This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by MSc La Thi Thuy - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
The frequency of venous thromboembolism is high in the elderly, especially in elderly patients hospitalized. In the UK about 10% of hospital deaths are due to venous thromboembolism. About 25% of patients with symptomatic deep vein thrombosis leave leg ulcers (post-thrombotic syndrome).
1. Frequency of venous thromboembolism
The most serious complication of venous thromboembolism is pulmonary embolism. Mortality from pulmonary embolism is about 30% if left untreated. With appropriate treatment of pulmonary embolism, the mortality rate is about 2%. The diagnosis of venous thromboembolism is often delayed because the symptoms are not clear and the clinician is less likely to think about it.
Venous thromboembolism is common in the elderly, the incidence of new venous thromboembolism (including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) increases linearly with age in the 65-69 age group, in the United Kingdom about 1.3% to 1.8% and increases to about 2.8% to 3.1% in the 85-89 age group. In elderly patients with a history of VTE, the frequency pulmonary embolism rate 2% to 8% in one year. Diagnosis is often missed in the elderly and is sometimes diagnosed only after the patient has died.
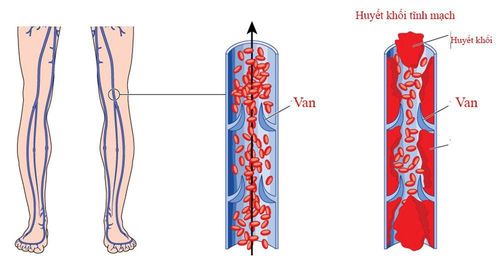
Thuyên tắc huyết khối tĩnh mạch có thể gây ra nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm
2. VTE risk factors
Risk factors for venous thromboembolism have long been diagnosed (table 1). Many risk factors are very common in the elderly, especially elderly patients who are hospitalized and have had orthopedic surgery (eg, immobilization, femur fracture, stroke, cancer). Hospitalization is a high risk factor for VTE (135 times higher than in the community).
The greatest risk of venous thromboembolism is in hospitalized medical patients, the rate is about 70% - 80%. In Europe, about one-third of postoperative patients develop VTE without prophylaxis.
Table 1: Risk factors for VTE
3. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis in elderly patients
One leg swelling is most common in the elderly; Calf pain is also occasional. Usually the patient has had orthopedic surgery, has a stroke, or has some other medical condition. Occasionally also experience anorexia, weight loss or other symptoms suggestive of cancer; however, most often there are no symptoms.
Clinical diagnosis is often difficult due to vague physical symptoms in the elderly. Patients may not complain of leg swelling due to dementia or speech disorders. Clinical diagnosis is based on swelling of one leg, warm skin, possibly with bulging superficial veins just below the skin. There may be pain in the calf area. Lower extremity swelling 2 cm larger than healthy limb should suggest deep vein thrombosis unless otherwise diagnosed.
Doppler ultrasound is used first for diagnosis with 96% sensitivity and 98% specificity in proximal deep vein thrombosis (from the popliteal vein upwards).
Contrast angiography is the gold standard for diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis, only used when clinical suspicion is high and Doppler ultrasound is negative. D-dimer (fibrin-degrading agent) has a good negative predictive value, used only in the diagnosis of exclusion in patients at low risk of DVT.

Dựa vào dấu hiệu lâm sàng, bác sĩ có thể chẩn đoán bệnh
4. Disease prevention
Many elderly hospitalized patients are at risk of VTE. Patients with stroke, pelvic fracture or orthopedic surgery are at high risk.
However the prevention rate is low even in western countries from 13% to 64%. Preventive treatment is particularly lower in medical patients. Preventive treatment reduces the risk of thromboembolism in many studies.
According to the recommendations of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP American College of Chest Physicians) can use LMWH or unfractionated heparin, fondaparinux for the preventive treatment of acute medical patients in hospital. Patients with contraindications can use compression stockings or intermittent compressions.
Many studies have shown that prophylactic anticoagulation reduces symptomatic VTE without increasing major bleeding compared with the control group.

Bệnh nhân thuyên tắc huyết khối tĩnh mạch rất dễ bị đột quỵ
5. Some points to note in the elderly in venous thromboembolism
Venous thromboembolism is an important cause of death and morbidity in the elderly. There have been many advances in diagnosis and treatment. Regardless of the progress in treatment, early diagnosis and close follow-up help reduce mortality and sequelae for the elderly.
Some summary points to note:
* Venous thromboembolism is an important cause of death in hospitalized patients and is more common in the elderly.
* Risk factors for venous thromboembolism are common in the elderly such as immobility, fracture, stroke.
* Elderly people who have had a stroke or have had orthopedic surgery but suddenly have difficulty breathing, chest pain, or fainting need to think about pulmonary embolism.
* Computed tomography of the pulmonary artery is the imaging technique that comes to mind first when pulmonary embolism is suspected.
* For the prevention and initial treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, the drug of first choice is low molecular weight heparin (commonly used today, enoxaparin).
* The elderly are more sensitive to the anticoagulant effects of warfarin.
* Many studies confirm an association between the degree of anticoagulant effect and the risk of bleeding.
* In patients with major pulmonary embolism, treatment includes thrombolytics and surgical embolectomy.
* Early diagnosis and careful follow-up during treatment will reduce mortality and morbidity due to venous thromboembolism in the elderly.

Khách hàng có thể đến Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec để được điều trị bệnh thuyên tắc huyết khối tĩnh mạch
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology. The hospital provides comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services, with a civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.