This is an automatically translated article.
Molantel has the main ingredient is Cilostazol, which belongs to the group of inhibitors of platelet aggregation and vasodilation. Molantel is indicated for the treatment of intermittent claudication due to chronic lower extremity artery disease to improve maximum walking distance.1. What is Molantel?
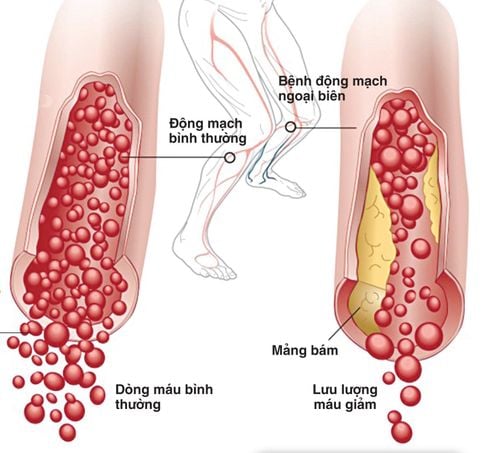
Molantel has the main ingredient is Cilostazol, which belongs to the group of inhibitors of platelet aggregation and vasodilation. Molantel is indicated for treatment in the following cases:Treatment of ischemic symptoms: Pain, ulceration, cold extremities in chronic arterial occlusion (common in Buerger's disease, arteriosclerosis occlusion), peripheral vascular complications due to diabetes). Use the drug for the purpose of preventing recurrent cerebral infarction (except in the case of cerebral embolism caused by heart). Claudication pain due to chronic lower extremity arterial disease with the aim of improving maximum walking distance. The drug is only indicated after the patient has failed to make lifestyle changes or other treatments (such as quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure, controlling diabetes, regulating blood fats, reducing fat) . Molantel is prepared in the form of tablets, each containing 100mg of Cilostazol.
2. Contraindications of Molantel
Contraindicated to use Molantel in the following cases:
Patients with a history of allergy, hypersensitivity to Cilostazol or any ingredient of the drug. The peptic ulcer is bleeding. Cerebrovascular accident due to cerebral hemorrhage within 6 months. Diabetic retinopathy. Uncontrolled hypertension. History of severe tachyarrhythmias, prolonged QT interval. Unstable angina. Patient has a history of myocardial infarction within 6 months. Patients with a history of coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass grafting within 6 months. Patients with congestive heart failure. Patients receiving concomitant treatment with 2 or more antiplatelet agents (eg, Clopidogrel, Acetylsalicylic Acid) or anticoagulants (eg, Heparin, Warfarin, Acenocoumarol, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban or Apixaban). Severe kidney failure. Moderate or severe liver failure.
3. Dosage and how to use Molantel
3.1. Dosage of Molantel Drug Adults:
Treatment of symptoms of intermittent claudication due to chronic lower extremity artery disease:
The usual dose is 100mg/time x 2 times/day. If using Molantel with other drugs (Omeprazol, Clarithromycin, Diltiazem, Erythromycin, Itraconazole, Ketoconazole) the dose should be reduced to 50mg/time x 2 times/day. Children: The safety and effectiveness of Molantel in children have not been established.
Other subjects
Patients with liver failure - renal failure:
Patients with renal failure with creatinine clearance > 25ml/min: No dose adjustment of Molantel is required. Patients with mild liver disease: No dosage adjustment of Molantel is required. Elderly: No dose adjustment of Molantel is required.
3.2. How to use the drug Molantel Molantel 100 is made in the form of tablets, the content of Cilostazol 100mg, used orally. Before taking, the patient carefully read the instructions for use of the drug on the leaflet. Take the medicine at least 30 minutes before the main meal or after 2 hours. Do not take the drug on an empty stomach to avoid unwanted side effects.
