This is an automatically translated article.
Oxafar is an oral antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity against a wide range of bacteria, particularly gram-negative bacteria. This drug is used under the prescription of a doctor, for infections caused by bacteria sensitive to this antibiotic.1. What disease does oxafar treat?
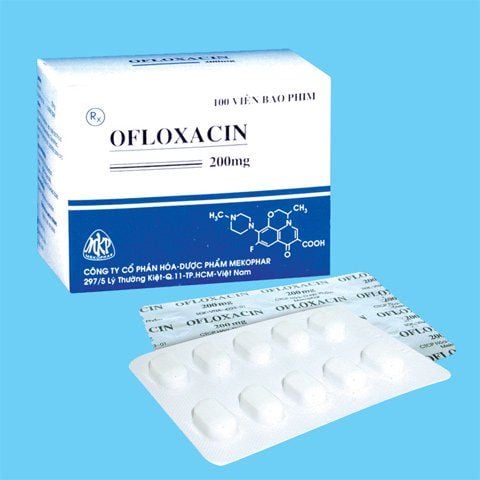
Oxafar is the brand name of the antibiotic Ofloxacin, that is, Oxafar has the main ingredient Ofloxacin 200mg, prepared in the form of film-coated tablets.Ofloxacine is an antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone class like ciprofloxacin, but oral ofloxacin has a bioavailability greater than 95%. Ofloxacin has a broad antibacterial spectrum including many bacteria such as Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus and some other gram-positive bacteria. It has been found that the antibiotic Ofloxacin is more effective than ciprofloxacin against Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and also works against some bacteria such as Mycobacterium leprae, and Mycobacterium spp. other.
Like other antibacterial quinolones, ofloxacin kills bacteria by inhibiting DNA-gyrase, an enzyme required in bacterial DNA replication, transcription, and repair.
2. Indications and contraindications of Oxafar
Oxafar is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible bacteria:Complicated and uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Infections of the skin and soft tissues. Prostatitis . Sexually transmitted diseases such as: Uncomplicated acute gonococcal infection of the urethra and cervix, urethritis and non-gonococcal cervicitis. Pneumonia caused by H. influenza or Streptococcus pneumoniae. Acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. Contraindications: Oxafar is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to ofloxacin or excipients. Or hypersensitivity to any quinolone derivative.
3. Usage and dosage of Oxafar
Usage: Oxafar is indicated for oral use, should be taken with plenty of water.Dosage:
Adults : Urinary tract infections: E. coli cystitis or K. pneumoniae cystitis: 200mg every 12 hours for 3 days. Cystitis caused by other bacterial infections: 200 mg every 12 hours for 7 days. Urethritis or cervicitis caused by C. trachomatis: 300mg every 12 hours for 7 days. Complicated urinary tract infections: 200mg every 12 hours for 10 days. Mild or moderate skin and soft tissue infections: 400mg every 12 hours for 10 days. Acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis or pneumonia: 400mg every 12 hours for 10 days. Sexually transmitted diseases: Uncomplicated gonococcal infection is 400mg a single dose. Prostatitis: 300mg every 12 hours for 6 days. Patients with renal impairment: dose reduction is required depending on creatinine clearance. Undesirable effects of Oxafa
Possible side effects of Oxafar include:
Gastrointestinal tract: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain. Skin: Itching, skin reactions due to increased photosensitivity, vasculitis , rash and skin redness. Central Nervous System: Possible dizziness, lightheadedness, forgetfulness, tremors, convulsions, paresthesias, increased excitability. Renal: Possible acute renal failure secondary to interstitial nephritis. Other organs: Blurred vision, eosinophilia, neutropenia, possibly thrombocytopenia, myalgia, gynecomastia. If you experience the above side effects or other side effects that you think are caused by taking the drug, you should tell your doctor or visit a doctor for advice.
4. What should be noted when using Oxafar
Patients with a known hypersensitivity to another fluoroquinolone or to quinolone derivatives with a similar chemical structure may also be susceptible to ofloxacin. Due to cross-sensitization, use extreme caution. The potential benefit and risk factors should be carefully considered when using ofloxacin in conditions such as central nervous system disease including epilepsy and cerebral arteriosclerosis. Photosensitivity reactions have been observed in some patients receiving fluoroquinolones. Avoid exposure to sunlight while taking the drug, use sunscreen or use protective measures. If photosensitivity reactions occur, the drug should be discontinued. The side effects on tendons and muscles of this drug are unknown, but like other antibiotics in the same class, you should use it with caution if you have muscle or tendon pain. If so, the drug should be stopped and checked. The safety and effectiveness of ofloxacin in children, people under 18 years of age, and pregnant and lactating women are unknown. Therefore, these subjects should not use the drug unless absolutely necessary. As with other quinolones, ofloxacin can also cause CNS stimulation causing tremors, lightheadedness, restlessness, confusion, and hallucinations. If these symptoms appear, the patient should stop taking the drug and seek medical attention for appropriate treatment. Geriatric: Studies have been performed that do not have specific complications in the elderly that warrant limiting the use of fluoroquinolones in this population. However, because the elderly often have a decline in renal function with age, it is necessary to adjust the dose when using fluoroquinolones. Storage: Store Oxafar at a temperature not exceeding 25 degrees Celsius, avoid moisture. Keep medicine out of reach of children. Oxafar antibiotic is a medicine prescribed by a doctor, so it should not be used without a prescription. If there is any abnormality while taking the drug, consult your doctor immediately.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.