This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Trinh Thi Thanh Huyen - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
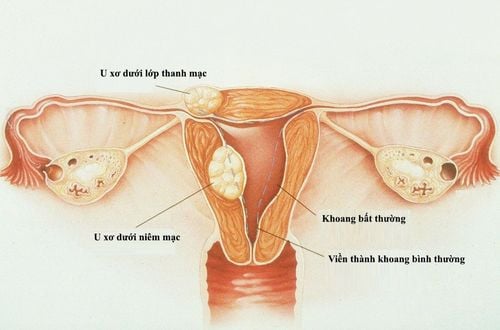
Fibroids are tumors that develop from muscle tissue in the uterus. This is a benign tumor. Fibroids can be as small as a pea or larger than a grapefruit. They can develop outside the uterine wall, inside the uterine cavity, or inside the uterine wall. Many women have multiple fibroids of different sizes.
1. Uterine fibroids
An estimated 40% to 60% of women get fibroids by age 35. Up to 80% of women get fibroids by age 50. But finding fibroids during pregnancy isn't always also easy. That's because it can be difficult for doctors to diagnose fibroids due to the thickening of the uterine muscle that occurs during pregnancy. For this reason, doctors believe that the number of known cases of uterine fibroids during pregnancy is lower than the actual number.
Most women who are diagnosed with fibroids have normal pregnancies, but sometimes tumors can cause some serious conditions for pregnant women.
2. How do uterine fibroids affect pregnancy?
Most fibroids don't grow while you're pregnant, but if this happens, they'll usually develop during the first 3 months of pregnancy. That's because fibroids need a hormone called estrogen to grow. Your body produces more of these hormones when you're pregnant.Uterine fibroids can cause a number of problems while you are pregnant, including:
Bleeding and pain . In a study of more than 4,500 women, researchers found that 11% of women with fibroids also had bleeding and 59% only had pain. But about 30% of women experience bleeding and pain during the first trimester of pregnancy. Miscarriage. Women with fibroids are more likely to have a miscarriage during early pregnancy than women who are not pregnant. And if you have multiple fibroids, your risk of miscarriage increases even more. The risk of miscarriage for women with uterine fibroids is 2 times higher than for those without the disease. Pain . This is the most common symptom of fibroids, especially as the size of the tumor grows. Uterine fibroids can cause stomach upset. In some cases, it can lead to miscarriage and premature delivery. Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) can relieve your pain. But avoid ibuprofen (Advil) early in pregnancy and during the third trimester. This can cause a miscarriage. Premature birth. If you have fibroids, you're likely to be born prematurely - meaning your baby is born before 37 weeks of pregnancy, compared with women without fibroids. Pain from fibroids can lead to uterine contractions, which can lead to premature birth. Fetal growth restriction: Large fibroids can prevent the fetus from growing fully due to its reduced size in the womb. Placental abruption: This occurs when the placenta detaches from the wall of the uterus because it is blocked by a fibroid. This reduces the oxygen and nutrients that are important for feeding the fetus. Caesarean section: According to some studies, it is estimated that women with fibroids are more likely to need a cesarean section, this risk is about 6 times higher than women without fibroids. Reverse position: Due to the irregular shape of the uterus, a breech position can form.

U xơ tử cung là nguy cơ gây sảy thai
3. Symptoms of fibroids
Some of the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids include:Pain Bleeding Anemia due to heavy or long-term bleeding Feeling mild pain in the lower abdomen Pain during sex Low back pain Constipation Problems fertility problems, including infertility, miscarriage, and premature birth Frequent urination Difficulty urinating If your doctor suspects you have a tumor growth, you will be asked to perform imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, to accurately diagnose the condition.
Fibroids often shrink after childbirth. In one study, researchers found that, between 3 and 6 months after giving birth, 70% of women saw their fibroids shrink by more than 50% from their pre-baby levels.

Đau bụng ở người bệnh có u xơ
4. Treatment of uterine fibroids during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the treatment of uterine fibroids is limited because of the possible risk to the fetus. Your doctor will prescribe you bed rest, hydration, and mild pain relievers to help expectant mothers manage the symptoms of fibroids.In rare cases, the doctor will perform fibroid removal surgery in the second half of pregnancy if the fibroids are large, subperitoneal fibroids and affecting the fetus. This procedure removes fibroids from the outside of the uterus or from the inside of the uterine wall while leaving the uterus intact. Fibroids growing in the uterine cavity are not usually indicated for this procedure because of the possible risks to the fetus.
Besides, if fibroids are found before pregnancy, the most common treatments to preserve fertility include:
Surgical removal: This surgical procedure is used to remove remove fibroids. It can increase the chance of a cesarean section, and you will likely have to wait about three months after the procedure before getting pregnant. Hormonal Birth Control Pills: While you are taking birth control pills, you will not be able to get pregnant. This birth control can help ease symptoms caused by fibroids, such as heavy bleeding and pain. IUD: Like the birth control pill, the IUD will keep you from getting pregnant as long as you're using it. However, it can help eliminate some of the symptoms caused by fibroids while preserving fertility. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) analogues: This medication blocks the production of the hormones that lead to ovulation and menstruation, so you won't be able to get pregnant while taking this medicine. It can help shrink fibroids. Vasodilation: Using an electric current, laser, or beam of radiofrequency energy to shrink the blood vessels that feed the fibroids. Each treatment method has its own risks and complications, so it's a good idea to consult with your doctor before deciding on a fibroid treatment.
You should consult your doctor about how long you will have to wait after treatment to be ready to get pregnant. With some treatments, such as birth control pills, if you want to get pregnant you can stop using them.

Khám phụ khoa định kỳ giúp chị em phụ nữ phát hiện bệnh lý sớm
If you have fibroids and want to get pregnant, talk to your doctor about the right treatment options and possible risks to make the most rational, safest decision for a future pregnancy This is yours.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Master. Trinh Thi Thanh Huyen is highly trained in obstetric ultrasound, laparoscopic surgery and hysteroscopy at the National Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology and has more than 13 years of experience working at Hai Phong Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital.
Currently, the doctor is an Obstetrician and Gynecologist at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com; Healthline.com