This is an automatically translated article.
Diurefar 40 contains the active ingredient furosemide, which is indicated in the treatment of hypertension and edema due to diseases such as cirrhosis, heart failure, kidney disease... Let's learn about its uses and notes when using it. medicine Diurefar 40 through the article below.
1. Uses of Diurefar
1.1. Indications Diurefar 40 contains the active ingredient furosemide 40mg, which is indicated in the treatment of the following diseases:
Hypertension; Edema due to cirrhosis of the liver, heart failure, kidney disease (including nephrotic syndrome). 1.2. Pharmacodynamics Furosemide is a rapid, potent, and dose-dependent sulfonamide derivative. Drugs belonging to the group of diuretics acting in the ascending loop of Henle should be classified as loop diuretics. The mechanism of action of the drug is to inhibit the process of Na + - K + - 2Cl - co-transporter at the thickening stage of the ascending loop of Henle, thereby increasing the elimination of electrolytes accompanied by an increase in water excretion.
Furosemide also reduces the reabsorption of Na +, Cl - and increases the elimination of K + in the distal tubule, acting directly on the proximal tubule. The drug does not inhibit carbonic anhydrase, does not antagonize aldosterone and increases renal excretion of Ca2+, Mg2+, ammonium, hydrogen, bicarbonate and even phosphate. The body loses a lot of hydrogen, potassium and chlorine which can cause metabolic alkalosis. The drug causes a decrease in plasma volume, which can lead to hypotension, but usually only mildly.
1.3. Pharmacokinetics Furosemide is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration, its bioavailability is about 60-70%. However, drug absorption is erratic and influenced by factors such as dosage form, presence of food, and disease process. In patients with heart failure, furosemide absorption is even more erratic. Bioavailability of the drug may be reduced to less than 10% in patients with renal disease and slightly increased in patients with liver disease. After oral administration, the drug has a rapid effect, appearing after 1-2 hours and reaching the maximum effect after 1-2 hours, lasting from 6-8 hours.
Furosemide is strongly bound to plasma albums (approximately 99%) and is eliminated mainly in the urine, mostly as unchanged drug. The half-life of the drug ranges from 30 to 210 minutes in normal healthy subjects and is often prolonged in patients with hepatic and renal impairment and in neonates.
The drug furosemide crosses the placental barrier and is distributed into breast milk, the clearance of the drug is not increased by hemodialysis.

Thuốc Diurefar 40 điều trị tăng huyết áp và một số bệnh lý liên quan khác
2. Dosage of Diurefar 40
The effect of diurefar 40 in the treatment of hypertension and edema depends on the specific dose as follows:
Treatment of edema in adults: The recommended dose is 1⁄2 - 2 tablets, administered once. during the day in the morning. In case the dose is not responsive, it can be increased by 20-40mg/time x 6-8 hours/time until the desired effect (including weight loss) is achieved. Thereafter, the maintenance dose is administered 1-2 times a day or every 2 to 4 days (the maintenance dose may be reduced in some patients). In case of severe edema, the dose can be adjusted to 600mg/day. Treatment of hypertension in adults h: The recommended dose is 20-40mg/time x 2 times/day. Patients should monitor blood pressure closely when treated with furosemide alone as well as when combined with other antihypertensive drugs, especially in the early stages of treatment.
3. Contraindications to the use of Furosemide
Contraindicated to use Furosemide drug in the following cases:
People with hypersensitivity to any ingredient of Diurefar 40mg drug; Patients who are allergic to furosemide or to sulfonamide derivatives; Patients with dehydration, hypovolemia (with or without hypotension); Severe hyponatremia and hypokalemia; Pre-coma or coma due to cirrhosis; Renal failure due to hepatic coma ; Patients with renal failure (creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min/1.73m2); Patients with digitalis toxicity, Addison's disease; Patients with porphyria; lactating women; Patients with impaired renal function. nephrotoxicity or anuria due to drugs that are toxic to the kidneys and liver.
4. Notes when using Furosemide
4.1. Side effects Some undesirable effects may be encountered when using Diurefar 40mg as follows: Common side effects (ADR > 1/100):
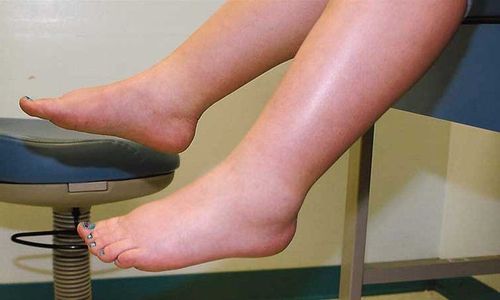
Circulation: Decreased blood volume in case of dose therapy orthostatic hypertension; Metabolism: Water and electrolyte imbalances including hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, and chloremic alkalosis.

