrink like a urinary catheter, Limit bladder stones, limit the possibility of urinary infections. Depending on the patient's ability to urinate, residual urine volume, patients have indications for intermittent catheterization with different times: Normal people: V residual urine < 50ml
If < 70ml – Do not insert Urinary catheter 70-100ml: consider catheterization 1 time/day 100-200ml: 1 time/day: preferably in the evening before going to bed to get a better night's sleep. 200-300ml: 2 times/day in the morning when waking up and in the evening before going to bed 300-400ml: 3 times/day >400: 4-6 times/day Cons: like other types of urinary catheters, through Intermittent urination can cause urinary tract infections, urethral damage, and very rarely bladder perforation. To avoid these disadvantages, patients need to comply with the regulations of urinary catheterization, applying gel (water-soluble gel - KY) Urinary catheterization on the pubic bone
Is an option for patients with urinary disorders and spinal cord injuries. where intermittent catheterization is not possible, e.g. patients with urethral injury, difficulty moving both arms (cervical trauma patients). Advantages: longer circulation time than urinary catheter, less bleeding when moving, can change the catheter on its own
Cons: risk of urinary tract infection, bladder shrinkage, bladder stones
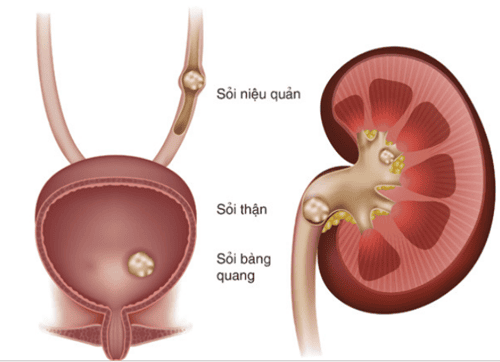
Đặt ống thông có thể gây sỏi bàng quang
3.2. Rehabilitation
For urinary disorders due to neurological causes, catheterization is the most optimal measure to protect the urinary tract. In addition, at the rehabilitation center, patients can participate in some treatment and intervention measures to improve the problem of urinary disorders.
These measures improve the function of the bladder and urethral sphincter, improve the ability to urinate, alleviate disorders, such as dysesthesia, bladder pain, urinary retention, leakage. urinating, which can improve quality of life:
Strong pelvic floor exercises for patients with urinary leakage due to weak urethral sphincter, weak pelvic floor muscles Bio-feedback exercises improve motor function of the sphincter and perineal muscles. Electroneurostimulation exercise improves the activity of the bladder wall muscles, the urethral sphincter and regulates bladder-sphincter activity, improves sensory disturbances, relieves bladder pain
3.3. Diet and other care
Drink a lot of water: Should drink about 2l of water / day, do not use carbonated water, should use more orange and lemon juice Increase the use of foods rich in Vitamin C Use drugs as prescribed by the doctor, do not arbitrarily Stop medication, stop catheterization without the doctor's consent. Keep a urine diary, check urine and urinary system regularly as indicated, measure urodynamics periodically with patients with indications Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination, consulting and service services. comprehensive and professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.