This is an automatically translated article.
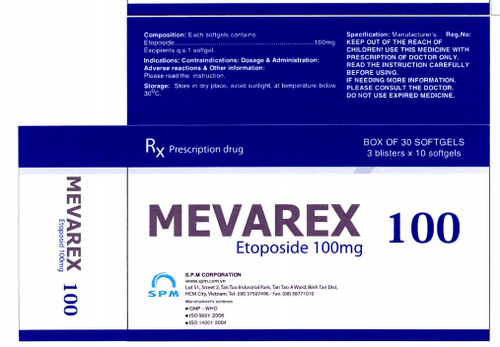
Etoposide belongs to a group of cancer drugs that are often used alone or in combination with chemotherapy to treat certain types of cancer such as: small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, prostate cancer, prostate cancer. leukemia, lymphoma. How is Etoposide used and used?1. What are the effects of Etoposide?
Etoposide is a semi-synthetic podophyllotoxin derivative with a mechanism of action that exerts cytotoxic effects by damaging DNA, thereby inhibiting or altering DNA synthesis. Etoposide is a cell cycle dependent and phase specific agent of the cycle that induces G2-phase arrest and late G2 and S phase cell death. Studies show the effects with different doses as follows:High concentrations (10 micrograms/ml) cause cell lysis when cells enter the process of cell division. Low concentrations (0.3 to 10 micrograms/ml) inhibit progenitor cells. Etoposide-induced DNA damage is clearly associated with the cytotoxicity of the drug, inducing single-strand DNA breakage. Indirectly Etoposide is usually indicated in the following cases:
Small cell cancer of the lung Acute monoclonal and myeloid-monocytic leukemia Hodgkin's disease Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma The drug has also been tested in the treatment of other solid tumors such as brain tumors, gastrointestinal tumors, ovarian tumors, thymus, trophoblasts during pregnancy and cancers in children
2. Dosage of Etoposide
Etoposide should only be given by slow intravenous infusion (30-60 minutes) because rapid infusion causes hypotension. Etoposide must not be administered intraperitoneally or intraperitoneally. Etoposide must be diluted before use, the resulting concentrations should not exceed 0.4 mg/ml because of possible precipitation. Usually Etoposide will be mixed with 250ml of 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% glucose. Dosage of Etoposide in adults is as follows:
Intravenous dose: 50-60 mg/m2/day for 5 consecutive days at 2-3 week intervals, the total dose should usually not exceed 400mg/m2 per session. For patients with hepatic impairment: Etoposide is contraindicated in cases of severe hepatic impairment and should be used with caution in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. In patients with renal impairment: because an unchanged amount of etoposide is excreted in the urine, a dose adjustment may be necessary for patients with renal impairment.
3. Etoposide drug side effects
The most life-threatening effect is the cardiotoxic bone marrow suppression caused by Etoposide. Common reactions include:
Myelosuppression: hematologic toxicity with major manifestations including leukopenia, less frequent thrombocytopenia and possible anemia Gastrointestinal system: nausea and vomiting can cure all symptoms Reversible hair loss Hypotension: may occur with rapid intravenous administration Allergies: anaphylactoid reactions with chills, fever, tachycardia, bronchospasm, dyspnea and hypotension Cardiovascular: myocardial infarction has been reported in patients with mediastinal irradiation Local reaction: phlebitis following intravenous administration of Etoposide usually with high concentrations in solution Contraindication of Etoposide include:
Patients with severe hepatic impairment Patients with hypersensitivity to any component of the injection Patients with severe myelosuppression Note that when taking Etoposide, do not mix with any other drugs, when injecting, the vial must be observed. Is the solution cloudy or discolored?
In summary, Etoposide is only used when prescribed by a doctor, so patients should strictly follow the instructions for the treatment to bring the best results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.