4. Undesirable effects of Molatel
Common undesirable effects of Molatel are as follows:
Systemic and skin: Infection, peripheral edema, dry skin, urticaria, increased creatinine, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia. Nervous system: Headache, feeling dizzy, dizzy. Digestive system: loose stools, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain. Respiratory system: Rhinitis, pharyngitis, cough. Cardiovascular system: Tachycardia, palpitations, palpitations. Musculoskeletal system: Muscle pain, low back pain. Uncommon side effects of Molatel are as follows:
Systemic and skin: Allergies, hyperglycemia. Blood: Anemia. Nervous system: Anxiety, insomnia. Cardiovascular system: Myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure. Five senses: Eye bleeding, nosebleed. Digestive system: Gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding. Respiratory system: Shortness of breath, pneumonia. Rare adverse effects of Molatel are as follows:
Blood: Prolonged bleeding time, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, decreased blood cell lines. Renal - urinary system: Renal failure. Cardiovascular system: Electrocardiographic disturbances (torsades de pointes, QT prolongation, complete atrioventricular block) and heart failure. Hemorrhage: Gastrointestinal bleeding, intracranial bleeding, subcutaneous bleeding, cerebrovascular accident due to cerebral hemorrhage, epidural and subdural hematoma. On the liver: Increased liver enzymes, jaundice. On the skin: Steven-Johnson syndrome, drug-induced dermatitis.
5. Precautions when using Molatel
Patients taking Molatel should note the following information:
Molatel is used to relieve claudication pain when walking long distances in people with chronic lower extremity artery disease and without complications of necrotizing lesions in the lower extremities. spend. Molatel should be used with caution in patients with atrial or ventricular extrasystoles, atrial fibrillation, or stable coronary artery disease due to a variety of adverse cardiovascular effects. Molatel should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus (high risk of intraocular bleeding) or patients undergoing or having recently undergone surgery (high risk of uncontrolled bleeding). Patients taking Molatel are at increased risk of bleeding or easy bruising during treatment. In case of retinal bleeding, immediately stop Molatel treatment. Molatel should be discontinued immediately if there are abnormalities in hematological and coagulation tests. Note to pregnant women: In experimental animals, Molatel has shown that Molatel reduces fetal weight, increases the rate of cardiovascular, renal, and skeletal abnormalities such as: abnormality of aortic arch, subclavian artery, abnormality. interventricular septum, slow ossification. Therefore, avoid taking Molatel in pregnant women. Note to nursing mothers: Molatel is excreted in milk in experimental animals, therefore nursing should be discontinued while taking the drug or discontinued due to the risk to the nursing infant. Precautions while driving and operating machines: Molatel may cause dizziness and patients should be warned to exercise caution before driving or operating machinery.
6. Overdose and missed dose of Molatel
6.1. Molatel Overdosage and Management Overdose and Toxicity:
Very little is known about Molatel overdose in humans. Symptoms of Molatel overdose can be predicted through the manifestation of excessive pharmacological effects: severe headache, diarrhea, hypotension, possible cardiac arrhythmia causing tachycardia,.... Overdose treatment:
There is no specific drug to treat Molatel overdose. Patients must be carefully monitored and supportive treatment, because Molatel binds to plasma proteins at a high rate, so it is not suitable for extra-renal dialysis. In case of severe overdose, the patient should immediately stop taking the drug and go to the nearest medical facility. Gastric emptying by induction of vomiting or gastric lavage can be used. 6.2. Missed dose of Molatel and what to do If the patient forgets to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if the dose of Molatel is too close to your next dose, skip the missed dose and take your next dose at the scheduled time. Do not take a double dose at the same time. If there are any questions, the patient can discuss further opinions from qualified medical staff. Molantel, whose main ingredient is Cilostazol, is indicated for the treatment of intermittent claudication due to chronic lower extremity artery disease in order to improve the maximum walking distance for pedestrians, and to prevent recurrent cerebral infarction (except obstructive pulmonary disease). cerebrovascular disease), treatment of ischemic symptoms. Because Molantel is a prescription drug, patients should not use it on their own, but need to contact a specialist directly for a suitable prescription to ensure safety for health.