This is an automatically translated article.
In stroke, the diagnosis and identification of the infarct core and boundary are indispensable to determine the treatment modality. With advances in technology, the value of magnetic resonance imaging in early diagnosis of stroke has been gradually asserted as a key role. This means allows to determine the size, location of the lesion and the boundary area, to determine the location of the thrombus to suggest which treatment is appropriate for the patient's condition.
1. Why is it necessary to use magnetic resonance imaging in early diagnosis of stroke?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging test that uses powerful radio waves and magnets to create high-contrast images of the brain. This tool can detect a variety of abnormalities in the brain and blood vessels, and can help visualize small differences between tissues that are not apparent on other modalities such as computed tomography (CT) scans. . In many cases, an MRI can also help show abnormal tissue that is too small or located in areas of the brain that CT cannot detect.
The first step in evaluating a patient for stroke is to determine whether the patient has experienced an ischemic stroke or a hemorrhagic stroke. Brain MRI is the first test performed to establish a definitive diagnosis between these two situations. Accordingly, MRI not only helps to detect brain tissue damaged by ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke, but MRI is also very sensitive and specific in differentiating ischemic lesions as well as types. except for diseases similar to acute cerebral stroke.
During an MRI scan, the radiologist or technologist will use several different sequences of MRI pulses in the same scan, and each sequence will highlight different aspects each other of brain tissue. As a result, the value of MRI is further confirmed in acute stroke situations.
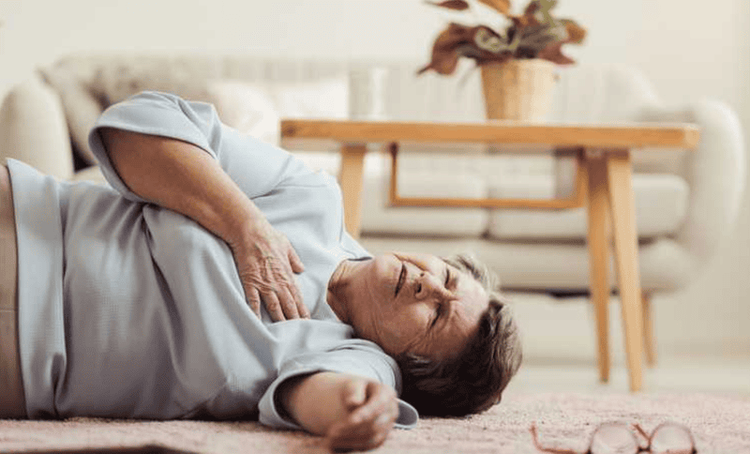

Bước đầu tiên để đánh giá một bệnh nhân đột quỵ là xác định xem bệnh nhân đã trải qua một cơn đột quỵ do thiếu máu cục bộ hay đột quỵ do xuất huyết
2. Results of MRI to detect acute stroke
Diffuse sequence MRI (DWI) can detect ischemic changes within minutes of onset. The reduced proton movement was detected as a sign of a decrease in the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC).
In the early stages of cerebral ischemia, perfusion imaging (PWI) using 1st contrast injection or spin tagging of protons in water in the blood, shows decreased flow cerebrospinal fluid, cerebrospinal blood volume, and increased mean blood travel time through brain tissue.
It is the diffuse and perfusion abnormalities of the brain that are consistent with the infarct region and are indicative of permanent neuronal necrosis. Diffusion and perfusion abnormalities, if mismatched, with a larger perfusion abnormality than a diffuse abnormality may be indicative of a reversible ischemic area.
A few hours after stroke onset, MRI will sometimes show loss of arterial emptying signal (in 30-40% of patients). This is best observed on T2-weighted images (T2-WI). At 2-4 hours, T1-WI (T1-WI) images showed signs of cerebral edema due to cytotoxic edematous response to necrosis. At 8 h, T2-WI showed high-intensity signals due to cytotoxicity and angioedema. At 16-24 h, T1-WI showed hypoechoic signal due to cytotoxicity and angioedema.
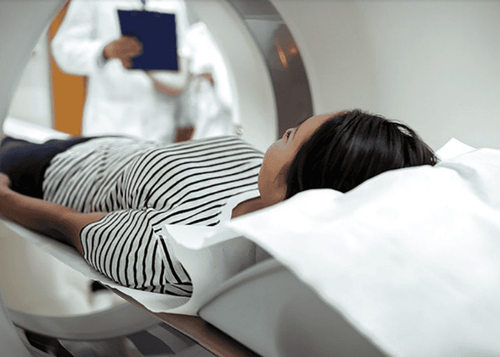
Chụp MRI với chuỗi xung khuếch tán (DWI) có thể phát hiện những thay đổi thiếu máu cục bộ trong vòng vài phút sau khi khởi phát
The findings on MRI in the early diagnosis of ischemic stroke can be summarized in the table below.
3. When is magnetic resonance imaging not possible?
If the patient has one of the following factors that would be considered a contraindication to performing an MRI:
There are metal implants in the body such as prosthetic joints, artificial heart valves or pacemakers permanent heart, although modern machines are now capable of allowing MRIs with a history of allergy to magnetic contrast material (gadolinium) Have claustrophobia. At this point, the patient needs to be clearly explained the purpose of the implementation to be able to cooperate better or to be prescribed mild sedation. Some types of MRI machines use an open system to help patients reduce feelings of fear; however, most open MRI scanners will provide poorer quality images. In the situations where the above contraindications are present, the diagnosis of stroke is entirely dependent on the principle of CT scan using conventional radiographs.
In summary, the current MRI modalities are very new and prominent, and are increasingly improving the diagnostic capacity in acute stroke. Since then, this tool has been the decisive foundation for treatment guidelines not only in the acute phase but also in the management of long-term brain damage in patients, secondary prevention in the future.
Bệnh nhân có tiền sử bị dị ứng với chất tương phản từ (gadolinium) chống chỉ định cho việc thực hiện MRI
In the past time; Vinmec has successfully treated many cases of stroke in a timely manner, leaving no sequelae: saving the life of a patient suffering from 2 consecutive strokes; Responding to foreign female tourists to escape the "death door" of a stroke;...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.













