This is an automatically translated article.
Incisional infection is one of the common nosocomial infections. Incisional infection prolongs the patient's time and illness, usually requiring a stay in the hospital from 1 week to 10 days for treatment. Not only that, it is also economically costly for the patient.
1. Diagnosis of wound infection
Incisional infection includes 3 levels: superficial, deep and organ.
1.1. Superficial wound infection People with superficial wound infection need to meet the following conditions:
Infection occurs within 30 days of surgery. Infection occurs only in the skin or under the skin at the incision. At least one of the following symptoms There is pus draining from the shallow incision. Isolation of bacteria from a culture of fluid or tissue taken aseptically from the surgical site One of the following symptoms: pain, swelling, heat, need to open the incision The doctor diagnoses a superficial wound infection
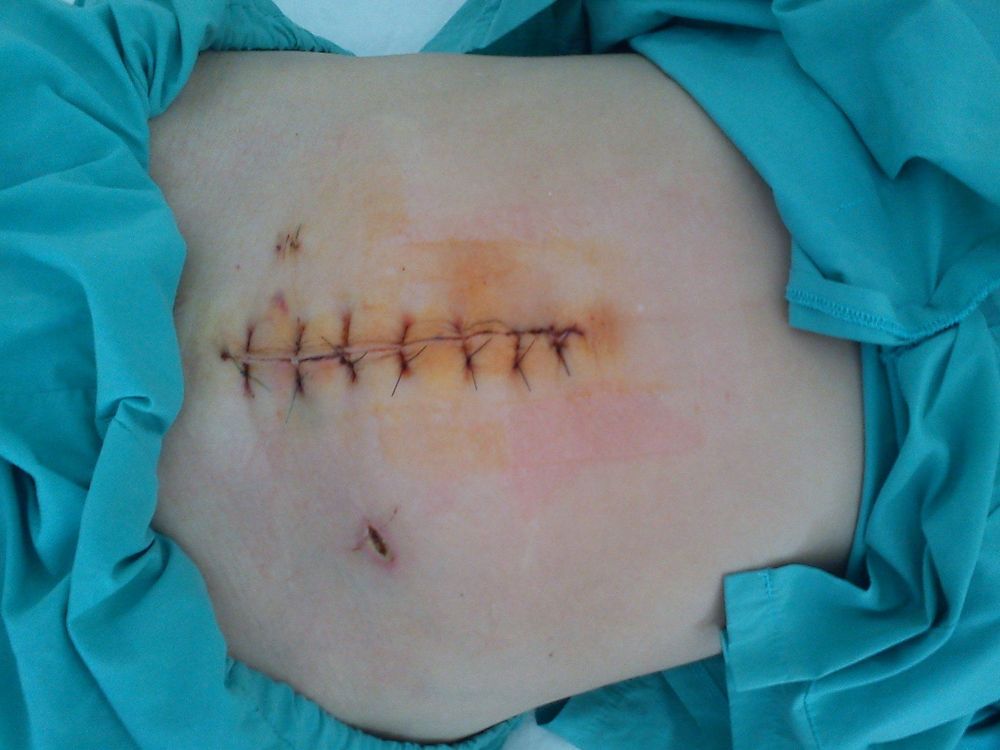
Nhiễm trùng vết mổ nông xảy ra tại vị trí vùng dưới da ở đường mổ
1.2. Deep incision infection Deep incision infection should satisfy the following conditions:
Infection occurs within 30 days of surgery or within 1 year for implant placement. The site of infection is in the deep soft tissue of the incision. Have at least one of the following symptoms: Purulent discharge from the deep incision but not from the organ or cavity where the surgery was performed. Natural deep open wound. The technician opens the incision when the patient has symptoms such as fever 38 degrees, swelling, pain, except in case the implant from the incision is negative. The doctor diagnosed a deep wound infection.
1.3. Incisional site or surgical cavity infection The following conditions must be met.
Infection occurs within 30 days of surgery or within 1 year of implant placement. Occurs in any viscera except skin, muscles, and tendons treated during surgery. There is at least one of the following cases: + There is purulent discharge from the drainage of the viscera.
+Isolation of bacteria cultured from tissue fluid or infection through reoperation, radiography or pathology.
2. Measures to prevent and control surgical site infection
2.1. General measures Wash and disinfect the patient before performing surgery. Disinfect surgical hands with alcohol-based hand sanitizer. Correct application of prophylactic antibiotic therapy. Strictly follow the aseptic procedure inside the operating room and surgical instruments. Regularly check blood sugar and warm the patient during surgery. 2.2. What patients need to do before surgery Perform blood sugar test before every surgery. Treat any foci of infection outside or at the surgical site prior to surgery. Patients must bathe with antibacterial soap, an antibacterial solution containing iodine or chlorhexidine the night before surgery.
2.3. Prophylactic antibiotic use in surgery Use prophylactic antibiotics when indicated and select it based on effectiveness against common pathogens. Especially causing wound infection according to each specific surgery and based on the recommendations issued. It is necessary to use prophylactic antibiotics in surgery when considering whether the surgery is clean or clean - infected. If prophylactic antibiotics are used, they should not be used for a long time after surgery, and if used for therapeutic purposes, they should be continued.
Thuốc kháng sinh được sử dụng trong dự phòng nhiễm khuẩn vết mổ
Prophylactic antibiotics should be given before skin incision ie when bacteria are introduced into the surgical site. Timing of the initial dose of prophylactic antibiotics should satisfy the bactericidal concentration of the drug established as soon as the incision is made. To ensure adequate tissue antibiotic concentrations, the most effective interval is within two hours preferably within 30 minutes prior to the first incision.
Thus, prophylactic antibiotics must be given by the anesthesiologist while waiting for the surgeons and preparing the surgical skin. However, this antibiotic may be adjusted according to the actual situation in our country. Vancomycin is not recommended as a prophylactic antibiotic.
3. Post-operative wound care
Bandage the wound after surgery with sterile gauze from 24 to 48 hours, only change in case the bandage is soaked with blood or contaminated when opened to examine the incision. Specific instructions for family members and patients how to monitor and detect unusual symptoms. If the patient has any abnormal symptoms, they should immediately call the doctor for timely examination and treatment. It is necessary to take preventive measures so that surgical site infection does not occur, leading to many negative consequences for the patient. Doctors and family members need to monitor the patient's condition after surgery to take timely measures.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.













