This is an automatically translated article.
Many patients go to the doctor and find out that they have vascular calcification without basic knowledge about this disease, so they are worried and do not know how vascular calcification affects their health, is it dangerous or not. ?1. What is vascular calcification?
Vascular calcification is the deposition of minerals such as calcium, which forms plaque on the walls of blood vessels. This phenomenon is also understood as hardening or atherosclerosis due to cholesterol deposition, or due to the aging process of the body, blood vessels lose elasticity with age.
The following factors are considered to increase the risk of vascular calcification:
Using stimulants such as tobacco, beer, alcohol, ... Sedentary, obesity, high blood pressure, often frequently consume fatty foods. Having high levels of substances in the blood such as lipids, cholesterol, triglycerides, blood sugar, etc. Being old, premature aging of blood vessels. Hormones in the body change during menopause. Due to genetics, someone in the family has early vascular calcification.

Bệnh béo phì gây nguy cơ cao mắc vôi hóa mạch máu
2. Is vascular calcification dangerous?
Vascular calcifications can occur in or in the middle of blood vessels. Depending on the location of the calcification, there will be different risks. At a severe level, calcification can impede the circulation of blood vessels, cause atherosclerosis, and lead to blockage of the lumen.
A person may not notice symptoms of calcified vascular disease until the following are present:
Heart attack, chest pain, myocardial infarction : The blood vessels calcify and harden, causing the blood vessels to harden. The heart must contract harder to pump blood. Blood clotting, increased risk of stroke: When plaque in the walls of blood vessels is shed, it can increase the risk of stroke, with symptoms such as dizziness, sudden weakness. Dementia: The risk of stroke caused by vascular calcification is associated with symptoms such as confusion, impaired speech and vision. Hands and feet are not supplied with enough blood: When the blood vessels are obstructed, the blood is not circulated well, causing pain or cramps in the legs, even when walking normally or climbing stairs. Renal failure: Vascular calcification is commonly found in patients with renal failure.
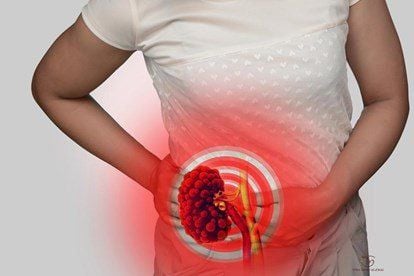
Vôi hóa mạch máu gây suy thận
3. Treatment and prevention of vascular calcification
Vascular calcifications that block the lumen can be treated in a variety of ways, be it medication or vascular surgery.
To reduce the risk of atherosclerotic plaque formation and prevent calcification of blood vessels, patients need:
Change lifestyle, have a healthy diet: Don't smoke, exercise regularly. If the patient is taking calcium supplements, they should consult and consult a doctor to be able to use the appropriate dose. The symptoms of vascular calcification are often difficult to recognize, so it is often difficult for patients to realize until the danger occurs, the most serious is the risk of stroke.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Learn about coronary artery disease What blood tests can show your risk for diseases? What is a blood clotting disorder? Indicators of blood clotting disorders