This is an automatically translated article.
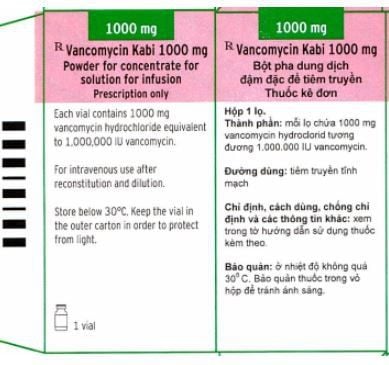
Vancomycin 1g is an antibiotic commonly indicated in the treatment of serious bacterial infections such as osteomyelitis, meningitis, pseudomembranous colitis, endocarditis...
1. What are the effects of Vancomycin?
Vancomycin is an antibiotic used to treat serious bacterial infections. Vancomycin 1g brand-name drug works by preventing the growth of bacteria.
Vancomycin 1g is usually used intravenously. However, the vial form can also be taken in oral form to treat serious intestinal conditions such as diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile infection. When taking Vancomycin 1g, your body does not absorb the drug, but keeps it in the intestine, so it prevents the growth of bacteria.
2. How to use Vancomycin 1g
Take Vancomycin 1g intravenously, usually 1 or 2 times a day or as directed by your doctor. Vancomycin 1g should be injected slowly over 1-2 hours. The dose of Vancomycin 1g is based on your medical condition, weight, kidney function, and response to treatment.
If you are self-administering Vancomycin 1g at home, learn all preparation steps and dosing instructions from your healthcare professional. Before taking Vancomycin 1g, check for residue or discoloration. If yes, you do not use that medicine. Plus, learn how to store Vancomycin 1g and dispose of medical supplies safely.
When taking Vancomycin 1g, mix each dose with at least 30 ml of water before taking it.
3. How should you store vancomycin?
You should store Vancomycin 1g at -20°C or less. Do not store in the bathroom or freezer. Each medicine will have different storage methods, so read the storage instructions on the package carefully or ask your doctor/pharmacist. Keep medicine out of reach of children and pets.
You should not throw Vancomycin 1g into the toilet or plumbing unless told to do so. Instead, dispose of it properly when it is past its expiration date or unusable.
4. What is the dose of Vancomycin 1g?
4.1. Dosage of Vancomycin 1g for adults Usual dose of Vancomycin 1g for adults with bacterial infections:
Use 15-20 mg/kg intravenously every 8-12 hours (use 2-3g/day); Doses of 25-30 mg/kg may be considered for patients with severe infections. The recommended dose of Vancomycin 500mg IV every 6 hours or Vancomycin 1g IV every 12 hours is recommended. Dosage of Vancomycin 1g for adults with sepsis:
Dose 15-20 mg/kg intravenously every 8-12 hours; The duration of treatment with vancomycin is 2-6 weeks, depending on the source and severity of the infection. Dosage of Vancomycin 1g for adults to prevent endocarditis:
For patients allergic to Penicillin, it is recommended to use Vancomycin 1g intravenously once. Vancomycin injection must be completed within 30 minutes of starting the injection. Gentamicin may be added to treat high-risk patients. Dosage of Vancomycin for adults with endocarditis:
Use a dose of 15-20 mg/kg IV every 8-12 hours, with or without other antibiotics depending on the cause of the infection. Treatment time for original valve users is 6 weeks, prosthetic valves at least 6 weeks. The maximum dose of vancomycin is 2 g/day, unless serum concentrations are low. Dosage of Vancomycin for adults with pseudomembranous colitis:
In case of diarrhea related to Clostridium difficile bacteria, use a dose of 125mg orally 4 times a day for 10 days; Treatment of enteritis caused by staphylococcal infection, using a dose of 500-2000mg/day, divided into 3 or 4 doses, taken for 7 to 10 days. Vancomycin dosage for adults with inflammatory bowel disease:
Treatment of diarrhea associated with Clostridium difficile, using Vancomycin 125mg dose 4 times a day for 10 days. Treatment of enteritis caused by staphylococcal infection, the dose of Vancomycin is 500-2000 mg/day divided into 3 or 4 doses, taken for 7 to 10 days. Vancomycin dose 1g for adults with meningitis:
Use a dose of Vancomycin 15-20 mg/kg intravenously, every 8-12 hours. The duration of meningitis treatment lasts from 10-14 days or at least 1 week after the patient's fever is gone, and the cerebrospinal fluid test is normal. For intraventricular, cortical inflammation, the therapeutic dose is usually 5-20 mg of the preservative-free formulation every 24 hours. Vancomycin dosage for adults with hospital-acquired pneumonia:
