This is an automatically translated article.
Guilaume drug with 2 main ingredients, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine, is indicated for use in combination antiretroviral therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults aged 18 years and older and for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV-infected patients. high-risk subjects. The following article provides you with information about the uses and precautions when using Guilaume.
1. What does Guilaume do?
Guilaume medicine contains 2 main ingredients: Tenofovir disoproxil 300mg and Emtricitabin 200mg.
Mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics:
Emtricitabine is a nucleoside analogue of the Cytidine group. In the body, Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is converted to Tenofovir, the nucleoside monophosphate (nucleotide) analogue of adenosine monophosphate. Tenofovir and Emtricitabine have specific activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-I, HIV-2) and hepatitis B virus. Tenofovir and Emtricitabine are phosphorylated by intracellular enzymes to form Tenofovir diphosphate and Emtricitabine triphosphate. In vitro studies have shown that both Emtricitabine and Tenofovir can be fully phosphorylated when administered together in cells. Tenofovir diphosphate and Emtricitabine triphosphate competitively inhibit HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, DNA chain termination. Tenofovir diphosphate and Emtricitabine triphosphate are both weak inhibitors of mammalian DNA polymerase and show no signs of mitochondrial toxicity either in vitro or in vivo. In vitro antiviral activity: Synergistic antiviral activity has been observed for the combination of Tenofovir and Emtricitabine in vitro. Studies have shown a synergistic or additive effect with the combination of protease inhibitors and HIV nucleoside and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Resistance: Resistance has been observed in vitro and in some HIV-I-infected patients due to the emergence of K65R mutations with Tenofovir and MI84V/I with Emtricitabine. No other cause of resistance to Tenofovir and Emtricitabine has been identified. Emtricitabine-resistant virus carrying the M184V/I mutation is cross-resistant to lamivudine, but maintains sensitivity to tenofovir, zalcitabine, didanosin, stavudin and zidovudine. The K65R mutation can be selective for Didanosin, Abacavir or Zalcitabine and reduce susceptibility to drugs such as Lamivudin, Emtricitabin and Tenofovir. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate should be avoided in HIV-I-infected patients carrying the K65R mutation. HIV-I-infected patients with three mutations associated with thymidine analogues (TAMs), M4IL or L210W mutations in reverse transcriptase have reduced susceptibility to Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Indications:
Guilaume is indicated for use in combination antiretroviral therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults 18 years of age and older. Guilaume is also indicated for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis for high-risk subjects. Contraindications:
Guilaume is contraindicated to use in case of hypersensitivity to Tenofovir, Emtricitabine or any of its ingredients.
2. How to take Guilaume
How to use:
This is a prescription drug, the patient needs to take Guilaume exactly as directed by the doctor. The drug should be started as prescribed by a physician experienced in the treatment of HIV infection. In case the patient has difficulty swallowing, the guillaume tablet can be dispersed in about 100ml of water, orange or grape juice and taken immediately after reconstitution. Reference dose for adults:
Recommended dose: 01 tablet/time/day. Guillaume combination tablets should be taken with food to optimize the absorption of Tenofovir. Even small amounts of food increase the absorption of Tenofovir from the combination tablet. When it is necessary to discontinue treatment with either component of the Guilaume combination tablet or to adjust the dose, a preparation containing each component of Tenofovir and Emtricitabine should be used separately. Reference Dose for Children and Adolescents:
The safety and efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine fixed-dose combination tablets have not been adequately studied in patients <18 years of age. Therefore, Guilaume combination tablets should not be used in children and adolescents. Reference dose in the elderly:
There are insufficient data available to make recommendations on appropriate dosing in patients > 65 years of age. There is no need to adjust the recommended dose of Guilaume for adults > 65 years unless there is evidence of renal impairment. Reference dose for patients with renal impairment:
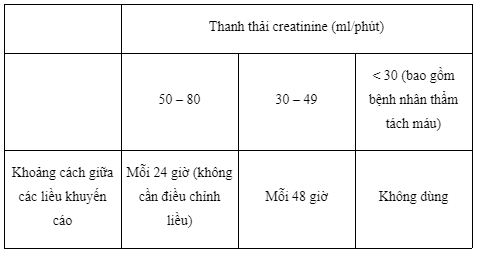
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine when administered to patients with moderate to severe renal impairment will increase absorption of these drugs, because Emtricitabine and Tenofovir are eliminated primarily through excretion. in the kidney. Several studies support a daily dose of 1 tablet of a combination of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine in patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 50-80 mL/min). The creatinine clearance, serum phosphorus, glucose and urine protein should be monitored when using Guilaume in this subject. If decreased creatinine clearance occurs in non-infectious patients receiving Guilaume, the causes, benefits, and risks of continued use of Guilaume should be assessed. The dosing interval of Guilaume should be adjusted in all patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance between 30 and 49 ml/min). Guidelines for adjusting dosing intervals for patients with moderate renal impairment are based on modeling of single-dose pharmacokinetic data in HIV-negative subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment. There are no data on the safety and efficacy of Guilaume in patients with a creatinine clearance of 30-49 ml/min, therefore, closely monitor clinical response to treatment and renal function in patients with renal function. this patient. Guilaume combination tablets should not be used in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min) and in patients on hemodialysis because the dose of the combination tablet cannot be reduced to suit the treatment requirements.
