This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 10 years of experience working in the field of General Gastroenterology.1. What is abdominal lavage?
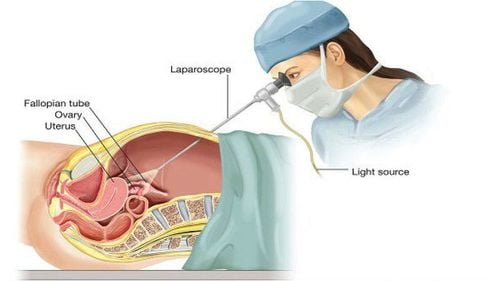
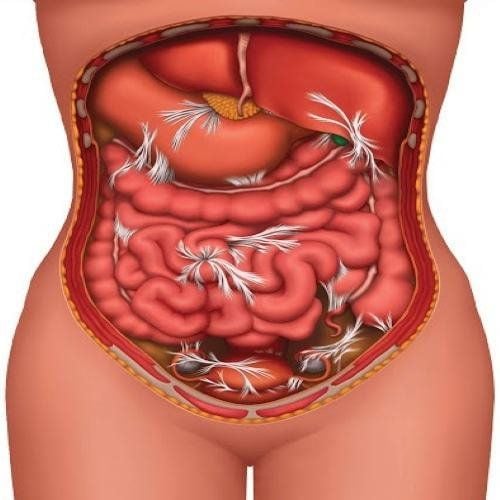
Abdominal lavage is an important step in many laparotomy techniques and even laparoscopic surgery, especially in operations where infection has spread from the initial site to cause inflammation of the surrounding tissues or throughout the cavity. belly. After surgical removal of the main cause of the disease, performing abdominal cleansing, removing infected tissues and surrounding abscesses carefully will help prevent inflammation from progressing, limiting the risk of infection. and other complications after surgery.
With appendicitis peritonitis surgery, after appendectomy, hemostasis, the operating team will pump isotonic sodium chloride saline to wash the peritoneal cavity, aspirate and clean if there is regional peritonitis. residence or all. Carry out aspiration several times at different locations in the abdomen, removing all the pseudomembranous membranes on the intestinal wall and between the bowel loops. Depending on the degree of intra-abdominal infection, the surgical team will decide to extend the time of intra-abdominal lavage. In surgery to suture gastroduodenal perforation, after suturing the perforation, abdominal lavage is an extremely important operation of the operation. Abdominal lavage will be combined with emptying of food and maximum possible pseudomembranous removal. The washing solution used is warm serum, the first washes may be diluted with betadine. After washing, wipe and pat dry with a large damp gauze.
2. The role of drain placement
Post-surgery drainage is placing a tube from an injured area or body cavity to drain blood, secretions, pus, gas,... out. Placement of a drain can serve a therapeutic or preventive purpose: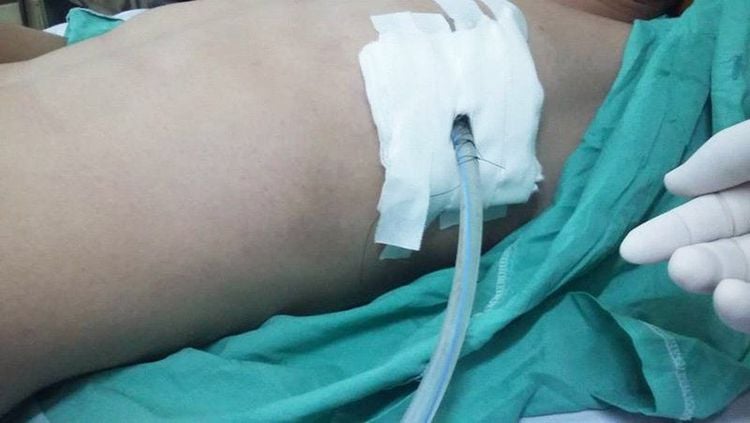
Treatment is indicated in localized peritonitis, generalized peritonitis, necrotizing pancreatitis, after cholecystectomy, after traumatic splenectomy, after suturing the bladder rupture,... Preventive drainage is used in cases such as: after partial pancreatectomy, partial rectal resection, after suture of perforation of peptic ulcer or duodenal apex. there is a high risk of leakage,... There are many types of drainage pipes with different sizes, shapes and materials. A suitable drain should be neither too hard nor too soft. A tube that is too soft can be flattened, while a tube that is too hard can damage tissues and organs of the body. The pipe surface should be smooth to minimize the risk of infection. The tube has a contrast line so it can be monitored during an X-ray.
The drain is usually kept until the fluid is drained, but it should not be kept for more than 72 hours.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Recommended video:Routine health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!