For hospital-acquired pneumonia, use Vancomycin 15-20 mg/kg intravenously every 8 to 12 hours. The recommended trough concentration is 15-20 mcg/mL. The duration of clinical treatment should be as short as possible to reduce the risk of superinfection with resistant bacteria. Vancomycin dosage for adults with pneumonia caused by Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Dosage is 15-20 mg/kg IV every 8 to 12 hours. Duration of treatment is about 7-21 days depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Vancomycin dosage for adults with osteomyelitis:
Use Vancomycin 15-20 mg/kg IV every 8 to 12 hours. Duration of treatment is 3-6 weeks or at least 8 weeks if the infection is caused by MRSA. Vancomycin dosage for adults with febrile neutropenia:
Use 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours. Continue treatment after the patient is stable, fever free for at least 24 hours, and neutrophils greater than 500/mm3. 4.2. Vancomycin dosage for children Vancomycin dose for children with bacterial infections:
Children younger than 7 days old and lighter than 1200g: Vancomycin dose is 15 mg/kg intravenously every 24 hours. Children younger than 7 days old, weighing from 1200-2000g: Vancomycin dose is 10-15 mg/kg intravenously every 12-18 hours. Children younger than 7 days old and weighing more than 2000g: Vancomycin dose is 10-15 mg/kg IV every 8-12 hours. Children aged 7 days to 1 month and weighing less than 1200g: The dose is 15 mg/kg IV every 24 hours. Children from 7 days old to 1 month old and weighing 1200-2000g: Vancomycin dose is 10-15 mg/kg intravenously every 8-12 hours. Children from 7 days old to 1 month old and weighing more than 2000 g: Vancomycin dose is 10-15 mg/kg IV every 6-8 hours. Children 1 month to 18 years of age: Vancomycin dose is 10 to 20 mg/kg IV every 6-8 hours (total 40-60 mg/kg/day) Recommended starting dose for neonates is 15 mg/kg, continued at 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for the first week after birth and every 8 hours thereafter until 1 month of age. Dosage of Vancomycin for children to prevent endocarditis:
Children 1 month of age and older who are allergic to penicillin use a dose of 20 mg/kg (maximum 1 g) once intravenously. An additional dose of Gentamicin 1.5 mg/kg (maximum 120 mg) may be added intravenously or intramuscularly for high-risk patients. Vancomycin dose for children with peritonitis:
Use a dose of 30 mg/kg or 30 mg/l intraperitoneally every 5-7 days. Vancomycin dose for children with pseudomembranous colitis:
Children aged 1-18 years use a dose of 40 mg/kg/day divided into 3 or 4 oral doses. The maximum dose of vancomycin is 2 g/day. The duration of treatment with Vancomycin is 7-10 days. Vancomycin dose for children with enteritis:
Children from 1-18 years old use a dose of Vancomycin 40 mg/kg/day divided into 3 or 4 oral doses. The maximum dose of vancomycin is 2 g/day. The duration of treatment is 7-10 days. Vancomycin dose for children for surgical prophylaxis:
Vancomycin dose is 15 mg/kg once intravenously. The injection should be completed within 30 minutes of the injection.
5. Vancomycin side effects
If Vancomycin is injected too quickly, "red man syndrome" may occur with symptoms such as flushing of the upper body, hypotension, dizziness or muscle pain/spasm in the chest - back. Pain, redness, and soreness at the Tinnitus injection site; Change in the amount of urine; Easy bleeding and bruising; Fever, sore throat; Persistent diarrhea ; Long-term or repeated use may cause oral thrush or vaginal yeast infection; severe allergic reaction such as rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat); dizziness, difficulty breathing. Not everyone experiences side effects like those on vancomycin. If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist for appropriate treatment.
Above is information about Vancomycin 1g drug, patients need to carefully read the instructions for storage information and instructions for use on the product packaging. Check the expiration date before taking the medicine. When the medicine is no longer in use, you need to collect and dispose of it according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.