Reference dose for patients with hepatic impairment:
No need to adjust the dose of Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for patients with hepatic impairment. The pharmacokinetics of Emtricitabine have not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. Guilaume overdose and management:
In case of Guilaume overdose, closely monitor symptoms of poisoning and apply standard supportive measures when needed. Up to 30% of a dose of Emtrieitabine and 10% of a dose of Tenofovir can be removed by hemodialysis. It is not known whether emtricitabine or tenofovir can be removed by peritoneal dialysis.
3. Undesirable effects when using the drug Guilaume
The most commonly reported adverse reactions associated with emtricitabine or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate were nausea (12%) and diarrhea (7%). Some other undesirable effects when using Guilaume have been reported including:
Nervous system: Dizziness, headache. Psychiatric: Insomnia, unusual dreams. Immunity: Allergic reactions. Hematology: Neutropenia. Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, increased blood lipase and amylase, pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary: Hyperbilirubinemia, increased liver enzymes, hepatitis. Skin and subcutaneous tissue: Urticaria, blistering rash, rash, pruritus, maculopapular rash, purulent rash, skin discoloration (hyperpigmentation). Metabolism and nutrition: Hypophosphataemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia, lactic acidosis (often accompanied by fatty liver). Urinary: Renal failure (acute and chronic), proteinuria, increased creatinine. Body as a whole: Weakness. In addition, anemia and skin discoloration are common when using Emtricitabine in pediatric patients.
In patients with co-infected HIV/HBV or HIV/HCV, elevations in AST and ALT are more common with the use of Emtricitabine and Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate combination tablets.
Combination antiretroviral therapy is often accompanied by metabolic disorders such as hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and hyperlactatemia. In addition, this therapy is also associated with redistribution of body fat (lipodystrophy) in HIV patients, including loss of peripheral fat and subcutaneous fat on the face, breast enlargement, fat accumulation in the neck and back, and increased fat. abdomen and internal organs.
In case of serious side effects, patients need to stop using Guilaume and go to the nearest medical facility for timely treatment.
4. Note when using the drug Guilaume
Proliferative adipose tissue: When using Guilaume, there may be redistribution or accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, anterior and posterior neck hypertrophy, mammary gland enlargement, and the appearance of a syndrome. cushing's syndrome.
Effects on bone: Concomitant use of Tenofovir with Efavirenz and Lamivudin in HIV patients showed a decrease in lumbar spine mineral density, an increase in serum parathyroid hormone levels, and an increase in the concentration of four biological factors. in bone metabolism. Monitor bone status in HIV-infected patients with a history of fracture or at risk of osteoporosis. Although calcium and vitamin D supplements have not been shown to be effective, their use may be beneficial for these patients. When any bone abnormalities appear, consult a doctor. Pregnancy: There is no information available on the use of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in pregnant women. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate should only be used when the benefit to the mother is demonstrated to outweigh the risk to the fetus. Use of Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in women of reproductive age should be accompanied by effective methods of contraception.
Lactation: There is no information on the excretion of Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate into breast milk. Therefore, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate should not be used in nursing women.
5. Drug interactions
Drugs affected or eliminated by the kidneys: Tenofovir interacts with drugs that compete for renal elimination or reduce renal function (Acyclovir, Ganciclovir, Valacyclovir, Cidofovir, Valganciclovir). Concomitant administration increases the plasma concentration of Tenofovir or the co-administered drugs. HIV protease inhibitors: There is an additive or synergistic interaction between Tenofovir and HIV protease inhibitors such as Atazanavir, Amprenavir, Indinavir, Saquinavir, Ritonavir. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Tenofovir and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (eg, Delavirdin, Nevirapin, Efavirenz) have additive or synergistic interactions. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Additive or synergistic interactions between tenofovir and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors such as Didanosin, Emtricitabine, Stavudin, Abacavir, Zalcitabine, Zidovudine. Above is the entire information about the drug Guilaume, patients need to carefully read the instructions for use, consult a doctor / pharmacist before using. Note, Guilaume is a prescription drug, patients need to use the drug as prescribed by the doctor, absolutely do not self-treat at home.