Khi sử dụng thuốc Diurefar 40mg người bệnh nên thận trọng với một số tác dụng phụ
Uncommon side effects (1/1000 < ADR < 1/100):
Gastrointestinal: Vomiting, nausea, digestive disorders; Metabolic: Increased uric acid and gout. Rare side effects: (ADR < 1/10,000):
Skin: Paresthesia, skin rash, purpura, pruritus, photosensitivity reaction, exfoliative dermatitis; Hypersensitivity reactions: Interstitial nephritis, fever, vasculitis; Blood: Leukopenia, bone marrow suppression, agranulocytosis, anemia; Metabolic: Glucoseuria, hyperglycemia, cholestatic jaundice and pancreatitis; Ear: Hearing loss, tinnitus, deafness. 4.2. Precautions for use During treatment with Diurefar 40mg, patients should be monitored for electrolyte levels (especially potassium, sodium) and hypotension, diabetes, gout, liver failure, kidney failure. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. In the elderly, appropriate dose reduction is required to reduce the risk of ototoxicity. In case of low urine volume, the patient should be compensated with enough blood volume before taking the drug.
Diurefar 40mg should be used with caution in children (especially when used for a long time), careful monitoring of water and electrolyte balance. Premature infants treated with furosemide may be at increased risk of developing ductal artery disease. Furosemide has the ability to displace biliburine at the albumin binding site, so caution should be exercised in its use in jaundiced children. The clearance of the drug in neonates is slower than in the elderly, the half-life (t1/2) in plasma is 8 times higher, so it should be calculated when administering a booster dose. The drug should be used with caution in patients with prostatic hypertrophy or dysuria as it may promote acute urinary retention. Furosemide is considered unsafe for treatment in patients with porphyria due to the risk associated with exacerbations of the disease. In patients with hypoparathyroidism, treatment with furosemide may cause stiffness because of the risk of hypocalcaemia. Pregnant women: Use this drug only when absolutely necessary, the benefits outweigh the risks. Lactation: Diurefar 40mg drug has the risk of inhibiting lactation, so breast-feeding should be discontinued during treatment with the drug.
5. Drug interactions
Possible drug interactions are as follows:
Use of Diurefar and other diuretics increases the effect of Diurefar, potassium-sparing diuretics may reduce potassium loss when treated with furosemide. Antibiotics: Use of Diurefar and antibiotics increases the side effects of these drugs, specifically cephalosporins increase nephrotoxicity, vancomycin increases ototoxicity, aminoglycosides increase ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Lithium salts: Increases blood levels of lithium and causes toxicity if used with furosemide. Therefore, the use of two drugs in combination should be limited in cases where the blood lithium concentration cannot be closely monitored. Cardiac Glycosides: Increased cardiotoxicity due to the drug's ability to lower blood potassium. Therefore, ECG and serum potassium levels should be monitored. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Decreased diuretic effect and increased risk of nephrotoxicity. Corticosteroids: Antagonize the diuretic effect of furosemide, increasing the risk of hypokalemia. Antidiabetic agents: Furosemide reduces the hypoglycemic effect of antidiabetic drugs. Anticoagulants: Furosemide enhances the anticoagulant effect of the drug. Non-depolarizing muscle relaxants: Increased muscle relaxant effect. Cisplatin used with furosemide increases nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Antihypertensives: Furosemide enhances the antihypertensive effect. In case of drug combination, appropriate dose adjustment is required, especially for angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors because blood pressure can be severely reduced. Antiepileptic drugs such as phenytoin reduce the effects of furosemide. Chloral hydrate: Concomitant use of furosemide causes tachycardia, flushing syndrome, sweating, increased blood pressure. Probenecid: Reduces the diuretic effect and renal clearance of furosemide. CNS depressants (diazepam, chlorpromazi, halothan, clonazepam, ketamine) potentiate the hypotensive effect of Diurefa. Diurefar 40 contains the active ingredient furosemide, which is indicated in the treatment of hypertension and edema caused by diseases such as cirrhosis, heart failure, kidney disease. To ensure effective treatment as well as avoid side effects, patients need to take medicine according to prescription or consult a doctor, pharmacist for advice.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.